-
摘要: 铥激光由于其高效的组织汽化切割能力、优异的止血性能以及较浅的热损伤深度,近年来在泌尿外科领域中的应用越来越为广泛。本文综述了铥激光的作用原理与特点,及其在良性前列腺增生、膀胱肿瘤、尿路结石以及上尿路疾病等多种泌尿外科疾病中的应用和最新进展。Abstract: The thulium laser has been increasingly used in the field of urology in recent years due to its high-performance tissue vaporization and cutting capabilities, excellent hemostasis, and shallow depth of thermal damage. This article reviews the principles and characteristics of the thulium laser, its application, and recent advances in a variety of urological conditions including benign prostatic hyperplasia, bladder neoplasms, urinary calculi, as well as diseases of the upper urinary tract.
-

-
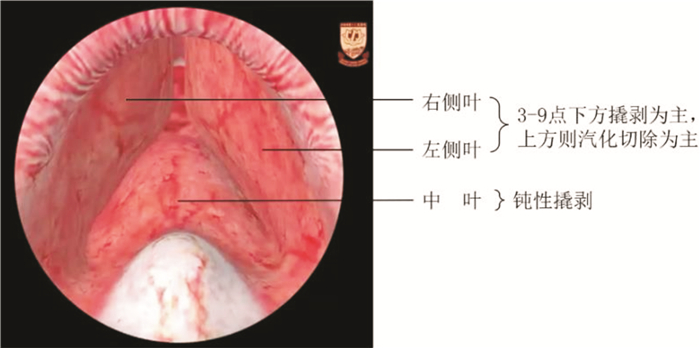
图 2 经尿道膀胱肿瘤电切术[19]
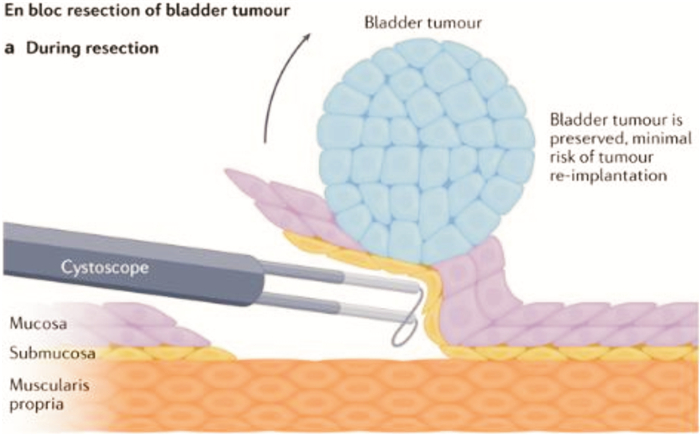
图 3 经尿道膀胱肿瘤整块切除术[19]
-
[1] Mulvaney WP, Beck CW. The laser beam in urology[J]. J Urol, 1968, 99(1): 112-115. doi: 10.1016/S0022-5347(17)62652-1
[2] 张安军, 段嘉霖, 邢颍滨, 等. 掺铥激光在生物医疗领域的应用[J]. 激光与光电子学进展, 2022, 59(1): 50-63. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JGDJ202201004.htm
[3] Fried NM, Irby PB. Advances in laser technology and fibre-optic delivery systems in lithotripsy[J]. Nat Rev Urol, 2018, 15(9): 563-573. doi: 10.1038/s41585-018-0035-8
[4] 王彩霞, 田云云. 医用激光在泌尿外科的应用及发展[J]. 应用激光, 2021, 41(1): 201-205. doi: 10.14128/j.cnki.al.20214101.201
[5] Niemz MH. Laser-Tissue Interactions: Fundamentals and Applications[M]. 4th ed. Cham: Springer International Publishing, 2019: 79-82.
[6] Huang SW, Tsai CY, Tseng CS, et al. Comparative efficacy and safety of new surgical treatments for benign prostatic hyperplasia: systematic review and network meta-analysis[J]. BMJ, 2019, 367: 15919.
[7] 夏术阶, 张沂南, 鲁军, 等. 铥激光"剥橘"式切除术治疗良性前列腺增生症[J]. 中华医学志, 2005, 85(45): 62-65. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHYX200545017.htm
[8] Xia SJ, Zhuo J, Sun XW, et al. Thulium laser versus standard transurethral resection of the prostate: a randomized prospective trial[J]. Eur Urol, 2008, 53(2): 382-389. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2007.05.019
[9] Bach T, Xia SJ, Yang Y, et al. Thulium: YAG 2 μm cw laser prostatectomy: where do we stand?[J]. World J Urol, 2010, 28(2): 163-168. doi: 10.1007/s00345-010-0522-x
[10] Pariser JJ, Famakinwa OJ, Pearce SM, et al. High-power thulium laser vaporization of the prostate: short-term outcomes of safety and effectiveness[J]. J Endourol, 2014, 28(11): 1357-1362. doi: 10.1089/end.2014.0336
[11] Gross AJ, Orywal AK, Becker B, et al. Five-year outcomes of thulium vapoenucleation of the prostate for symptomatic benign prostatic obstruction[J]. World J Urol, 2017, 35(10): 1585-1593. doi: 10.1007/s00345-017-2034-4
[12] Becker B, Herrmann TR, Gross AJ, et al. Thulium vapoenucleation of the prostate versus holmium laser enucleation of the prostate for the treatment of large volume prostates: preliminary 6-month safety and efficacy results of a prospective randomized trial[J]. World J Urol, 2018, 36(10): 1663-1671. doi: 10.1007/s00345-018-2321-8
[13] 安子彦, 符伟军, 宋勇, 等. 经尿道前列腺铥光纤激光分叶剜除术后下尿路症状对生活质量的影响[J]. 临床泌尿外科杂志, 2022, 37(10): 773-777. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.1001-1420.2022.10.010 https://lcmw.whuhzzs.com/article/doi/10.13201/j.issn.1001-1420.2022.10.010
[14] Sun Q, Guo WH, Cui D, et al. Thulium laser enucleation versus thulium laser resection of the prostate for prevention of bladder neck contracture in a small prostate: a prospective randomized trial[J]. World J Urol, 2019, 37(5): 853-859. doi: 10.1007/s00345-018-2463-8
[15] 夏术阶, 王东文. 铥激光治疗机团体标准及其临床应用操作指南[M]. 北京: 中国医药科技出版社, 2021: 45-47.
[16] Netsch C, Bach T, Herrmann TR, et al. Evaluation of the learning curve for Thulium VapoEnucleation of the prostate(ThuVEP)using a mentor-based approach[J]. World J Urol, 2013, 31(5): 1231-1238. doi: 10.1007/s00345-012-0894-1
[17] Jordan B, Meeks JJ. T1 bladder cancer: current considerations for diagnosis and management[J]. Nat Rev Urol, 2019, 16(1): 23-34. doi: 10.1038/s41585-018-0105-y
[18] Pecoraro M, Takeuchi M, Vargas HA, et al. Overview of VI-RADS in bladder cancer[J]. AJR Am J Roentgenol, 2020, 214(6): 1259-1268. doi: 10.2214/AJR.20.22763
[19] Teoh JY, Kamat AM, Black PC, et al. Recurrence mechanisms of non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer-a clinical perspective[J]. Nat Rev Urol, 2022, 19(5): 280-294. doi: 10.1038/s41585-022-00578-1
[20] Sylvester RJ, van der Meijden AP, Oosterlinck W, et al. Predicting recurrence and progression in individual patients with stage Ta T1 bladder cancer using EORTC risk tables: a combined analysis of 2596 patients from seven EORTC trials[J]. Eur Urol, 2006, 49(3): 466-477. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2005.12.031
[21] Kim LH, Patel MI. Transurethral resection of bladder tumour(TURBT)[J]. Transl Androl Urol, 2020, 9(6): 3056-3072. doi: 10.21037/tau.2019.09.38
[22] Kitamura K, Kataoka K, Fujioka H, et al. Transurethral resection of a bladder tumor by the use of a polypectomy snare[J]. J Urol, 1980, 124(6): 808-809.
[23] Yang Y, Wei Z, Zhang X, et al. Transurethral partial cystectomy with continuous wave laser for bladder carcinoma[J]. J Urol, 2009, 182(1): 66-69. doi: 10.1016/j.juro.2009.02.154
[24] Li K, Xu Y, Tan M, et al. A retrospective comparison of thulium laser en bloc resection of bladder tumor and plasmakinetic transurethral resection of bladder tumor in primary non-muscle invasive bladder cancer[J]. Lasers Med Sci, 2019, 34(1): 85-92. doi: 10.1007/s10103-018-2604-8
[25] Teoh JY, Maclennan S, Chan VW, et al. An international collaborative consensus statement on en bloc resection of bladder tumour incorporating two systematic reviews, a two-round Delphi survey, and a consensus meeting[J]. Eur Urol, 2020, 78(4): 546-569. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2020.04.059
[26] Kramer MW, Altieri V, Hurle R, et al. Current evidence of transurethral en-bloc resection of nonmuscle invasive bladder cancer[J]. Eur Urol Focus, 2017, 3(6): 567-576. doi: 10.1016/j.euf.2016.12.004
[27] Fried NM. Thulium fiber laser lithotripsy: an in vitro analysis of stone fragmentation using a modulated 110-watt thulium fiber laser at 1.94 microm[J]. Lasers Surg Med, 2005, 37(1): 53-58. doi: 10.1002/lsm.20196
[28] Panthier F, Doizi S, Lapouge P, et al. Comparison of the ablation rates, fissures and fragments produced with 150 μm and 272 μm laser fibers with superpulsed thulium fiber laser: an in vitro study[J]. World J Urol, 2021, 39(6): 1683-1691. doi: 10.1007/s00345-020-03186-z
[29] Andreeva V, Vinarov A, Yaroslavsky I, et al. Preclinical comparison of superpulse thulium fiber laser and a holmium: YAG laser for lithotripsy[J]. World J Urol, 2020, 38(2): 497-503. doi: 10.1007/s00345-019-02785-9
[30] Lee H, Ryan RT, Teichman JM, et al. Stone retropulsion during holmium: YAG lithotripsy[J]. J Urol, 2003, 169(3): 881-885. doi: 10.1097/01.ju.0000046367.49923.c6
[31] Ventimiglia E, Doizi S, Kovalenko A, et al. Effect of temporal pulse shape on urinary stone phantom retropulsion rate and ablation efficiency using holmium: YAG and super-pulse thulium fibre lasers[J]. BJU Int, 2020, 126(1): 159-167. doi: 10.1111/bju.15079
[32] Hardy LA, Vinnichenko V, Fried NM. High power holmium: YAG versus thulium fiber laser treatment of kidney stones in dusting mode: ablation rate and fragment size studies[J]. Lasers Surg Med, 2019, 51(6): 522-530. doi: 10.1002/lsm.23057
[33] Keller EX, De Coninck V, Doizi S, et al. Thulium fiber laser: ready to dust all urinary stone composition types?[J]. World J Urol, 2021, 39(6): 1693-1698. doi: 10.1007/s00345-020-03217-9
[34] Martov AG, Ergakov DV, Guseinov MA, et al. Initial experience in clinical application of thulium laser contact lithotripsy for transurethral treatment of urolithiasis[J]. Urologiia, 2018, (1): 112-120.
[35] Ulvik ∅, Æsøy MS, Juliebø-jones P, et al. Thulium fibre laser versus holmium: YAG for ureteroscopic lithotripsy: outcomes from a prospective randomised clinical trial[J]. Eur Urol, 2022, 82(1): 73-79. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2022.02.027
[36] Enikeev D, Taratkin M, Klimov R, et al. Thulium-fiber laser for lithotripsy: first clinical experience in percutaneous nephrolithotomy[J]. World J Urol, 2020, 38(12): 3069-3074. doi: 10.1007/s00345-020-03134-x
[37] Korolev D, Akopyan G, Tsarichenko D, et al. Minimally invasive percutaneous nephrolithotomy with superpulsed thulium-fiber laser[J]. Urolithiasis, 2021, 49(5): 485-491. doi: 10.1007/s00240-021-01258-2
[38] Türk C, Petřík A, Sarica K, et al. EAU guidelines on interventional treatment for urolithiasis[J]. Eur Urol, 2016, 69(3): 475-482. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2015.07.041
[39] Jones P, Beisland C, Ulvik ∅. Current status of thulium fibre laser lithotripsy: an up-to-date review[J]. BJU Int, 2021, 128(5): 531-538. doi: 10.1111/bju.15551
[40] Wang Y, Shao J, Lü Y, et al. Thulium Laser-Assisted versus conventional laparoscopic partial nephrectomy for the small renal mass[J]. Lasers Surg Med, 2020, 52(5): 402-407. doi: 10.1002/lsm.23153
[41] Rehan M, Elnady EA, Khater S, et al. Comparative study between thulium laser and cold knife visual urethrotomy for treatment of short bulbomembranous urethral stricture[J]. Medicine(Baltimore), 2022, 101(35): e30235.
[42] Wen J, Ji ZG, Li HZ. Treatment of upper tract urothelial carcinoma with ureteroscopy and thulium laser: a retrospective single center study[J]. BMC Cancer, 2018, 18(1): 196. doi: 10.1186/s12885-018-4118-y
-

| 引用本文: | 徐峻豪, 荆翌峰. 铥激光在泌尿外科中的应用与进展[J]. 临床泌尿外科杂志, 2023, 38(5): 350-354. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.1001-1420.2023.05.008 |
| Citation: | XU Junhao, JING Yifeng. Application and progress of thulium laser in urology[J]. J Clin Urol, 2023, 38(5): 350-354. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.1001-1420.2023.05.008 |
- Figure 1.
- Figure 2.
- Figure 3.



 下载:
下载: