-
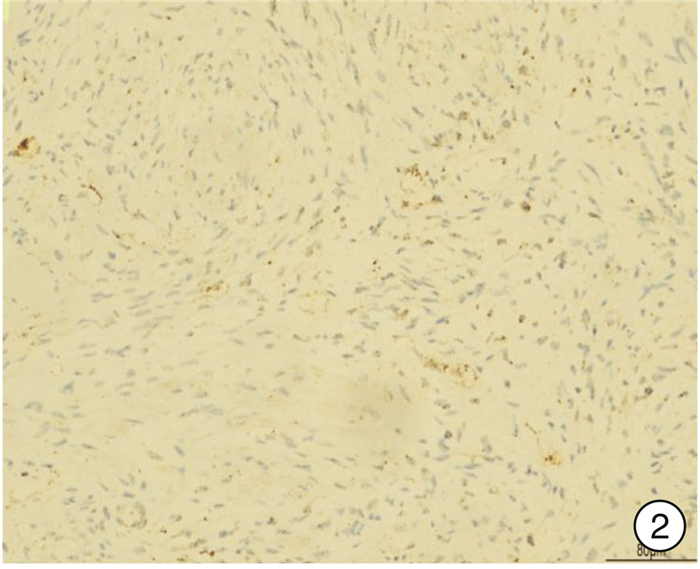
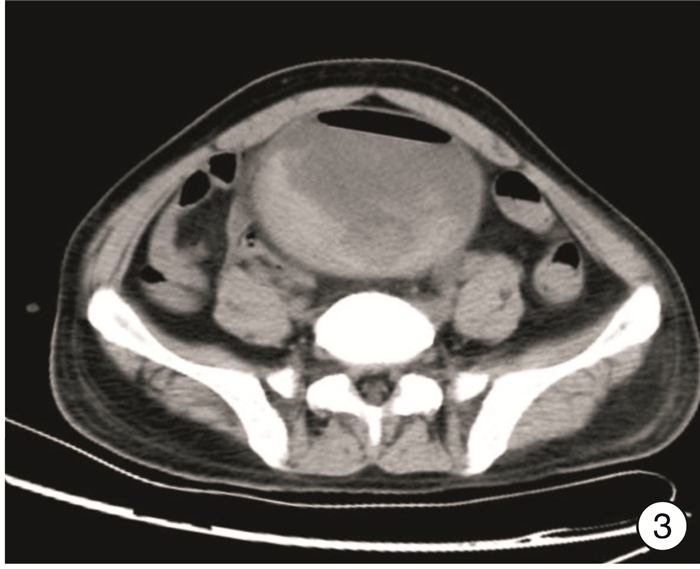
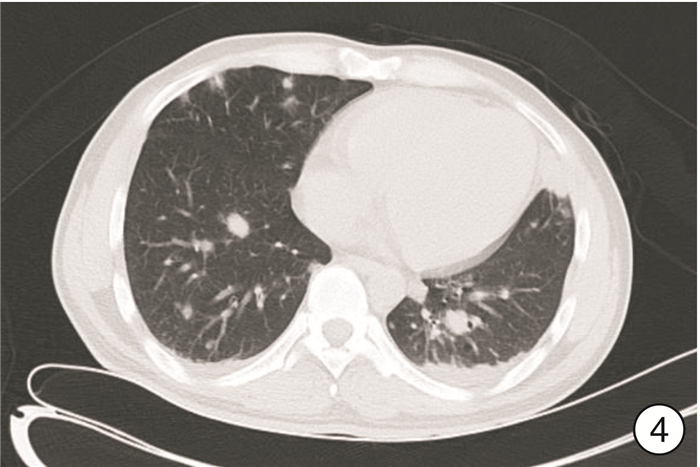
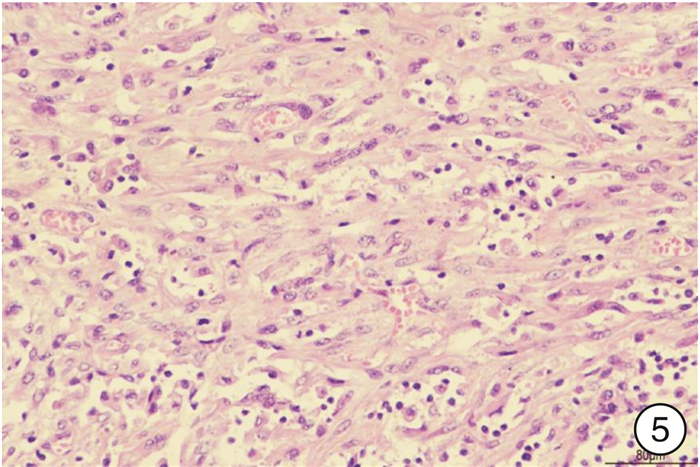
摘要: 2例膀胱炎性肌纤维母细胞瘤(IMTB)患者临床表现以血尿及排尿困难为主,超声及CT较难将IMTB与膀胱其他肿瘤相鉴别,ALK(+)对于IMTB的诊断具有较高的价值,Vimentin蛋白的表达也有助于鉴别诊断。2例病例预后差异较大,术后均随访3个月,1例因呼吸衰竭死亡,1例未见肿瘤复发。
-
关键词:
- 膀胱炎性肌纤维母细胞瘤 /
- 血尿 /
- 免疫组织化学 /
- 手术治疗
Abstract: The main clinical manifestations of 2 patients with inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor of the urinary bladder (IMTB) were hematuria and dysuria. It is difficult to distinguish IMTB from other bladder tumors by ultrasound and CT. ALK (+) has a high value for the diagnosis of IMTB, and the expression of Vimentin protein is also helpful for the differential diagnosis. The prognosis of the two cases was quite different. After 3 months of follow-up, one case died of respiratory failure, and the other case had no tumor recurrence. -

-
[1] Surabhi VR, Chua S, Patel RP, et al. Inflammatory myofibroblastic tumors: current update[J]. Radiol Clin North Am, 2016, 54(3): 553-563. doi: 10.1016/j.rcl.2015.12.005
[2] 张玉华, 董格红, 武迎, 等. 膀胱炎性肌纤维母细胞肿瘤临床病理及分子遗传学分析[J]. 诊断病理学杂志, 2021, 28(6): 423-428. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-8096.2021.06.002
[3] 王宇昊, 夏佳东, 薛建新, 等. 机器人辅助腹腔镜下膀胱部分切除术治疗膀胱炎性肌纤维母细胞瘤1例[J]. 临床泌尿外科杂志, 2019, 34(10): 842-844. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.1001-1420.2019.10.021
[4] Teoh JYC, Chan NH, Cheung HY, et al. Inflammatory myofibroblastic tumors of the urinary bladder: a systematic review[J]. Urology, 2014, 84(3): 503-508. doi: 10.1016/j.urology.2014.05.039
[5] Chen C, Huang M, He H, et al. Inflammatory Myofibroblastic Tumor of the Urinary Bladder: An 11-Year Retrospective Study From a Single Center[J]. Frontiers in Medicine, 2022, 9: 831952. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.831952
[6] Matsui Y. A case of inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor of the urinary bladder with emergency clinical symptoms similar to bladder cancer[J]. Urol Case Rep, 2021, 38: 101740. doi: 10.1016/j.eucr.2021.101740
[7] Dobrosz Z, Ryś J, Paleń P, et al. Inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor of the bladder-an unexpected case coexisting with an ovarian teratoma[J]. Diagn Pathol, 2014, 9: 138. doi: 10.1186/1746-1596-9-138
[8] Song D, Gao Z, Liu N, et al. Inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor of urinary bladder with severe hematuria: A Case report and literature review[J]. Medicine, 2019, 98(1): e13987. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000013987
[9] Lecuona AT, Van Wyk AC, Smit SG, et al. Inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor of the bladder in a 3-year-old boy[J]. Urology, 2012, 79(1): 215-218. doi: 10.1016/j.urology.2011.04.052
[10] Wong-You-Cheong JJ, Woodward PJ, Manning MA, et al. Inflammatory and nonneoplastic bladder masses: radiologic-pathologic correlation[J]. Radiographics, 2006, 26(6): 1847-1868. doi: 10.1148/rg.266065126
[11] 钱斌, 鲍健, 陈宏伟, 等. 膀胱炎性肌纤维母细胞瘤的影像表现及临床分析[J]. 南京医科大学学报(自然科学版), 2011, 31(2): 256-259. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NJYK201102030.htm
[12] 葛长峰, 王伟根, 梁文杰. 膀胱炎性肌纤维母细胞瘤影像学分析[J]. 现代实用医学, 2010, 22(4): 420-421. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-0800.2010.04.037
[13] 邹飞, 赵锦洪, 杨建新. 膀胱炎性肌纤维母细胞瘤2例CT影像报告并文献复习[J]. 实用癌症杂志, 2021, 36(1): 159-161. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5930.2021.01.040
[14] Kumar A, Bhatti SS, Sharma S, et al. Inflammatory pseudotumor of urinary bladder-a diagnostic and management dilemma[J]. Int Urol Nephrol, 2007, 39(3): 799-802. doi: 10.1007/s11255-006-9113-6
[15] WHO Classification of Tumours Editorial Board. WHO classification of tumours of soft tissue and bone tumours[M]. 5th ed. Lyon: IARC Press, 2020: 109-111.
[16] 丁茹, 盛少洁, 贡其星. 炎性肌纤维母细胞瘤的分子遗传学研究进展[J]. 中华病理学杂志, 2021, 50(12): 1415-1418. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112151-20210723-00527
[17] Wynes MW, Sholl LM, Dietel M, et al. An international interpretation study using the ALK IHC antibody D5F3 and a sensitive detection kit demonstrates high concordance between ALK IHC and ALK FISH and between evaluators[J]. J Thorac Oncol, 2014, 9(5): 631-638. doi: 10.1097/JTO.0000000000000115
[18] 曹博, 乔保平. 膀胱炎性肌纤维母细胞瘤10例临床分析[J]. 河南外科学杂志, 2020, 26(2): 69-71. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HLWK202002034.htm
[19] Libby EK, Ellis LT, Weinstein S, et al. Metastatic inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor of the bladder[J]. Urol Case Rep, 2019, 23: 10-12. doi: 10.1016/j.eucr.2018.11.007
[20] Coffin CM, Hornick JL, Fletcher CDM. Inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor: comparison of clinicopathologic, histologic, and immunohistochemical features including ALK expression in atypical and aggressive cases[J]. Am J Surg Pathol, 2007, 31(4): 509-520. doi: 10.1097/01.pas.0000213393.57322.c7
[21] Mossé YP, Voss SD, Lim MS, et al. Targeting ALK with crizotinib in pediatric anaplastic large cell lymphoma and inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor: a Children's Oncology Group Study[J]. J Clin Oncol, 2017, 35(28): 3215. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2017.73.4830
[22] Honda K, Kadowaki S, Kato K, et al. Durable response to the ALK inhibitor alectinib in inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor of the head and neck with a novel SQSTM1-ALK fusion: a case report[J]. Invest New Drugs, 2019, 37(4): 791-795. doi: 10.1007/s10637-019-00742-2
-

| 引用本文: | 张博文, 侯四川. 膀胱炎性肌纤维母细胞瘤2例[J]. 临床泌尿外科杂志, 2023, 38(5): 397-400. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.1001-1420.2023.05.019 |
| Citation: | ZHANG Bowen, HOU Sichuan. Inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor of bladder: report of 2 cases[J]. J Clin Urol, 2023, 38(5): 397-400. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.1001-1420.2023.05.019 |
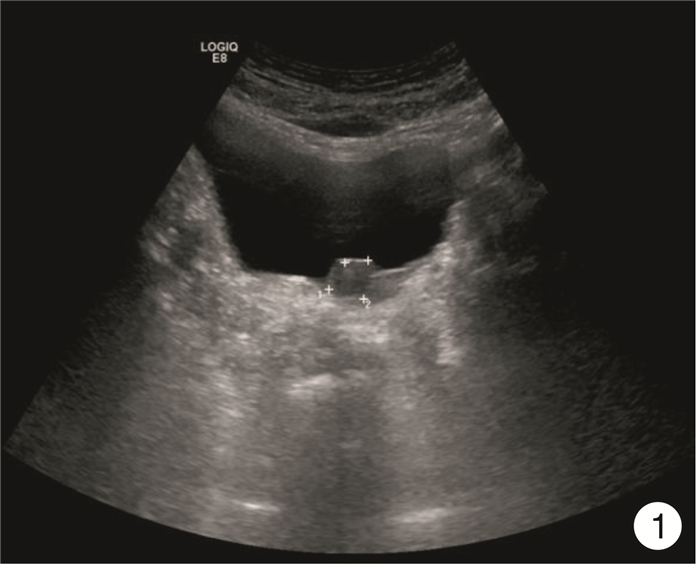
- Figure 1.
- Figure 2.
- Figure 3.
- Figure 4.
- Figure 5.
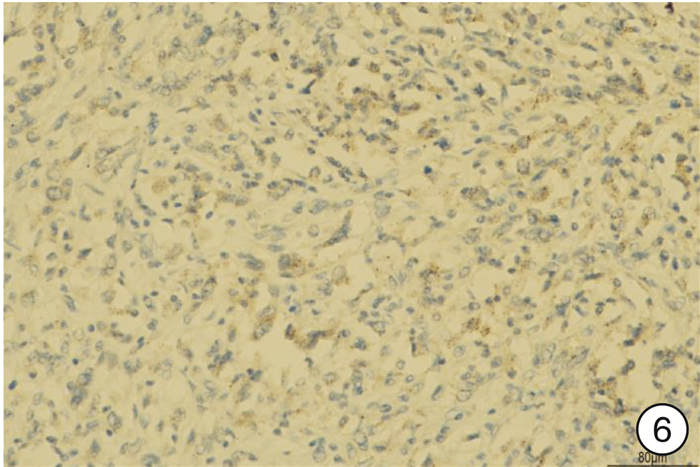
- Figure 6.



 下载:
下载: