Study on the temperature change around the fiber during super-pulse thulium fiber laser extracorporeal lithotripsy
-
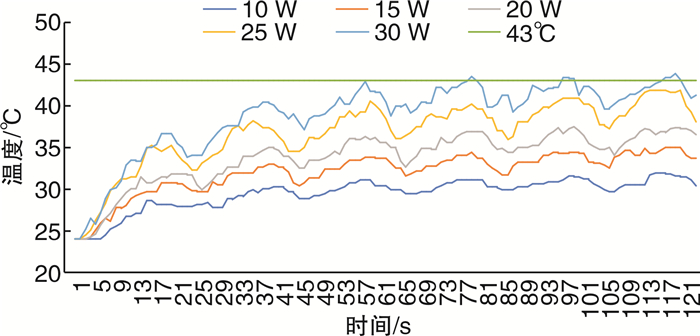
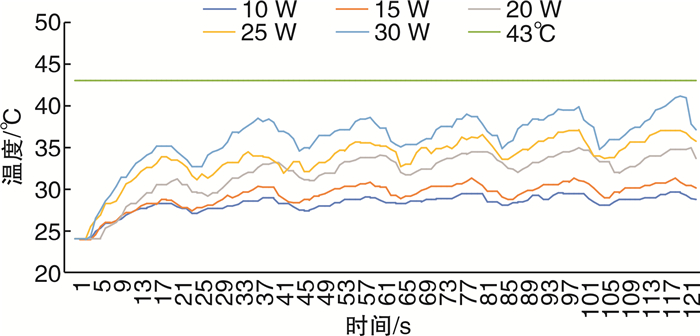
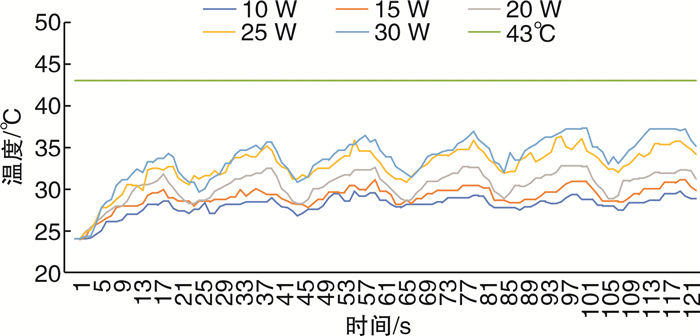
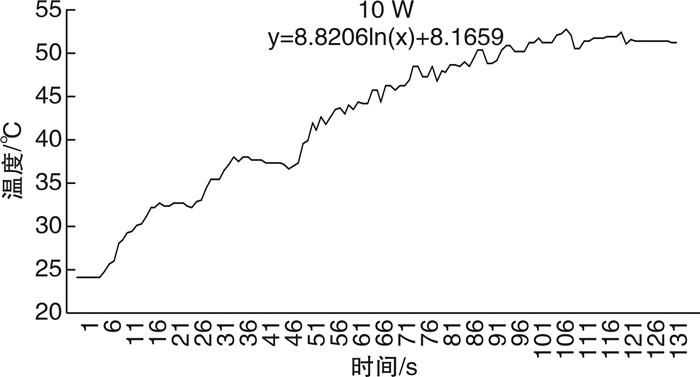
摘要: 目的 探讨国产超脉冲铥光纤激光体外碎石过程中光纤周围温度的变化。方法 将大小1 cm×1 cm×1 cm的人造立方体结石置于的体外圆柱形模型中,由同一名医生行体外软性输尿管镜激光碎石术,温度探头位于光纤周围5 mm处,激光激发15 s,间断5 s,每组实验周期为120 s,每组重复5次实验。激光功率为10、15、20、25、30 W,灌注速率为0、10、15、25 mL/min,激光设备为超脉冲铥光纤激光,光纤直径为272 μm,脉宽为7 ms。实时记录光纤周围温度变化情况,比较不同功率、不同灌注速度下光纤周围温度的变化情况。结果 在碎石功率为10 W时,灌注流速为0 mL/min时,周围温度每分钟升高0.2℃,在57 s时光纤周围温度达到安全阈值43℃。当灌注速度为15 mL/min,碎石功率20 W时,光纤平台期温度36.9~37.25℃,未超过安全阈值43℃。当灌注速度为20 mL/min,碎石功率25 W时,光纤平台期温度36.8~37.05℃,未超过安全阈值43℃。当灌注速度为25 mL/min,碎石功率30 W时,光纤平台期温度37.05~37.2℃,未超过安全阈值43℃。结论 体外软性输尿管镜超脉铥光纤激光碎石术中,安全灌流速度与激光功率成正相关,碎石功率≤20 W时需保持灌注速度≥15 mL/min,碎石功率≤25 W时需保持灌注速度≥20 mL/min,碎石功率≤30 W时需保持灌注速度≥25 mL/min。Abstract: Objective To investigate the changes of temperature around the fiber during in vitro lithotripsy with domestic super-pulse thulium fiber laser.Methods An artificial cube stone of 1 cm×1 cm×1 cm was placed in an external cylindrical model, and the same doctor performed external flexible ureteroscopic laser lithotripsy. The temperature probe was located 5 mm around the optical fiber, and the laser excitation was performed for 15 s with an interval of 5 s. The experiment period of each group was 120 s, and the experiment was repeated for 5 times in each group. The laser power was 10, 15, 20, 25, 30 W, and the perfusion rate was 0, 10, 15, 25 mL/min. The laser equipment was ultra pulse thulium fiber laser, the fiber diameter was 272 μm, and the pulse width was 7 ms. The temperature change around the fiber was recorded in real time, and the temperature change around the fiber was compared under different power and different perfusion speed.Results When the gravel power was 10 W and the perfusion flow rate was 0 mL/min, the surrounding temperature increased by 0.2℃ per minute, and the surrounding temperature reached the safe threshold of 43℃ at 57 s. When the perfusion rate was 15 mL/min and the crushed stone power was 20 W, the fiber plateau temperature was 36.9-37.25 ℃, which did not exceed the safe threshold of 43℃. When the perfusion rate was 20 mL/min and the crushed stone power was 25 W, the temperature of the fiber platform phase was 36.8-37.05℃, which did not exceed the safe threshold of 43℃. When the perfusion rate is 25 mL/min and the crushed stone power is 30 W, the temperature of the fiber platform phase is 37.05-37.2℃, which does not exceed the safe threshold of 43℃.Conclusion The safe perfusion velocity is positively correlated with the laser power in the extracorporeal flexible ureteroscope ultra pulse thulium fiber laser lithotripsy. The perfusion velocity should be maintained ≥15 mL/min when the lithotripsy power is less than 20 W, ≥20 mL/min when the lithotripsy power is less than 25 W, and ≥25 mL/min when the lithotripsy power is less than 30 W.
-
Key words:
- super-pulse thulium fiber laser /
- temperature /
- lithotripsy /
- safe threshold
-

-
[1] Zeng G, Mai Z, Xia S, et al. Prevalence of kidney stones in China: an ultrasonography based cross-sectional study[J]. BJU Int, 2017, 120(1): 109-116. doi: 10.1111/bju.13828
[2] Huusmann S, Lafos M, Meyenburg I, et al. Tissue effects of a newly developed diode pumped pulsed Thulium: YAG laser compared to continuous wave Thulium: YAG and pulsed Holmium: YAG laser[J]. World J Urol, 2021, 39(9): 3503-3508. doi: 10.1007/s00345-021-03634-4
[3] Fried NM, Irby PB. Advances in laser technology and fibre-optic delivery systems in lithotripsy[J]. Nat Rev Urol, 2018, 15(9): 563-573. doi: 10.1038/s41585-018-0035-8
[4] Traxer O, Keller EX. Thulium fiber laser: the new player for kidney stone treatment? A comparison with Holmium: YAG laser[J]. World J Urol, 2020, 38(8): 1883-1894. doi: 10.1007/s00345-019-02654-5
[5] Kronenberg P, Traxer O. The laser of the future: reality and expectations about the new thulium fiber laser-a systematic review[J]. Transl Androl Urol, 2019, 8(Suppl 4): S398-S417.
[6] Rapoport LM, Gazimiev MA, Korolev DO, et al. Flexible ureteroscopy for lower pole renal stones: novel superpulse thulium(TM)fiber laser lithotripsy[J]. Urologiia, 2020(6): 89-92.
[7] Cinman NM, Andonian S, Smith AD. Lasers in percutaneous renal procedures[J]. World J Urol, 2010, 28(2): 135-142. doi: 10.1007/s00345-009-0423-z
[8] Traxer O, Corrales M. Managing Urolithiasis with Thulium Fiber Laser: Updated Real-Life Results-A Systematic Review[J]. J Clin Med, 2021, 10(15): 3390. doi: 10.3390/jcm10153390
[9] Ventimiglia E, Doizi S, Kovalenko A, et al. Effect of temporal pulse shape on urinary stone phantom retropulsion rate and ablation efficiency using holmium: YAG and super-pulse thulium fibre lasers[J]. BJU Int, 2020, 126(1): 159-167. doi: 10.1111/bju.15079
[10] Dong H, Peng Y, Li L, et al. Prevention strategies for ureteral stricture following ureteroscopic lithotripsy[J]. Asian J Urol, 2018, 5(2): 94-100. doi: 10.1016/j.ajur.2017.09.002
[11] Thomsen S, Pearce JA. Thermal Damage and Rate Processes in Biologic Tissues[M]// Welch AJ, van Gemert MJC, eds. Optical-Thermal Response of Laser-Irradiated Tissue. Dordrecht: Springer Netherlands, 2011: 487-549.
[12] Hein S, Petzold R, Schoenthaler M, et al. Thermal effects of Ho: YAG laser lithotripsy: real-time evaluation in an in vitro model[J]. World J Urol, 2018, 36(9): 1469-1475. doi: 10.1007/s00345-018-2303-x
[13] Aldoukhi AH, Ghani KR, Hall TL, et al. Thermal Response to High-Power Holmium Laser Lithotripsy[J]. J Endourol, 2017, 31(12): 1308-1312. doi: 10.1089/end.2017.0679
[14] He X, McGee S, Coad JE, et al. Investigation of the thermal and tissue injury behaviour in microwave thermal therapy using a porcine kidney model[J]. Int J Hyperthermia, 2004, 20(6): 567-593. doi: 10.1080/0265673042000209770
[15] Cinman NM, Andonian S, Smith AD. Lasers in percutaneous renal procedures[J]. World J Urol, 2010, 28(2): 135-142. doi: 10.1007/s00345-009-0423-z
[16] Peng Y, Liu M, Ming S, et al. Safety of a Novel Thulium Fiber Laser for Lithotripsy: An In Vitro Study on the Thermal Effect and Its Impact Factor[J]. J Endourol, 2020, 34(1): 88-92. doi: 10.1089/end.2019.0426
[17] Taratkin M, Laukhtina E, Singla N, et al. Temperature changes during laser lithotripsy with Ho: YAG laser and novel Tm-fiber laser: a comparative in-vitro study[J]. World J Urol, 2020, 38(12): 3261-3266. doi: 10.1007/s00345-020-03122-1
[18] Andreeva V, Vinarov A, Yaroslavsky I, et al. Preclinical comparison of superpulse thulium fiber laser and a holmium: YAG laser for lithotripsy[J]. World J Urol, 2020, 38(2): 497-503. doi: 10.1007/s00345-019-02785-9
[19] Taratkin M, Laukhtina E, Singla N, et al. Temperature changes during laser lithotripsy with Ho: YAG laser and novel Tm-fiber laser: a comparative in-vitro study[J]. World J Urol, 2020, 38(12): 3261-3266. doi: 10.1007/s00345-020-03122-1
[20] Hardy LA, Wilson CR, Irby PB, et al. Thulium fiber laser lithotripsy in an in vitro ureter model[J]. J Biomed Opt, 2014, 19(12): 128001. doi: 10.1117/1.JBO.19.12.128001
[21] 李成文, 刘畅, 齐士勇. 预测肾结石腔内手术后发生尿脓毒症列线图模型的建立[J]. 临床泌尿外科杂志, 2022, 37(3): 175-179. https://lcmw.whuhzzs.com/article/doi/10.13201/j.issn.1001-1420.2022.03.004
[22] 赵蓉, 沈昊, 周家杰, 等. 肾盂尿及结石细菌培养与经皮肾镜取石术后尿脓毒症的相关性研究[J]. 临床泌尿外科杂志, 2019, 34(7): 557-561. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCMW201907016.htm
[23] 杨嗣星, 郑府, 柯芹, 等. 软性输尿管镜碎石术中肾盂内压力监测方法及意义[J]. 中华泌尿外科杂志, 2014, 35(8): 575-578.
-




 下载:
下载: