-
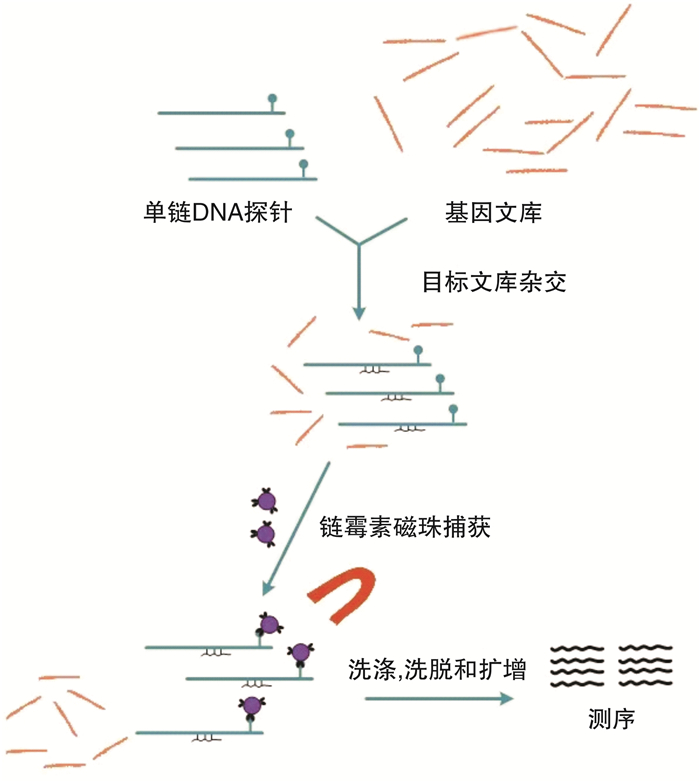
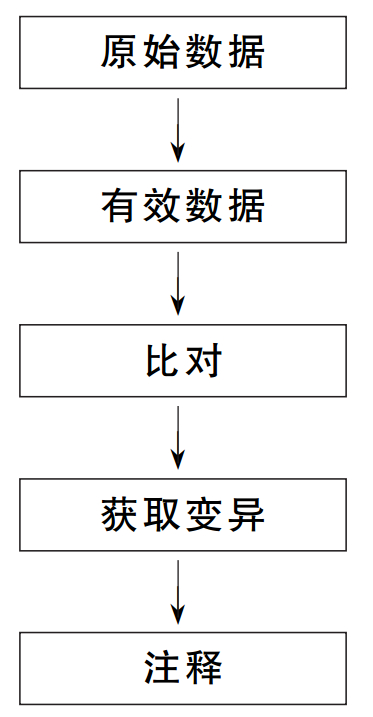
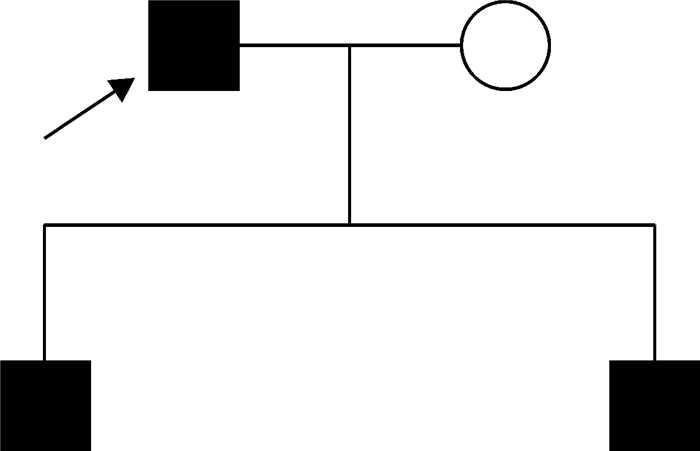
摘要: 目的 对收治的1个隐睾症家系进行全外显子测序(WES),筛选并分析该家系中与隐睾症发生相关的突变位点,为该疾病的遗传学病因提供证据。方法 收集本中心收治的一对同时患有单侧隐睾且存在家族史的同卵双生双胞胎兄弟及其父母的血液DNA样本,对该家系进行NextSeq500 PE150测序,以GATK、VarScan软件对SNP和InDel进行低频变异检测,并关联多个数据库(dbSNP、1000g、ESP6500、HGMD、OMIM等)对变异结果进行注释。结果 基因组分析显示,双胞胎患儿中,ROR2基因(c.2249G>A.p.G750D)存在杂合子非同义变异,变异来源为父亲。AR基因(c.1625G>A;p.R542Q)存在半合子非同义变异,变异来源于母亲。这两处变异在基因数据库中较为少见,预测与隐睾相关。结论 ROR2基因突变(c.2249G>A.p.G750D)与AR基因突变(c.1625G>A;p.R542Q)可能是该家系发生隐睾症的遗传学病因。Abstract: Objective To perform whole exome sequencing(WES) on an admitted family with cryptorchidism, to screen and analyze the mutation sites associated with cryptorchidism in the family, and to provide evidence for the genetic etiology of the disease.Methods The blood DNA samples of a pair of identical twin brothers with unilateral cryptorchidism and family history and their parents were collected in our center. The family was sequenced by NextSeq500 PE150, and SNP and InDel were detected by GATK and VarScan software for low-frequency variants, and multiple databases(dbSNP, 1000g, ESP6500, HGMD, OMIM, etc.) were associated to annotate the variant results.Results Genomic analysis showed that there was a heterozygous non-synonymous variant in the ROR2 gene(c. 2249G>A. p. G750D) in the twin children, and the source of the variant was the father. AR gene(c. 1625G>A; p. R542Q) has a hemizygous non-synonymous variant, which originates from the mother. These two variants are rare in genetic databases and we predict that they are associated with cryptorchidism.Conclusion ROR2 gene mutation(c. 2249G>A. p. G750D) and AR gene mutation(c. 1625G>A; p. R542Q) may be the genetic causes of cryptorchidism in this family.
-
Key words:
- cryptorchidism /
- heredity /
- exon sequencing /
- gene mutation
-

-
表 1 测序基本统计数据
样本 RawData/Mb CleanData/Mb Mapped target Coverage/% Depth ≥4X/% ≥10X/% ≥20X/% Duplication/% Chip 兄弟A:
20C244461_R1
03_CapNGS20 132.92 19 702.75 19 563.46 99.66 172.42 99.29 98.83 97.54 17.19 MGN-ExomeV2 兄弟B:
20C244460_R1
03_CapNGS20 586.55 20 017.28 19 869.73 99.67 184.75 99.30 98.86 97.73 14.86 MGN-ExomeV2 父亲:
20C244462_R1
03_CapNGS20 146.91 19 669.77 19 530.1 99.68 178.88 99.31 98.86 97.65 15.48 MGN-ExomeV2 母亲:
20C244463_R1
03_CapNGS22 315.04 21 674.95 21 512.44 99.59 200.8 99.15 98.76 97.82 13.99 MGN-ExomeV2 RawData:原始碱基数;CleanData:质控后的碱基数;Mapped target:比对到目标区域上的碱基数;Coverage:目标区域上的覆盖度;Depth:平均测序深度;≥4X:目标区域碱基测序深度不低于4X所占的比例;≥10X:目标区域碱基测序深度不低于10X所占的比例;≥20X:目标区域碱基测序深度不低于20X所占的比例;Duplication:PCR反应造成的数据冗余度;Chip:分析坐标。 表 2 可疑基因突变位点信息
样本 突变基因 突变位置 转录本编号 外显子编号 核苷酸变化 氨基酸变化 纯合/杂合 千人基因组中频率 疾病/表型 变异来源 兄弟A AR chrX:669
05791NM_001
348064exon2 c.1625
G>Ap.R542Q hemi 0.001 854 3 X连锁尿道下裂1型;部分雄激素不敏感症;雄激素不敏感综合征;肯尼迪病 母亲 兄弟B AR chrX:669
05791NM_001
348064exon2 c.1625
G>Ap.R542Q hemi 0.001 854 3 X连锁尿道下裂1型;部分雄激素不敏感症;雄激素不敏感综合征;肯尼迪病 母亲 兄弟A ROR2 chr9:944
86527NM_004
560exon9 c.2249
G>Ap.G750D het 0.000 199 681 常染色体隐性Robinow综合征;短指(趾)畸形B1型 父亲 兄弟B ROR2 chr9:944
86527NM_004
560exon9 c.2249
G>Ap.G750D het 0.000 199 681 常染色体隐性Robinow综合征;短指(趾)畸形B1型 父亲 -
[1] Chul Kim S, Kyoung Kwon S, Pyo Hong Y. Trends in the incidence of cryptorchidism and hypospadias of registry-based data in Korea: a comparison between industrialized areas of petrochemical estates and a non-industrialized area[J]. Asian J Androl, 2011, 13(5): 715-718. doi: 10.1038/aja.2010.53
[2] Schneuer FJ, Holland AJ, Pereira G, et al. Age at Surgery and Outcomes of an Undescended Testis[J]. Pediatrics, 2016, 137(2): e20152768. doi: 10.1542/peds.2015-2768
[3] 曹海波, 刘振勇, 李一帆. 腹腔镜下经改良Prentiss路径睾丸下降固定术治疗小儿高位隐睾临床研究[J]. 临床泌尿外科杂志, 2021, 36(12): 937-941. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.1001-1420.2021.12.004
[4] Baranzini SE, Mudge J, van Velkinburgh JC, et al. Genome, epigenome and RNA sequences of monozygotic twins discordant for multiple sclerosis[J]. Nature, 2010, 464(7293): 1351-1356. doi: 10.1038/nature08990
[5] Feng S, Ferlin A, Truong A, et al. INSL3/RXFP2 signaling in testicular descent[J]. Ann N Y Acad Sci, 2009, 1160: 197-204. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2009.03841.x
[6] Ayers K, Kumar R, Robevska G, et al. Familial bilateral cryptorchidism is caused by recessive variants in RXFP2[J]. J Med Genet, 2019, 56(11): 727-733. doi: 10.1136/jmedgenet-2019-106203
[7] Komarowska MD, Hermanowicz A, Debek W. Putting the pieces together: cryptorchidism-do we know everything?[J]. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab, 2015, 28(11-12): 1247-1256.
[8] Arendt LH, Lindhard MS, Henriksen TB, et al. Maternal Diabetes Mellitus and Genital Anomalies in Male Offspring: A Nationwide Cohort Study in 2 Nordic Countries[J]. Epidemiology, 2018, 29(2): 280-289. doi: 10.1097/EDE.0000000000000781
[9] Kurpisz M, Havryluk A, Nakonechnyj A, et al. Cryptorchidism and long-term consequences[J]. Reprod Biol, 2010, 10(1): 19-35. doi: 10.1016/S1642-431X(12)60035-7
[10] Huang Z, Rivas B, Agoulnik AI. Insulin-like 3 signaling is important for testicular descent but dispensable for spermatogenesis and germ cell survival in adult mice[J]. Biol Reprod, 2012, 87(6): 143.
[11] Elamo HP, Virtanen HE, Toppari J. Genetics of cryptorchidism and testicular regression[J]. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab, 2022, 36(1): 101619. doi: 10.1016/j.beem.2022.101619
[12] Tekgül S, Riedmiller H, Dogan HS, et al. Guidelines on pediatricurology[J]. EAU Update, 2013: 11-13.
[13] Winkel A, Stricker S, Tylzanowski P, et al. Wnt-ligand-dependent interaction of TAK1(TGF-beta-activated kinase-1) with the receptor tyrosine kinase Ror2 modulates canonical Wnt-signalling[J]. Cell Signal, 2008, 20(11): 2134-2144. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2008.08.009
[14] Schwabe GC, Trepczik B, Süring K, et al. Ror2 knockout mouse as a model for the developmental pathology of autosomal recessive Robinow syndrome[J]. Dev Dyn, 2004, 229(2): 400-410. doi: 10.1002/dvdy.10466
[15] Kaftanovskaya EM, Huang Z, Barbara AM, et al. Cryptorchidism in mice with an androgen receptor ablation in gubernaculum testis[J]. Mol Endocrinol, 2012, 26(4): 598-607. doi: 10.1210/me.2011-1283
[16] Nation TR, Buraundi S, Balic A, et al. The effect of flutamide on expression of androgen and estrogen receptors in the gubernaculum and surrounding structures during testicular descent[J]. J Pediatr Surg, 2011, 46(12): 2358-2362. doi: 10.1016/j.jpedsurg.2011.09.026
[17] Hutson JM, Balic A, Nation T, et al. Cryptorchidism[J]. Semin Pediatr Surg, 2010, 19(3): 215-224. doi: 10.1053/j.sempedsurg.2010.04.001
[18] Radpour R, Falah M, Aslani A, et al. Identification of a critical novel mutation in the exon 1 of androgen receptor gene in 2 brothers with complete androgen insensitivity syndrome[J]. J Androl, 2009, 30(3): 230-232. doi: 10.2164/jandrol.108.005520
[19] Kaftanovskaya EM, Huang Z, Barbara AM, et al. Cryptorchidism in mice with an androgen receptor ablation in gubernaculum testis[J]. Mol Endocrinol, 2012, 26(4): 598-607. doi: 10.1210/me.2011-1283
[20] Kalfa N, Gaspari L, Ollivier M, et al. Molecular genetics of hypospadias and cryptorchidism recent developments[J]. Clin Genet, 2019, 95(1): 122-131. doi: 10.1111/cge.13432
-

| 引用本文: | 黄文琳, 徐勇, 刘劲戈. 1例隐睾症家系的外显子测序分析[J]. 临床泌尿外科杂志, 2023, 38(5): 382-386. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.1001-1420.2023.05.015 |
| Citation: | HUANG Wenlin, XU Yong, LIU Jin'ge. Exon sequencing analysis of cryptorchidism in one family[J]. J Clin Urol, 2023, 38(5): 382-386. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.1001-1420.2023.05.015 |
- Figure 1.
- Figure 2.
- Figure 3.



 下载:
下载: