Analysis on the occurrence and risk factors of inguinal hernia after radical prostatectomy with different surgical methods
-
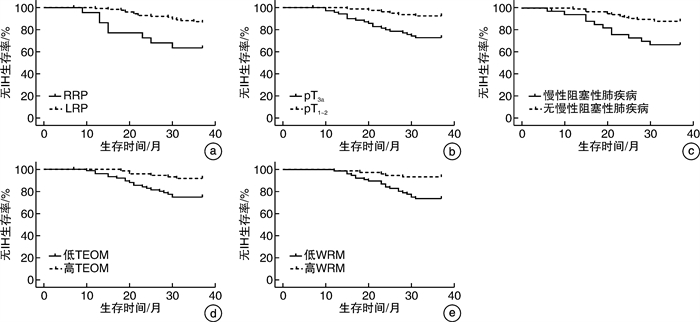
摘要: 目的 探讨不同术式前列腺癌(PCa)根治术后腹股沟疝(IH)发生情况,分析影响PCa根治术后IH发生的危险因素。方法 回顾性选择2018年1月—2021年12月我院泌尿外科收治的156例接受根治性前列腺切除术的PCa患者,收集临床资料,统计术后IH发生情况,采用多因素logistic回归分析PCa根治术后IH的危险因素,Kaplan-Meier绘制PCa根治术后无IH生存曲线。结果 6例失访,余150例患者中接受耻骨后根治性前列腺切除术(RRP)治疗23例,接受腹腔镜前列腺切除术(LRP)治疗127例。中位随访20(6~37)个月,共25例(16.67%)发生IH,接受RRP、LRP治疗的PCa患者术后IH发生率分别为37.78%、13.39%。IH组年龄、2型糖尿病、慢性阻塞性肺疾病比例、既往腹部手术史、Gleason 3~5级、pT3a、RRP、腹股沟内环扩张比例均高于无IH组(均P < 0.05),BMI、腹外斜肌厚度(TEOM)、腹直肌宽度(WRM)低于无IH组(均P < 0.05)。多因素logistic分析结果显示,RRP、pT3a、慢性阻塞性肺疾病是PCa根治术后IH的危险因素(OR=3.865、1.652、1.406,均P < 0.05),TEOM、WRM是保护性因素(OR=0.494、0.530,P < 0.05)。Kaplan-Meier分析结果显示,RRP、pT3a、慢性阻塞性肺疾病、低TEOM、低WRM的PCa患者根治术后无IH生存率低于LRP、pT1~2、无慢性阻塞性肺疾病、高TEOM、高WRM的PCa患者(均P < 0.05)。结论 RRP术后IH发生率偏高,手术方式、TEOM、WRM、肿瘤分期、慢性阻塞性肺疾病是PCa根治术后IH发生的相关因素,应加强高危患者干预以降低IH风险。Abstract: Objective To investigate the incidence and analyze risk factors of inguinal hernia (IH) after radical resection of prostate cancer (PCa) with different surgical methods.Methods A total of 156 PCa patients who received radical prostatectomy in the Urology Department of our hospital from January 2018 to December 2021 were retrospectively selected. Clinical data were collected, and the incidence of postoperative IH was statistically analyzed. Multivariate logistic regression analysis was conducted to analyze the risk factors affecting postoperative IH after PCa radical resection. Kaplan-Meier was used to plot the survival curve without IH after PCa radical resection.Results Among the remaining 150 patients, 23 were treated with retropubic radical prostatectomy (RRP) and 127 were treated with laparoscopic radical prostatectomy (LRP). After a median follow-up of 20 (6-37) months, 25 patients developed IH, with an incidence of 16.67% (25/150). The incidence of IH in PCa patients treated with RRP and LRP were 37.78% and 13.39%, respectively. Age, proportion of type 2 diabetes mellitus, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, history of previous abdominal surgery, proportion of Gleason grade 3-5, pT3a, RRP and internal inguinal ring dilation in IH group were higher than those in non-IH group (all P < 0.05), and body mass index, thickness of external oblique muscle (TEOM) and width of rectus muscle (WRM) were lower than those in non-IH group (all P < 0.05). Multivariate logistic analysis showed that RRP, pT3a and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease were risk factors for IH after PCa radical resection (OR=3.865, 1.652, 1.406, all P < 0.05), while TEOM and WRM were protective factors (OR=0.494, 0.530, both P < 0.05). Kaplan-Meier analysis showed that the IH-free survival rate of PCa patients with RRP, pT3a, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, low TEOM and low WRM was lower than that of PCa patients with LRP, pT1-2, no chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, high TEOM and high WRM (all P < 0.05).Conclusion The incidence of IH after RRP is high, and surgical method, TEOM, WRM, tumor stage and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease are the related factors affecting IH after PCa radical resection. We should take steps to reduce the risk of IH in high-risk patients.
-
Key words:
- prostate cancer /
- inguinal hernia /
- radical prostatectomy /
- risk factors
-

-
表 1 2组患者基线资料
例(%),M(P25,P75),X±S 项目 IH组(25例) 无IH组(125例) t/z/χ2 P值 年龄/岁 68.15±5.12 64.03±4.39 4.164 < 0.001 BMI/(kg/m2) 22.68±1.42 24.71±1.35 6.805 < 0.001 高血压 13(52.00) 60(48.00) 0.133 0.714 2型糖尿病 17(68.00) 57(45.60) 4.182 0.041 高脂血症 10(40.00) 52(41.60) 0.022 0.882 慢性阻塞性肺疾病 11(44.00) 23(18.40) 7.789 0.005 既往腹部手术史 12(48.00) 33(26.40) 4.629 0.031 IH家族史 7(28.00) 30(24.00) 0.179 0.672 分化程度 1.569 0.210 中低分化 17(68.00) 68(54.40) 高度分化 8(32.00) 57(45.60) 肿瘤分期 6.552 0.010 pT1~2 6(24.00) 65(52.00) pT3a 19(76.00) 60(48.00) 组织学分级 5.509 0.019 Gleason 1~2级 6(24.00) 62(49.60) Gleason 3~5级 19(76.00) 63(50.40) 淋巴结转移 10(40.00) 27(21.60) 3.796 0.051 术前PSA/(ng/mL) 12.71±2.41 12.28±2.03 0.936 0.351 术中PLND 11(44.00) 25(20.00) 0.506 0.477 手术方式 6.419 0.011 RRP 8(32.00) 15(12.00) LRP 17(68.00) 110(88.00) 腹股沟内环扩张 9(36.00) 21(16.80) 4.800 0.028 手术时间/min 365(302,416) 363(289,408) 0.316 0.752 术中出血量/mL 401(251,511) 400(243,503) 0.128 0.898 TEOM/mm 7.23±2.03 12.55±3.56 7.228 < 0.001 WEOM/mm 45.32±6.09 46.02±6.18 0.518 0.605 TRM/mm 16.35±3.49 16.89±3.71 0.671 0.504 WRM/mm 42.11±5.32 52.13±7.91 6.057 < 0.001 表 2 PCa根治术后IH危险因素的logistic回归分析结果
因素 β SE Wald χ2 OR(95%CI) P 常数项 8.002 2.145 13.917 0.000 RRP 1.352 0.302 20.042 3.865(2.138~6.986) < 0.001 pT3a 0.502 0.153 10.765 1.652(1.224~2.230) < 0.001 慢性阻塞性肺疾病 0.341 0.119 8.211 1.406(1.114~1.776) 0.003 TEOM -0.706 0.198 12.714 0.494(0.335~0.728) < 0.001 WRM -0.635 0.187 11.531 0.530(0.367~0.765) < 0.001 -
[1] Culp MB, Soerjomataram I, Efstathiou JA, et al. Recent Global Patterns in Prostate Cancer Incidence and Mortality Rates[J]. Eur Urol, 2020, 77(1): 38-52. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2019.08.005
[2] 李壮志, 李俊平, 刘周强, 等. 腹腔镜保留部分前列腺包膜的膀胱根治性切除-原位回肠新膀胱术的临床效果观察[J]. 临床泌尿外科杂志, 2017, 32(5): 397-399. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.1001-1420.2017.05.018
[3] Liu Z, Li D, Chen Y. Endoscopic extraperitoneal radical prostatectomy after radical resection of pT1-pT2 rectal cancer: a report of thirty cases[J]. Wideochir Inne Tech Maloinwazyjne, 2017, 12(1): 68-74. http://europepmc.org/articles/PMC5397545?pdf=render
[4] Iwamoto H, Morizane S, Hikita K, et al. Postoperative inguinal hernia after robotic-assisted radical prostatectomy for prostate cancer: evaluation of risk factors and recommendation of a convenient prophylactic procedure[J]. Cent European J Urol, 2019, 72(4): 418-424. http://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32015914/
[5] 毛祖杰, 刘锋, 祁小龙, 等. 腹腔镜前列腺癌根治术后腹股沟疝13例诊治分析[J]. 中华全科医学, 2017, 15(6): 944-946. doi: 10.16766/j.cnki.issn.1674-4152.2017.06.010
[6] 中华医学会外科学分会疝与腹壁外科学组, 中华医师协会外科医师分会疝和腹壁外科医师委员会. 成人腹股沟疝诊断和治疗指南(2018年版)[J]. 中国普通外科杂志, 2018, 27(7): 803-807. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZPWZ201807001.htm
[7] ICheng L, Montironi R, Bostwick DG, et al. Staging of prostate cancer[J]. Histopathology, 2012, 60(1): 87-117. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2559.2011.04025.x
[8] Stranne J, Aus G, Bergdahl S, et al. Post-radical prostatectomy inguinal hernia: a simple surgical intervention can substantially reduce the incidence——results from a prospective randomized trial[J]. J Urol, 2010, 184(3): 984-989. doi: 10.1016/j.juro.2010.04.067
[9] Alder R, Zetner D, Rosenberg J. Incidence of Inguinal Hernia after Radical Prostatectomy: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis[J]. J Urol, 2020, 203(2): 265-274. doi: 10.1097/JU.0000000000000313
[10] Zhu S, Zhang H, Xie L, et al. Risk factors and prevention of inguinal hernia after radical prostatectomy: a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. J Urol, 2013, 189(3): 884-890. doi: 10.1016/j.juro.2012.08.241
[11] Nielsen RA, Zetner D, Rosenberg J. Radical prostatectomy increases the incidence of inguinal hernia[J]. Ugeskr Laeger, 2019, 181(25): V01190068.
[12] Yamada Y, Fujimura T, Fukuhara H, et al. Incidence and risk factors of inguinal hernia after robot-assisted radical prostatectomy[J]. World J Surg Oncol, 2017, 15(1): 61. doi: 10.1186/s12957-017-1126-3
[13] Zhu S, Zhang H, Xie L, et al. Risk factors and prevention of inguinal hernia after radical prostatectomy: a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. J Urol, 2013, 189(3): 884-890. doi: 10.1016/j.juro.2012.08.241
[14] Lin BM, Hyndman ME, Steele KE, et al. Incidence and risk factors for inguinal and incisional hernia after laparoscopic radical prostatectomy[J]. Urology, 2011, 77(4): 957-962. doi: 10.1016/j.urology.2010.12.011
[15] Ku JY, Lee CH, Park WY, et al. The cumulative incidence and risk factors of postoperative inguinal hernia in patients undergoing radical prostatectomy[J]. Int J Clin Oncol, 2018, 23(4): 742-748.
[16] Liu L, Xu H, Qi F, et al. Incidence and risk factors of inguinal hernia occurred after radical prostatectomy-comparisons of different approaches[J]. BMC Surg, 2020, 20(1): 218. http://www.socolar.com/Article/Index?aid=200259865422&jid=200000025499
[17] Melwani R, Malik SJ, Arija D, et al. Body Mass Index and Inguinal Hernia: An Observational Study Focusing on the Association of Inguinal Hernia With Body Mass Index[J]. Cureus, 2020, 12(11): e11426. http://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33312822/
[18] Aigon A, Billecocq S. Prevalence and impact on quality of life of urinary incontinence in an adult population with chronic obstructive pulmonary diseases, literature review[J]. Prog Urol, 2018, 28(17): 962-972.
-




 下载:
下载: