Study on influence of CT pelvimetry and clinicopathological parameters on the difficulty of laparoscopic radical cystectomy for bladder cancer
-
摘要: 目的 利用术前CT测量骨盆各径线和临床病理参数评估腹腔镜下膀胱癌根治术难度的影响因素。方法 收集2018年1月—2021年8月连续腹腔镜下膀胱癌根治手术的70例患者,通过薄层增强CT建立三维图像,测量骨盆各径线大小,根据骨盆各径线参数和基础资料,判断对因变量手术时间和术中出血量的影响,对这些参数进行单变量和多变量分析,筛选出可能影响手术时间和出血量的因素。再将筛选出来的危险因素进行logistic多因素分析,根据logistic回归分析特点对危险因素赋值,建立评分系统,最后利用受试者工作曲线(ROC)评价该评分系统效能,并用校准曲线判断其预测准确性。结果 中骨盆前后径、上耻骨到尾骨的距离以及中骨盆棘突直径对手术操作难度的影响较大。根据以上因素建立函数Y,ROC曲线结果表明,Y值为0.83可作为判断腹腔镜下膀胱癌根治术难易程度的预测值,其灵敏度和特异度分别为97.1%和66.6%。结论 术前CT骨盆测量可以为腹腔镜下膀胱癌根治术难度的评估提供有用的指标。Abstract: Objective To evaluate the influencing factors of difficulty of laparoscopic radical cystectomy by measuring the diameter of pelvis and clinicopathologic parameters with preoperative CT.Methods From January 2018 to August 2021, 70 consecutive patients who underwent radical cystectomy were examined by three-dimensional images established by thin-section contrast-enhanced CT to measure the size of each diameter line of the pelvis. According to the parameters of each diameter line of the pelvis and basic data, the effects on the dependent operation time and intraoperative blood loss were judged. Univariate and multivariate analyses were performed for these parameters to screen out the factors that may affect the operation time and blood loss. Logistic multivariate analysis was performed on the selected risk factors, and the risk factors were assigned values according to the characteristics of logistic regression analysis to establish a scoring system. Finally, the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) was used to evaluate the efficacy of the scoring system, and the calibration curve was used to determine its prediction accuracy.Results The anteroposterior diameter of the middle pelvis, the distance from the suprapubic bone to the coccyx, and the diameter of the spinous process of the middle pelvis had a greater impact on the difficulty of surgical operation. The results of ROC curve showed that Y 0.83 could be used as the predictive value to determine the ease of laparoscopic cystectomy, and its sensitivity and specificity were 97.1% and 66.6%, respectively.Conclusion Preoperative CT pelvis measurement can provide a useful index for evaluating the difficulty of laparoscopic radical cystectomy.
-
Key words:
- bladder cancer /
- laparoscopy /
- pelvis measurement /
- clinical pathology /
- difficulty of surgery
-
2021年世界癌症报告数据显示,膀胱癌位居全球男性恶性肿瘤发病率的第4位,死亡率的第8位[1],且呈逐年升高趋势。大约75%的患者最初被诊断为非肌层浸润性膀胱癌(NMIBC)[2],治疗方法主要为手术治疗,经尿道膀胱肿瘤电切术(TURBt)+膀胱灌注。NMIBC复发率和进展率较高,有研究显示首次TURBt后肿瘤残余率为31.6%[3]。5年复发率达到31%~78%,5年后有40%的NMIBC进展为肌层浸润性膀胱癌(MIBC)[4]。对于肌层浸润性及反复复发性的NMIBC,腹腔镜下膀胱癌根治术+标准盆腔淋巴结清扫术是目前主要治疗手段[5],其目的是治愈和避免复发,腹腔镜下膀胱癌根治术+标准盆腔淋巴结清扫术已经是一项成熟的手术方式。腔镜手术的优势主要是创伤小、患者恢复快、对机体的内环境扰动小[6],并且对手术视野的暴露也很有帮助。腹腔镜的放大作用,使得血管辨认更加清晰,不易损伤。在实际手术中,由于盆底血供丰富、手术操作空间小、耗时长、并发其他疾病风险高等因素,腹腔镜下膀胱癌根治术一直担当着泌尿外科最高难度、最具挑战的手术代表之一[7-9],尤其是肥胖或骨盆深窄狭小的患者手术难度会明显增加。骨盆因素影响着手术的暴露和手术相关操作,所以盆腔内进行的膀胱癌根治术难度更大。如何通过术前影像学相关检查及临床病理参数来预判腹腔镜下膀胱癌根治术难度目前还没有一个参考标准。术前CT骨盆测量和临床病理参数对腹腔镜下膀胱癌根治术难度的影响研究对腹腔镜下膀胱癌根治术方式、入路及术前准备具有指导意义。基于此,术前利用CT或临床病理参数建立预测模型,评估盆腔解剖因素对腹腔镜下膀胱癌根治术难度的影响。
本研究的目的主要是通过分析临床病理和盆腔解剖参数对腹腔镜下膀胱癌根治术时间和术中出血量进行手术难度的预测。手术时间和术中出血量用于评估手术难度,因为它们已经在以往的腹腔镜手术相关文献中得到了客观的验证[10-11]。本研究由蚌埠医学院第一附属医院伦理委员会批准。
1. 资料与方法
1.1 一般资料
选取2018年1月—2021年8月于蚌埠医学院第一附属医院泌尿外科收治行腹腔镜下膀胱癌根治术+标准盆腔淋巴结清扫术的男性膀胱癌患者70例,年龄41~81岁,平均(64.96±9.60)岁。
纳入标准:①男性;②病理确诊为极高危NMIBC或无远处转移、局部可切除的MIBC(T2~4a,N0~x,M0);③行腹腔镜下膀胱癌根治术。排除标准:①腹部既往手术史;②肿瘤侵犯膀胱外盆壁或腹壁等;③凝血系统异常;④骨盆骨折史。收集患者年龄、体重指数(BMI)、病理分级、临床分期、手术时间和术中出血量、有无合并基础疾病(高血压、糖尿病、脑梗死史)等资料。其中合并有高血压、糖尿病或者脑梗死病史44例,不合并基础疾病的26例。
1.2 CT测量指标
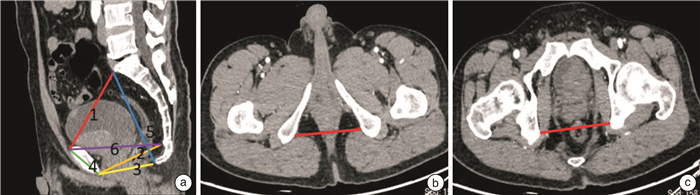
由2名具有2年以上丰富经验的影像学医师分别测量以下指标,取两者平均值作为参考值。骨盆解剖参数定义及示例见表 1和图 1。
表 1 骨盆径线测量及定义骨盆测量参数/mm 定义 骨盆入口前后径 耻骨联合上缘中点到骶骨岬前缘中点的一条线 中骨盆前后径 耻骨联合下缘中点经坐骨棘连线中点到骶尾交界的距离 骨盆出口前后径 从耻骨联合的正中下方到尾骨顶端的一条线 耻骨联合高度 耻骨联合两端中点的连线 骶尾部距离 从骶角到尾骨尖端的距离 耻骨上端到尾骨距离 从耻骨联合的正中上部到尾骨顶端的一条线 中骨盆棘突直径 中骨盆横径、两侧坐骨棘最内点之间的距离 坐骨结节间径 坐骨结节最内点之间的距离 1.3 临床病例分期
病理分级以WHO2004年膀胱癌分级系统进行区分:尿路上皮癌占绝大部分,有69例,剩余1例为印戒细胞癌;低级别有27例,高级别43例。临床分期以UICC在2017年发布的第8版TNM分期为准:T1期14例,T2期24例,T3期22例,T4期10例;N0期65例,N1期4例,N3期1例。
1.4 手术方法
1.4.1 体位和气腹建立
气管内插管全身麻醉成功后,头低脚高25°~30°仰卧位,利用重力的作用,使肠管自然垂向上腹部,便于盆腔手术操作。消毒铺巾,脐下正中纵向做一2 cm切口,用气腹针进行穿刺,置入10 mm trocar,建立气腹,气腹压力维持在12~14 mmHg(1 mmHg=0.133 kPa)。30°腹腔镜直视下进入腹腔,腹腔镜视野下在两侧腹直肌外缘脐下两横指及右侧髂前上棘内上方位置分别穿刺置入10 mm、10 mm、5 mm trocar,将操作器械置入腹腔。
1.4.2 标准盆腔淋巴结清扫
于右骨盆入口处髂总血管表面切开腹膜,沿髂外血管走行向远端延长切口,纵行切开髂总及髂外动脉血管鞘,切除髂外淋巴脂肪组织,远端至旋髂深静脉跨越髂外动脉处。近端沿髂内动脉游离,显露分支及闭孔神经,清除髂内及闭孔淋巴脂肪组织,向远端汇合后,整块切除右盆腔淋巴脂肪组织,相同方法清扫左侧淋巴结。
1.4.3 程序化膀胱切除
输尿管游离:于输尿管跨过髂血管处寻及输尿管,沿输尿管走行向下分离,直至膀胱壁外,以带线的Hem-o-lok夹标记并离断。膀胱后面游离:横行切开膀胱直肠陷凹腹膜,于双侧输精管及精囊腺后方游离至狄氏筋膜并切开,继续向远端分离前列腺与直肠之间的间隙达前列腺尖部。膀胱前面游离:倒“U”形切开脐正中襞及脐外侧襞腹膜返折,向远端游离膀胱和前列腺前面至前列腺尖部,切开盆底筋膜和耻骨前列腺韧带,2-0可吸收线缝扎阴茎背深静脉复合体。膀胱前列腺侧方离断:Hem-o-lok夹或血管闭合器分束结扎两侧膀胱和前列腺侧方血管蒂直至前列腺尖部。离断取出标本:在前列腺尖部分离尿道足够长度后切断尿道,完整切除膀胱前列腺。将标本置入取物袋,延长腹部切开取出标本,最后行不同的尿流改道术式。
1.5 手术难度评估指标
手术均由同一个手术团队进行操作,方式均为腹腔镜下膀胱癌根治术+标准盆腔淋巴结清扫术。手术时间为从开腹至膀胱切除所需时间;术中出血量为从开腹至膀胱切除为止,吸引瓶中血液量与纱布中浸润血液量之和,纱布中血液量为湿纱布与干纱布重量之差除以血液密度(血液密度估算为1 g/mL)。根据患者膀胱切除的手术时间或截止膀胱切除的术中出血量进行分组,手术时间≥125 min或术中出血量>200 mL为困难组,否则为容易组,其中困难组34例,容易组36例。
1.6 统计学方法
采用SPSS 26.0和R软件进行统计分析。骨盆解剖参数、年龄和BMI采用独立样本t检验(用X±S表示),不符合正态分布或方差齐性的计量资料采用非参数检验(用四分位数间距表示),计数资料采用例(%)表示。分析各参数在2组间差异有无统计学意义,筛选出可能影响手术难度的危险因素,再对每个筛选出来的计量资料进行ROC曲线分类处理,取约登指数最大时的参数作为截断值转为计数资料。然后进行二元logistic多因素分析,用皮尔逊相关函数对多因素分析得到的自变量进行相关性分析,当相关性分析结果系数>0.8时,提示存在共线性问题,否则可认为无共线性问题。根据logistic回归系数对危险因素赋值,得出预测函数。利用受试者工作特征ROC曲线和校准曲线对函数准确性进行检验。以P < 0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2. 结果
2.1 2组临床和病理资料的单因素分析
通过单因素分析提示骨盆入口前后径(P=0.028)、中骨盆前后径(P=0.009)、上耻骨到尾骨距离(P=0.019)、中骨盆棘突间径(P < 0.001)、坐骨结节间径(P=0.045),差异有统计学意义(表 2);2组间病理分级(P=0.955)及临床分期(T分期:P=0.231, N分期:P=0.350)比较,差异无统计学意义(表 3)。将上述5个经单因素分析差异有统计学意义的变量进行ROC处理,取约登指数最大时的参数值作为截断值进行二分类。骨盆入口前后径≤108.95 mm取值为1,>108.95 mm取值为2;中骨盆前后径≤100.25 mm为1,>100.25 mm为2;上耻骨到尾骨距离≤112.45 mm为1,>112.45 mm为2;中骨盆棘突间径≤100.95 mm为1,>100.95 mm为2;坐骨结节间径≤79.80 mm为1,>79.80 mm为2。
表 2 单因素分析骨盆各径线和基础资料例(%),X±S 因素 容易组 困难组 P 年龄/岁 64.89±8.84 65.03±10.49 0.952 BMI 24.20±5.70 24.00±5.50 0.529 有无基础疾病 0.138 无 10(15.9) 16(47.1) 有 26(84.1) 18(52.9) 骨盆入口前后径/mm 110.16±4.34 107.68±4.90 0.028 中骨盆前后径/mm 100.24±5.64 97.12±3.89 0.009 骨盆出口前后径/mm 91.04±7.26 89.09±4.67 0.184 耻骨联合高度/mm 42.60±2.02 43.35±2.73 0.197 耻骨上端到尾骨距离/mm 114.11±6.97 111.02±2.80 0.019 骶尾部距离/mm 117.91±7.13 116.11±3.43 0.187 中骨盆棘突间径/mm 103.45±9.91 93.95±5.83 < 0.001 坐骨结节间径/mm 87.80±9.07 83.48±8.60 0.045 表 3 单因素分析病理分级及临床分期例 组别 病理分级 T分期 N分期 低级别 高级别 T1 T2 T3 T4 N0 N1 N2 N3 容易组 14 22 10 9 12 5 35 1 0 0 困难组 13 21 4 15 10 5 30 3 0 1 P 0.955 0.231 0.350 2.2 影响手术难易程度的多因素logistic分析
将上述单因素分析结果有统计学意义的变量纳入多因素二元分类logistics回归分析,结果显示:中骨盆前后径(OR=0.021, 95%CI:0.009~0.679)、上耻骨到尾骨距离(OR=0.036, 95%CI:0.052~0.908)、中骨盆棘突间径(OR=0.007, 95%CI:0.002~0.380)差异有统计学意义(表 4)。通过对多变量分析结果有意义的变量进行皮尔逊相关性分析,系数的绝对值均 < 0.7,提示这些变量不存在共线性问题。根据多因素分析的影响因素,取其截断值将中骨盆前后径、上耻骨到尾骨距离、棘突间径分成较短组和较长组,比较各组在手术时间和术中出血量之间差异有无统计学意义,进行反向验证,结果均P < 0.05(表 5),提示这3个变量是影响手术难易程度的独立危险因素。
表 4 多因素分析影响腹腔镜下膀胱癌根除术难度的危险因素变量 β SE Wald df P Exp(β) 95%CI 骨盆入口前后径 0.504 0.835 0.364 1 0.546 1.655 0.322~8.494 中骨盆前后径 -2.571 1.114 5.322 1 0.021 0.076 0.009~0.679 上耻骨到尾骨距离 -1.529 0.731 4.374 1 0.036 0.217 0.052~0.908 棘突间径 -3.575 1.330 7.224 1 0.007 0.028 0.002~0.380 坐骨结节间径 -1.580 0.865 3.335 1 0.068 0.206 0.038~1.123 常量 11.584 2.987 表 5 2组在手术时间和出血量之间的差异比较X±S 组别 中骨盆前后径 上耻骨到尾骨距离 棘突间径 手术时间/min 出血量/mL 手术时间/min 出血量/mL 手术时间/min 出血量/mL 较短组 129.46±13.24 218.80±42.70 129.31±13.82 219.23±43.61 130.96±13.33 225.32±40.48 较长组 118.25±10.10 185.00±35.61 122.42±11.90 196.45±40.21 116.65±6.72 176.09±27.76 P 0.001 0.003 0.031 0.028 <0.001 <0.001 2.3 预测模型的建立及验证
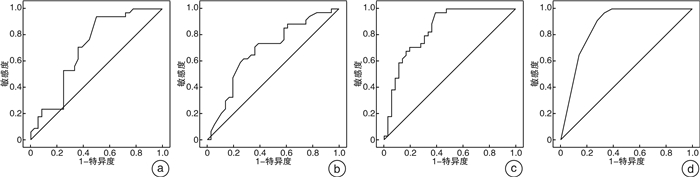
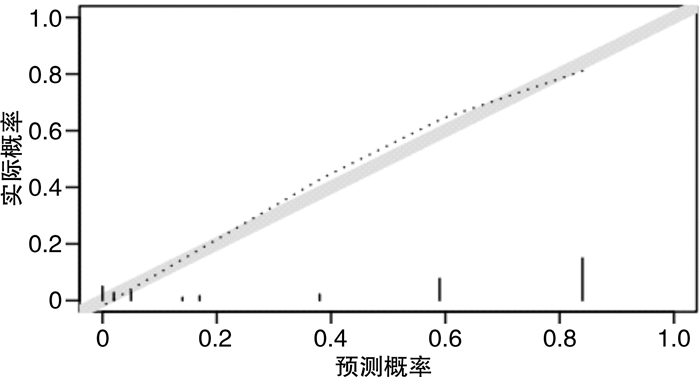
根据logistic回归分析特点进行赋值:中骨盆前后径(≤100.25 mm为1分,>100.25 mm为2分)、上耻骨到尾骨距离(≤112.45 mm为1分,>112.45 mm为2分),中骨盆棘突间径(≤100.95 mm为1分,>100.95 mm为2分)。得分(Y)=11.58—2.57×中骨盆前后径—1.53×上耻骨到尾骨距离—3.58×中骨盆棘突间径。根据上述评分公式对本研究的70例患者进行评分,绘制ROC曲线评估该评分系统效能并用校正曲线判断其准确性。并将多因素分析和手术难度有关的参数(中骨盆前后径、上耻骨到尾骨距离、中骨盆棘突间径)也进行绘制ROC曲线(图 2)。中骨盆前后径ROC曲线下面积(AUC)为0.703(SE=0.063,P=0.004,95%CI:0.578~0.827)、上耻骨到尾骨距离AUC为0.686(SE=0.064,P=0.008,95%CI:0.560~0.812)、中骨盆棘突间径AUC为0.839(SE=0.048,P < 0.001,95%CI:0.746~0.933)、函数Y的AUC为0.871(SE=0.044,P < 0.001,95%CI:0.785~0.958)(表 6)。比较AUC可知,函数Y的AUC最大,同时由校准图可看出,函数Y预测手术难易程度的概率和实际手术难度概率具有较好的一致性(图 3)。诊断手术难度的准确性更高,根据ROC曲线特点,当约登指数最大时,取其参数值作为截断值,函数Y的截断值为0.83。在本研究中,得分>0.83为困难组,≤0.83为容易组。
表 6 各危险因素和模型函数Y的ROC曲线下面积参数 AUC SE P 95%CI 中骨盆前后径 0.703 0.063 0.004 0.578~0.827 上耻骨到尾骨距离 0.686 0.064 0.008 0.560~0.812 棘突间径 0.839 0.048 < 0.001 0.746~0.933 函数Y 0.871 0.044 < 0.001 0.785~0.958 3. 讨论
虽然输尿管镜、肾镜或TURBt等微创手术在泌尿外科已有近一个世纪的历史,但第1次腹腔镜手术在泌尿外科直到1976年才被描述[12]。近几十年来,腹腔镜在泌尿外科得到了飞速发展。有研究证明腹腔镜下膀胱癌根治术与开放性手术治疗相比,腹腔镜对患者造成的创伤更小、出血量更少。患者恢复时间和出院时间显著缩短,术后并发症发生率更低,术后预后更好[13]。曾蜀雄等[14]基于我国人群的对照研究也证实了同样的特点。夏照明等[15]通过对围手术期的回顾性分析显示:术前有无糖尿病、肾功能不全,术后白蛋白、血红蛋白水平是围手术期并发症的独立危险因素。目前腹腔镜下膀胱癌根治术+标准盆腔淋巴结清扫术这一技术已经趋向于成熟,近年来我国也逐渐开始应用这一术式,腹腔镜手术的可行性、围术期治疗效果已经得到证实,一些远期的肿瘤控制效果报道也证实了腹腔镜手术的安全性[16-17]。外科医生依据工作经验发现,女性的骨盆相较于男性的骨盆宽而浅,入口更宽更圆。典型的男性骨盆有突出的坐骨棘和弯曲的骶骨,在一定程度上增加了手术的难度。腹腔镜下的盆腔内手术视野受骨盆生理结构的影响,尤其是肥胖和深窄骨盆的患者,操作空间狭小、视野暴露不良,腹腔镜手术会增加术中出血量的风险[18]。增加手术损伤和中转开放发生率,严重妨碍手术的顺利进行。
基于Ogiso等[19]通过对影响腹腔镜直肠癌前切除术难度因素的评估研究证明,手术时间随着盆腔前后径的减小和盆腔深度的增加而增加。同为盆腔内器官,泌尿外科医生在手术中发现骨盆有些径线对术中膀胱根治切除过程存在着明显影响。影像学的飞速发展,使得可以通过高分辨CT、骨盆三维重建合成三维图像,医师可以在任意轴线上对骨盆进行测量,能更准确地评估骨盆,现在多数研究采用三维螺旋CT测量[20]。膀胱癌目前的术前评估有传统盆腔横断面CT平扫加增强、多参数磁共振成像(MRI)和基于MRI技术的VIRADS评分[21]。根据目前CT测量骨盆参数和临床病理参数对直肠切除[22-24]、前列腺切除的术前评估[25]。我们了解到骨盆大小和病理参数是腹腔镜下盆腔脏器根治切除的明显影响因素,因为肥胖和骨盆狭小导致的术中大出血、中转开放及其引起的术中并发症等并不少见。因此,术前能够评估手术难度,对膀胱根治切除有十分重要的意义。本研究创新性地利用了骨盆参数和临床病理对腹腔镜下膀胱癌根治术进行术前评估,通过单因素分析年龄、体重指数、有无合并基础疾病等参数在2组间比较,差异无统计学意义,提示这些参数对手术难度的影响并不大,基线可比。骨盆入口前后径、中骨盆前后径、上耻骨到尾骨距离、中骨盆棘突间径、坐骨结节间径参数2组间差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05),这代表着骨盆前后径偏小和深窄骨盆可能导致手术难度的增加。进一步多因素分析结果显示:中骨盆前后径、上耻骨到尾骨距离、中骨盆棘突间径差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05),且经皮尔逊相关系数分析不存在共线性问题,提示这几个变量是影响手术难度的独立危险因素。本研究根据logistic回归曲线的特点,建立了评价手术难度的相关函数,并通过ROC曲线判断其准确性。ROC曲线提示:AUC为0.871(SE=0.044,P < 0.001,95%CI:0.785~0.958),具有一定的准确性。在校准图中,可以看到预测概率与实际概率之间有较好的拟合程度(图 3),因此,认为此模型具有一定的准确度,可以用来术前评估手术难度。根据多因素分析和ROC曲线结果(图 2),证实了骨盆解剖参数对手术难度的预测价值。
本研究创新性地提出了通过CT测量骨盆各径线,建立预测模型用于评估腹腔镜下膀胱癌根治术的手术难度,为膀胱癌根治术难度评估提供了新的方向,便于主刀医生有更充分地准备和预期方案来应对术中的问题,使得患者有充分的心理准备,利于术前有效医患沟通。对于根据术前CT测量骨盆解剖参数预估手术难度较大的病例,例如深窄狭小骨盆或肥胖患者,我们建议让更有手术经验的医师去完成。术前应有手术难度的预期,术前备血。深窄骨盆患者,术中操作时,可以先行双侧盆腔清扫术开阔视野,利于后续膀胱切除的显露。深窄骨盆合并中重度前列腺增生的患者,膀胱切除时后层面分离及盆底筋膜打开缝扎阴茎背静脉复合体时显露尤其困难。可以通过增加操作孔、膀胱悬吊等方法增加暴露膀胱后层面分离及狄氏筋膜的打开。视野不清时尤其要注意直肠的保护。膀胱后层面显露、分离十分困难时,我们可以改变程序化步骤,先行分离膀胱前层面,离断尿道后,向头侧牵拉前列腺尖部,逆行进入直肠前狄氏间隙,打开狄氏筋膜分离精囊后层面,达到逆行根治切除膀胱的效果。深窄骨盆游离膀胱前层面时,需要有经验的扶镜助手,变换不同角度显露视野,切忌视野显露不清时盲目操作致静脉丛出血。采用2-0倒刺缝合线缝扎阴茎背静脉复合体节省了打结步骤,方便了视野显露不佳时的操作。同时,缝扎背静脉复合体时,主刀要灵活选用左侧或右侧进针缝合方法,可能需要熟练的手术技巧。
本研究仍存在一定局限性,样本量较小导致的评分系统不稳定,但随着手术次数的增多,手术熟练度增加,手术时间和术中出血量会相应缩短和减少等,但是它所反映的骨盆径线对手术难度的影响价值并没有变化。本研究中只关注了骨盆各径线、年龄、BMI和有无合并基础疾病对手术难度的影响,没有进一步分析前列腺增生大小等其他影响盆腔显露的因素;同时对需要保留支配尿道的自主神经来改善术后尿控、保留血管神经束改善性功能的要求也未考虑在内。本研究表明,腹腔镜下膀胱癌根治术难度受多种因素影响,其中中骨盆前后径、上耻骨到尾骨距离和中骨盆棘突间径对手术时间及术中出血量影响较大,提示骨盆前后径偏小和深窄骨盆可能导致手术难度的增加。所有病例是由一个手术团队完成,减少了手术误差。未来期待更全面、更少偏倚的前瞻性大样本队列进行研究。
利益冲突 所有作者均声明不存在利益冲突
-
表 1 骨盆径线测量及定义
骨盆测量参数/mm 定义 骨盆入口前后径 耻骨联合上缘中点到骶骨岬前缘中点的一条线 中骨盆前后径 耻骨联合下缘中点经坐骨棘连线中点到骶尾交界的距离 骨盆出口前后径 从耻骨联合的正中下方到尾骨顶端的一条线 耻骨联合高度 耻骨联合两端中点的连线 骶尾部距离 从骶角到尾骨尖端的距离 耻骨上端到尾骨距离 从耻骨联合的正中上部到尾骨顶端的一条线 中骨盆棘突直径 中骨盆横径、两侧坐骨棘最内点之间的距离 坐骨结节间径 坐骨结节最内点之间的距离 表 2 单因素分析骨盆各径线和基础资料
例(%),X±S 因素 容易组 困难组 P 年龄/岁 64.89±8.84 65.03±10.49 0.952 BMI 24.20±5.70 24.00±5.50 0.529 有无基础疾病 0.138 无 10(15.9) 16(47.1) 有 26(84.1) 18(52.9) 骨盆入口前后径/mm 110.16±4.34 107.68±4.90 0.028 中骨盆前后径/mm 100.24±5.64 97.12±3.89 0.009 骨盆出口前后径/mm 91.04±7.26 89.09±4.67 0.184 耻骨联合高度/mm 42.60±2.02 43.35±2.73 0.197 耻骨上端到尾骨距离/mm 114.11±6.97 111.02±2.80 0.019 骶尾部距离/mm 117.91±7.13 116.11±3.43 0.187 中骨盆棘突间径/mm 103.45±9.91 93.95±5.83 < 0.001 坐骨结节间径/mm 87.80±9.07 83.48±8.60 0.045 表 3 单因素分析病理分级及临床分期
例 组别 病理分级 T分期 N分期 低级别 高级别 T1 T2 T3 T4 N0 N1 N2 N3 容易组 14 22 10 9 12 5 35 1 0 0 困难组 13 21 4 15 10 5 30 3 0 1 P 0.955 0.231 0.350 表 4 多因素分析影响腹腔镜下膀胱癌根除术难度的危险因素
变量 β SE Wald df P Exp(β) 95%CI 骨盆入口前后径 0.504 0.835 0.364 1 0.546 1.655 0.322~8.494 中骨盆前后径 -2.571 1.114 5.322 1 0.021 0.076 0.009~0.679 上耻骨到尾骨距离 -1.529 0.731 4.374 1 0.036 0.217 0.052~0.908 棘突间径 -3.575 1.330 7.224 1 0.007 0.028 0.002~0.380 坐骨结节间径 -1.580 0.865 3.335 1 0.068 0.206 0.038~1.123 常量 11.584 2.987 表 5 2组在手术时间和出血量之间的差异比较
X±S 组别 中骨盆前后径 上耻骨到尾骨距离 棘突间径 手术时间/min 出血量/mL 手术时间/min 出血量/mL 手术时间/min 出血量/mL 较短组 129.46±13.24 218.80±42.70 129.31±13.82 219.23±43.61 130.96±13.33 225.32±40.48 较长组 118.25±10.10 185.00±35.61 122.42±11.90 196.45±40.21 116.65±6.72 176.09±27.76 P 0.001 0.003 0.031 0.028 <0.001 <0.001 表 6 各危险因素和模型函数Y的ROC曲线下面积
参数 AUC SE P 95%CI 中骨盆前后径 0.703 0.063 0.004 0.578~0.827 上耻骨到尾骨距离 0.686 0.064 0.008 0.560~0.812 棘突间径 0.839 0.048 < 0.001 0.746~0.933 函数Y 0.871 0.044 < 0.001 0.785~0.958 -
[1] Siegel RL, Miller KD, Fuchs HE, et al. Cancer Statistics, 2021[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2021, 71(1): 7-33. doi: 10.3322/caac.21654
[2] Antoni S, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, et al. Bladder Cancer Incidence and Mortality: A Global Overview and Recent Trends[J]. Eur Urol, 2017, 71(1): 96-108. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2016.06.010
[3] 蒋书算, 曹健, 韩惟青, 等. 非肌层浸润性膀胱癌首次电切术后肿瘤残余及二次电切术后复发相关因素分析[J]. 临床泌尿外科杂志, 2021, 36(4): 264-269. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCMW202104003.htm
[4] Babjuk M, Bohle A, Burger M, et al, EAU guidelines on non-muscle-invasive urothelial carcinoma of the bladder: update 2016[J]. Eur Urol, 2017, 71(3): 447-461. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2016.05.041
[5] Lázaro M, Gallardo E, Doménech M, et al. SEOM Clinical Guideline for treatment of muscle-invasive and metastatic urothelial bladder cancer(2016)[J]. Clin Transl Oncol, 2016, 18(12): 1197-1205. doi: 10.1007/s12094-016-1584-z
[6] Borgna V, Vidal I, Castillo OA. Open vs Laparoscopic Radical Cystectomy: Comparison of perioperative and Mid-term oncological outcomes[J]. Arch Esp Urol, 2020, 73(1): 32-40.
[7] Tyson MD, Barocas DA. Quality of Life After Radical Cystectomy[J]. Urol Clin North Am, 2018, 45(2): 249-256. doi: 10.1016/j.ucl.2017.12.008
[8] 蔡芳震, 马潞林. 根治性全膀胱切除术的治疗进展[J]. 临床泌尿外科杂志, 2015, 30(8): 758-762. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCMW201508029.htm
[9] 宋明泽, 根治性膀胱切除术的进展[J]. 临床外科杂志, 2019, 27(11): 1005-1007. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-6483.2019.11.026
[10] Escal L, Nougaret S, Guiu S, et al. MRI-based score to predict surgical difficulty in patients with rectal cancer[J]. Br J Surg, 2018, 105(1): 140-146.
[11] Hong J, Brown K, Waller J, et al. The role of MRI pelvimetry in predicting technical difficulty and outcomes of open and minimally invasive total mesorectal excision: a systematic review[J]. Tech Coloproctol, 2020, 24(10): 991-1000. doi: 10.1007/s10151-020-02274-x
[12] Cortesi N, Ferrari P, Zambarda E, et al. Diagnosis of bilateral abdominal cryptorchidism by laparoscopy[J]. Endoscopy, 1976, 8(1): 33-34. doi: 10.1055/s-0028-1098372
[13] 祝广峰, 杨帆. 腹腔镜和开放手术膀胱癌根治术的临床效果比较[J]. 临床医学研究与实践, 2018, 3(20): 42-43. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YLYS201820020.htm
[14] 曾蜀雄, 张振声, 宋瑞祥, 等. 腹腔镜下与开放式根治性膀胱切除术后早期并发症的对比研究[J]. 中华泌尿外科杂志, 2015, 36(5): 333-336. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1000-6702.2015.05.004
[15] 夏照明, 土应果, 郭民, 等. 根治性膀胱切除术后30 d内并发症的发生情况及危险因素分析[J]. 临床泌尿外科杂志, 2021, 36(9): 709-712, 720. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCMW202109007.htm
[16] 邢毅飞, 宋亚荣, 汪良, 等. 腹腔镜与开放膀胱根治性切除原位膀胱术并发症和肿瘤控制比较[J]. 临床泌尿外科杂志, 2016, 31(5): 406-409. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCMW201605004.htm
[17] Sathianathen NJ, Kalapara A, Frydenberg M, et al. Robotic Assisted Radical Cystectomy vs Open Radical Cystectomy: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis[J]. J Urol, 2019, 1(4): 715-720.
[18] 戴青松, 陈远志, 孙伟, 等. 肥胖对腹腔镜直肠癌手术的影响[J]. 腹腔镜外科杂志, 2021, 26(5): 339-342, 346. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FQJW202105006.htm
[19] Ogiso S, Yamaguchi T, Hata H, et al. Evaluation of factors affecting the difficulty of laparoscopic anterior resection for rectal cancer: "narrow pelvis" is not a contraindication[J]. Surg Endosc, 2011, 25(6): 1907-1912. doi: 10.1007/s00464-010-1485-0
[20] Takehiro S, Tsuruta M, Hasegawa H, et al. Pelvic inlet shape measured by three-dimensional pelvimetry is a predictor of the operative time in the anterior resection of rectal cancer[J]. Surgery Today, 2018, 48(1): 51-57. doi: 10.1007/s00595-017-1547-1
[21] Panebianco V, Narumi Y, Altun E, et al. Multiparametric Magnetic Resonance Imaging for Bladder Cancer: Development of Ⅵ-RADS(Vesical Imaging-Reporting And Data System)[J]. Eur Urol, 2018, 74(3): 294-306. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2018.04.029
[22] Zhou XC, Su M, Hu KQ, et al. CT pelvimetry and clinicopathological parameters in evaluation of the technical difficulties in performing open rectal surgery for mid-low rectal cancer[J]. Oncol Lett, 2016, 11(1): 31-38. doi: 10.3892/ol.2015.3827
[23] 周洋, 骨盆影像学测量对腹腔镜中低位直肠癌手术术前决策的影响[D]. 重庆: 重庆医科大学, 2018.
[24] 张海鑫, 苏琪. 术前CT下骨盆测量及病理参数对腹腔镜下中低位直肠癌根治术手术难度的预测及预测系统的建立[J]. 临床与病理杂志, 2019, 39(2): 358-364. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WYSB201902021.htm
[25] 宫正. 骨盆径线及多参数对前列腺癌根治术后尖部切缘阳性的影响分析[D]. 沈阳: 中国医科大学, 2018.
-




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: