Comparison among different surgical methods in treatment of small sized prostatic hyperplasia: a network meta-analysis
-
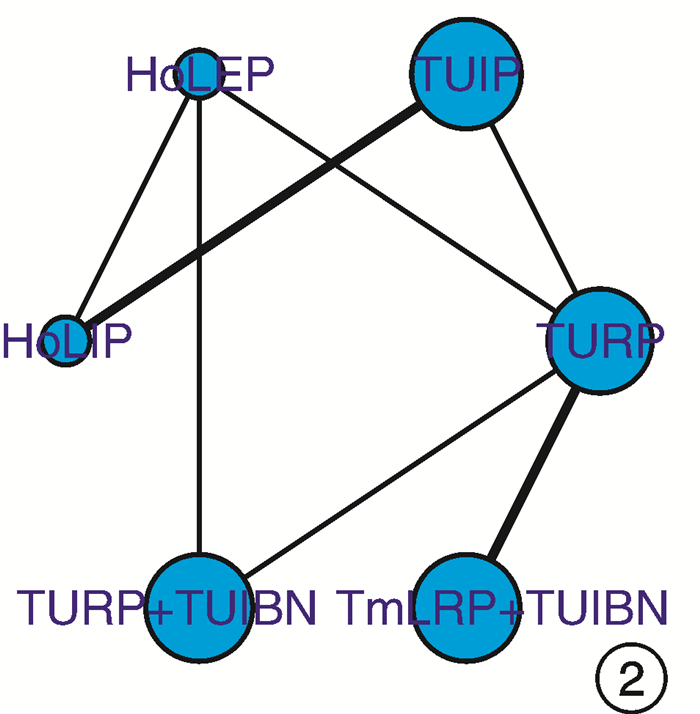
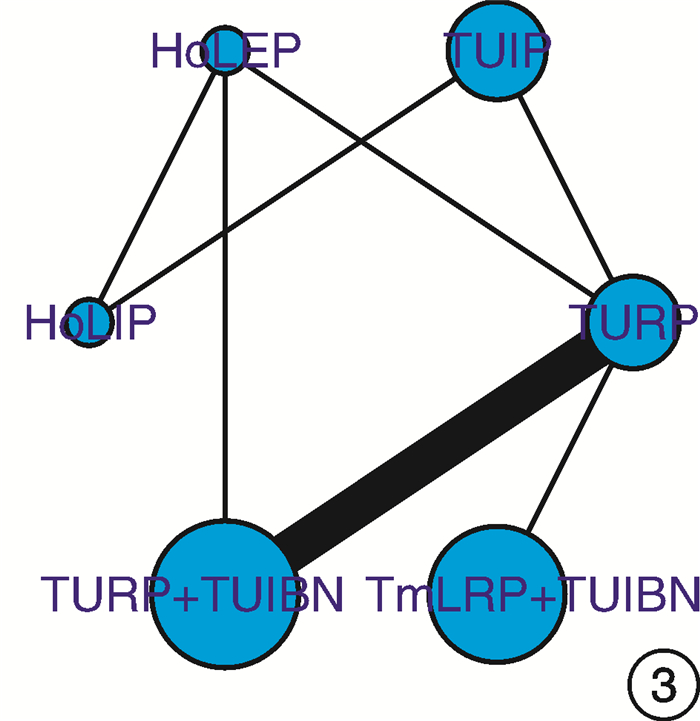
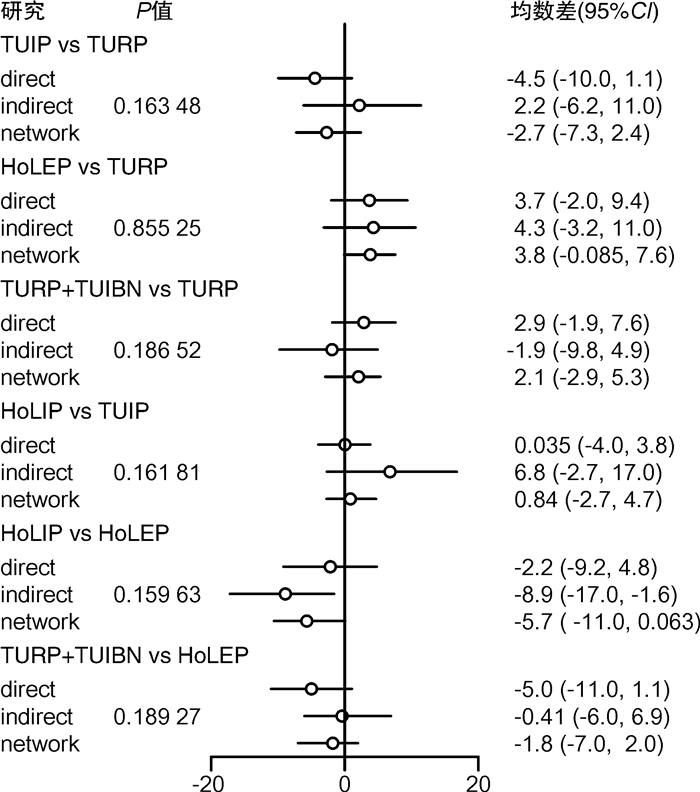
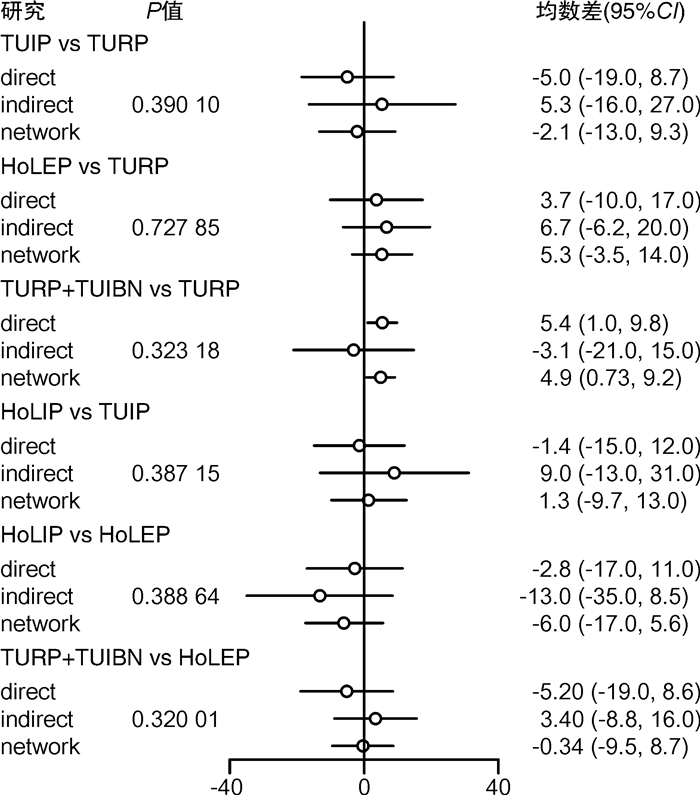
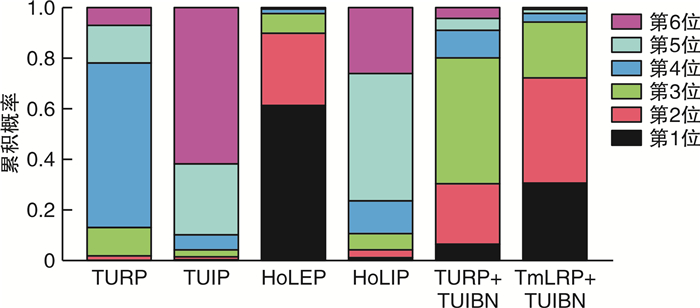
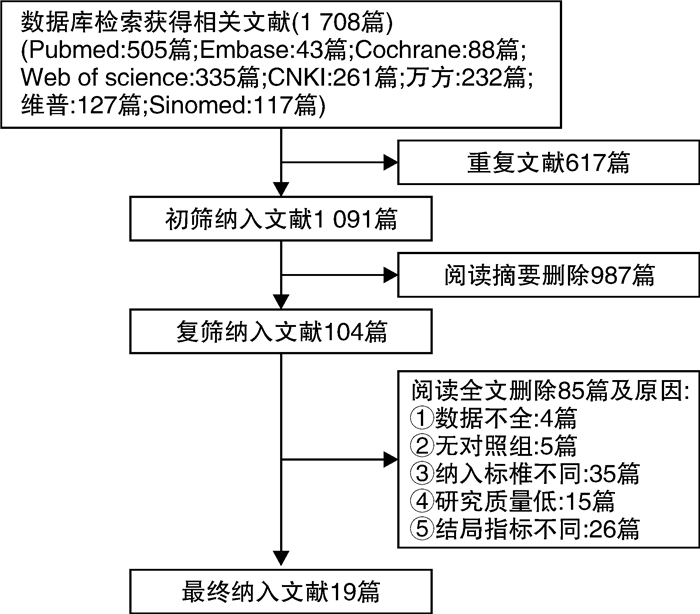
摘要: 目的 采用网状meta分析评价不同手术方式对小体积前列腺增生术后尿流率的影响。方法 通过以下数据库检索小体积前列腺增生术后尿流率的随机对照研究和病例对照研究:Pubmed、Embase、Cochrane library、Web of science、中国知网、维普、万方、中国生物医学文献数据库等,检索时间为建库至2022年12月;由2名研究人员分别检索、筛选文献,单独评价纳入研究的文献质量并提取文献数据,符合纳入标准的文献通过R4.2.2统计软件进行网状meta分析。结果 共纳入19项研究,1 460例患者,涉及6种手术方式,包括经尿道前列腺电切术(transurethral resection of the prostate,TURP)、经尿道前列腺切开术(transurethral incision of the prostate,TUIP)、经尿道钬激光前列腺剜除术(holmium laser enucleation of the prostate,HoLEP)、经尿道钬激光前列腺切开术(holmium laser transurethral incision of the prostate,HoLIP)、经尿道前列腺电切术联合经尿道膀胱颈切开术(transurethral resection of the prostate combined with transurethral incision of the bladder neck,TURP+TUIBN)、经尿道铥激光汽化术联合经尿道膀胱颈切开术(thulium laser resection of the prostate combined with transurethral incision of the bladder neck,TmLRP+TUIBN)。网状meta分析结果显示:术后3个月最大尿流率(maximum flow rate,Qmax)排序为:HoLEP>TmLRP+TUIBN>TURP+TUIBN>TURP>HoLIP>TUIP,术后6个月Qmax排序为:HoLEP>TURP+TUIBN>TmLRP+TUIBN>TURP>HoLIP>TUIP,膀胱颈预防性切开及前列腺剜除可以改善术后尿流率。结论 6种手术方式治疗小体积前列腺增生各有优势,HoLEP、TmLRP+TUIBN、TURP+TUIBN在改善术后尿流率方面优于TURP,可以作为小体积前列腺增生优先选择的手术方式。
-
关键词:
- 小体积良性前列腺增生 /
- 尿流率 /
- 手术方式 /
- 网状meta分析
Abstract: Objective To compare the postoperative maximum flow rate among different transurethral surgical methods in treatment of small sized prostatic hyperplasia using network meta-analysis.Methods Randomized controlled trials(RCTs) and case control study(CCS) were retrieved in Pubmed, Embase, Cochrane library, Web of Science, China Knowledge Network Database, VIP Database, Wanfang Database, China Biomedical Literature Database from databases establishment to December 2022. Two reviewers searched and evaluated the literature respectively. The software R4.2.2 was used to perform network meta-analysis in this study.Results Nineteen researches with a total of 1 460 patients were screened, including TURP, TUIP, HoLEP, HoLIP, TURP+TUIBN and TmLRP+TUIBN. Our analysis showed that the order of Qmax 3 months after operation were as follows: HoLEP>TmLRP+TUIBN>TURP+TUIBN>TURP>HoLIP>TUIP, and the order of Qmax 6 months after operation were: HoLEP>TURP+TUIBN>TmLRP+TUIBN>TURP>HoLIP>TUIP. Prophylactic bladder incision and enucleation of the prostate contribute to postoperative Qmax.Conclusion The six surgical methods show their own advantages in the treatment of small sized prostatic hyperplasia. HoLEP, TmLRP+TUIBN and TURP+TUIBN can be used as superior surgical options for small sized prostatic hyperplasia. -

-
表 1 纳入文献基线特征
纳入研究 研究类型 手术方式 样本量 年龄
/岁前列腺体积
/(g或mL)IPSS/分 Qmax/
(mL/s)PVR/mL Jahnson 1998[7] RCT TURP 42 70.80±7.25 25.40±4.95 NA NA 109 TUIP 43 70.20±8.75 26.20±4.40 NA NA 139 徐仁方2003[8] CCS TURP 22.0 70.4 26.8 21.8±5.6 8.2±3.3 96±38 TURP+TUIBN 36 71.6 27.0 23.6±5.8 8.6±3.2 103±42 Aho 2005[2] RCT HoLEP 20 65.1±11.5 30.3±6.6 NA 8.3±3.0 NA HoLIP 20 64.9±10.1 30.5±5.9 NA 9.7±1.3 NA 董明君2005[9] CCS HoLIP 9 60.4±4.7 21.3±6.7 20.6±1.3 7.4±1.1 NA TUIP 14 63.4±3.5 23.7±5.8 22.1±1.4 7.9±0.9 NA 徐初样2010[10] CCS TURP 50 69.0±3.0 27.8±2.6 22.4±3.5 8.9±1.5 NA TURP+TUIBN 60 70.0±5.0 27.5±3.2 22.6±4.3 8.7±1.2 NA 刘南2013[11] RCT TURP 54 57 23 NA <12 ≥60 TURP+TUIBN 50 58 25 NA <12 ≥60 杜利斌2014[12] RCT TURP 50 71.98±5.69 28.36±1.63 22.97±1.51 7.85±1.72 121.06±25.34 TURP+TUIBN 50 72.02±5.73 28.27±2.59 23.13±1.42 7.92±1.64 118.73±25.29 范刚2014[13] RCT TURP 24 61.2±3.5 <15 NA NA NA TURP+TUIBN 24 61.2±3.5 <15 NA NA NA 张畅2015[14] RCT TURP 48 58.3±5.7 <30 25.8±4.2 7.6±2.2 87.6±2.2 TURP+TUIBN 48 58.3±5.7 <30 24.9±5.3 7.8±3.1 88.8±3.1 曾营华2015[15] CCS TURP 32 71.56±4.97 28.32±1.95 22.89±1.53 7.79±1.68 NA TURP+TUIBN 36 71.56±4.97 28.32±1.95 23.07±1.40 7.88±1.61 NA Bansal 2016[16] RCT HoLIP 69 56.7±13.7 26.4±3.5 NA 7.8±3.6 95.6±34.7 TUIP 70 58.3±4.7 25.9±3.9 NA 8.1±2.7 101.3±28.6 王凤龙2016[17] CCS TURP 20 65.7 22.34±6.59 21.56±3.64 8.95±1.54 NA TURP+TUIBN 37 65.7 22.34±6.59 22.35±3.21 9.42±1.73 NA 王宁华2018[18] RCT TURP 35 67.32±2.46 <15 22.95±1.44 7.6±1.49 98.67±14.15 TURP+TUIBN 35 67.11±2.27 <15 23.1±1.43 7.74±1.57 99.12±13.33 郭吉楠2019[19] CCS TURP 32 66.52±8.21 24.25±5.71 12.82±6.31 7.48±2.25 41.46±20.25 TmLRP+TUIBN 30 65.84±9.15 25.35±3.63 13.42±9.53 7.29±2.14 39.65±21.36 刘伟2020[20] RCT TURP 43 58.03±3.71 28.94±2.72 22.69±1.73 7.79±1.09 99.81±12.62 TURP+TUIBN 43 57.51±3.64 29.05±2.62 22.81±1.58 7.84±1.06 102.24±11.84 陈超2021[21] RCT TURP 40 69.46±3.74 27.93±5.62 NA NA NA HoLEP 40 68.23±3.48 27.82±5.43 NA NA NA 李康乐2021[22] CCS TURP 37 61.97±4.18 25.67±2.18 NA 7.39±0.87 39.76±6.17 TmLRP+TUIBN 38 62.24±4.31 25.9±2.25 NA 7.51±0.92 41.05±6.31 龙蠡2022[23] RCT THoLEP 33 62.4±7.7 21.0±8.7 22.3±1.7 8.3±2.7 35.3±9.7 TURP+TUIBN 32 62.5±7.2 22.3±7.5 22.8±1.5 7.9±2.8 34.1±9.5 刘愿光2022[24] CCS TURP 46 63.64±5.78 23.98±1.95 NA 8.64±3.11 127.38±20.16 TmLRP+TUIBN 48 62.87±5.84 24.61±1.79 NA 7.91±2.98 131.26±18.57 注:NA:未报道;RCT:随机对照研究;CCS:病例对照研究;IPSS:国际前列腺症状评分;PVR:残余尿。 表 2 术后3个月Qmax排序概率表
术式 第1位 第2位 第3位 第4位 第5位 第6位 TURP 0.001 3 0.019 1 0.112 2 0.653 9 0.145 1 0.068 4 TUIP 0.003 9 0.010 4 0.028 9 0.057 7 0.272 5 0.626 6 HoLEP 0.609 9 0.288 9 0.078 4 0.016 7 0.004 5 0.001 6 HoLIP 0.011 7 0.030 3 0.061 4 0.126 8 0.514 7 0.255 1 TURP+TUIBN 0.065 3 0.242 9 0.493 0 0.110 6 0.048 1 0.040 1 TmLRP+TUIBN 0.307 8 0.408 5 0.226 2 0.034 2 0.015 1 0.008 2 表 3 术后6个月Qmax排序概率表
术式 第1位 第2位 第3位 第4位 第5位 第6位 TURP 0.000 8 0.029 3 0.181 5 0.363 5 0.273 6 0.151 3 TUIP 0.031 6 0.053 8 0.095 3 0.147 8 0.280 8 0.390 7 HoLEP 0.374 3 0.291 3 0.192 7 0.090 9 0.035 3 0.015 5 HoLIP 0.064 7 0.093 6 0.140 0 0.173 5 0.269 0 0.259 2 TURP+TUIBN 0.283 3 0.388 4 0.221 9 0.082 4 0.022 2 0.001 8 TmLRP+TUIBN 0.245 3 0.143 5 0.168 6 0.142 0 0.119 1 0.181 5 -
[1] Gravas S, Cornu J, Gacci M, et al. EAU Guidelines on Management of Non-Neurogenic Male Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms(LUTS)[J]. Eur Urol, 2022.
[2] Aho TF, Gilling PJ, Kennett KM, et al. Holmium laser bladder neck incision versus holmium enucleation of the prostate as outpatient procedures for prostates less than 40 grams: a randomized trial[J]. J Urol, 2005, 174(1): 210-214. doi: 10.1097/01.ju.0000161610.68204.ee
[3] Elshal AM, Elkoushy MA, Elmansy HM, et al. Holmium: YAG transurethral incision versus laser photoselective vaporization for benign prostatic hyperplasia in a small prostate[J]. J Urol, 2014, 191(1): 148-154. doi: 10.1016/j.juro.2013.06.113
[4] Lee MH, Yang HJ, Kim DS, et al. Holmium laser enucleation of the prostate is effective in the treatment of symptomatic benign prostatic hyperplasia of any size including a small prostate[J]. Korean J Urol, 2014, 55(11): 737-741. doi: 10.4111/kju.2014.55.11.737
[5] Kim KS, Lee SH, Cho HJ, et al. Comparison of bipolar plasma vaporization versus standard holmium laser enucleation of the prostate: surgical procedures and clinical outcomes for small prostate volumes[J]. J Clin Med, 2019, 8(7): 1007.
[6] 谢克基, 李涛, 汤平, 等. 良性前列腺增生患者前列腺体积参数与膀胱出口梗阻的相关性研究[J]. 中华实验外科杂志, 2006, 23(8): 962-964. doi: 10.3760/j.issn:1001-9030.2006.08.022
[7] Jahnson S, Dalén M, Gustavsson G, et al. Transurethral incision versus resection of the prostate for small to medium benign prostatic hyperplasia[J]. Br J Urol, 1998, 81(2): 276-281. doi: 10.1046/j.1464-410X.1998.00535.x
[8] 徐仁方, 何小舟, 经浩, 等. TURP联合TUIBN治疗小体积前列腺增生的临床研究[J]. 江苏医药, 2003, 29(12): 911-912. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-3685.2003.12.013
[9] 董明君. 经尿道钬激光前列腺切开术与前列腺切开术治疗小体积前列腺增生的疗效比较[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2005.
[10] 徐初样, 徐五书, 钟学文. 两种经尿道手术治疗小体积良性前列腺增生的临床效果比较[J]. 咸宁学院学报(医学版), 2010, 24(2): 136-138. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-0635.2010.02.022
[11] 刘南, 李元, 罗宏, 等. 两种术式经尿道手术治疗小体积前列腺增生的比较[J]. 重庆医学, 2013, 42(21): 2463-2465. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-8348.2013.21.008
[12] 杜利斌. 对使用TURP联合TUIBN治疗小体积前列腺增生临床疗效的分析[J]. 当代医药论丛, 2014, 12(17): 259. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-7629.2014.17.224
[13] 范刚. 不同手术治疗小体积前列腺增生的临床疗效观察[J]. 吉林医学, 2014, 35(15): 3227-3228. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JLYX201415017.htm
[14] 张畅, 屈平保, 张瑜, 等. TURP联合经尿道膀胱颈切开术治疗小体积前列腺增生所致膀胱出口梗阻的疗效分析[J]. 现代生物医学进展, 2015, 15(7): 1256-1258, 1280. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWCX201507015.htm
[15] 曾营华. 联合应用经尿道前列腺电切术和膀胱颈内切开术治疗小体积前列腺增生的疗效分析[J]. 当代医药论丛, 2015, 13(1): 276-277. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-7629.2015.01.242
[16] Bansal A, Sankhwar S, Kumar M, et al. Holmium laser vs monopolar electrocautery bladder neck incision for prostates less than 30 grams: a prospective randomized trial[J]. Urology, 2016, 93: 158-163.
[17] 王凤龙, 葛庆生, 桑士仿, 等. 经尿道前列腺电切加膀胱颈内切开治疗小体积前列腺增生[J]. 微创医学, 2016, 11(3): 432-433. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WCYX201603042.htm
[18] 王宁华, 董锐, 袁静, 等. 小体积前列腺增生的手术治疗[J]. 当代医学, 2018, 24(4): 131-132. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DDYI201804066.htm
[19] 郭吉楠, 肖克峰, 袁谦, 等. 选择性经尿道铥激光前列腺汽化切除联合膀胱颈多点切开术治疗小体积前列腺增生的疗效分析[J]. 国际泌尿系统杂志, 2019, 39(4): 637-640. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-EBED202203015.htm
[20] 刘伟. 前列腺电切术联合尿道膀胱颈切开术对小体积前列腺增生的疗效分析[J]. 大医生, 2020(8): 55-57. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XLYK202006171.htm
[21] 陈超. HoLEP与TURP治疗小体积良性前列腺增生的疗效比较[J]. 临床研究, 2021, 29(6): 100-102. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCYN202106052.htm
[22] 李康乐, 朱要辉, 柳应旭. 经尿道铥激光汽化术联合膀胱颈多点切开术治疗小体积前列腺增生[J]. 四川生理科学杂志, 2021, 43(9): 1577-1579. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-EBED202203015.htm
[23] 龙蠡, 杨华伟, 唐汇龙, 等. 刀口变向钬激光前列腺剜除术肌层无损伤解剖性松解膀胱颈治疗小体积前列腺增生[J]. 中国现代手术学杂志, 2022, 26(1): 45-50. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDSS202201009.htm
[24] 刘愿光. 经尿道铥激光汽化术联合膀胱颈内多点切开术治疗小体积前列腺增生的效果[J]. 临床医学, 2022, 42(3): 41-43. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-EBED202203015.htm
[25] Tao H, Jiang YY, Jun Q, et al. Analysis of risk factors leading to postoperative urethral stricture and bladder neck contracture following transurethral resection of prostate[J]. Int Braz J Urol, 2016, 42(2): 302-311.
[26] Cindolo L, Marchioni M, Emiliani E, et al. Bladder neck contracture after surgery for benign prostatic obstruction[J]. Ital J Urol Nephrol, 2017, 69(2): 133-143.
[27] 魏武, 高建平, 张征宇, 等. 经尿道前列腺电切术后膀胱颈挛缩多因素分析[J]. 中华男科学, 2004, 10(4): 287-289. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NKXB200404015.htm
[28] 肖恒军, 张浩, 刘小彭, 等. 前列腺电切术后反复发生膀胱颈挛缩原因浅析[J]. 中华腔镜泌尿外科杂志(电子版), 2011, 5(4): 332-334. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHQJ201104022.htm
[29] Abd-El Kader O, Mohy El Den K, El Nashar A, et al. Transurethral incision versus transurethral resection of the prostate in small prostatic adenoma: long-term follow-up[J]. Afr J Urol, 2012, 18(1): 29-33.
[30] 王建锋, 孟宏舟, 王国平. 小体积前列腺增生患者应用TURP联合TUIBN治疗对IPSS、Qmax及PVR的影响分析[J]. 浙江创伤外科, 2015, 20(5): 992-993. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZJCW201505071.htm
[31] 王明刚. TURP与TUIBN联合治疗小体积前列腺增生的临床分析[J]. 临床和实验医学杂志, 2014, 13(14): 1205-1207. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYLC201414033.htm
[32] 刘启祥, 张立冬, 谢家恩, 等. 冷刀切开膀胱颈防止小体积前列腺电切术后膀胱颈挛缩[J]. 临床合理用药杂志, 2017, 10(23): 137-138. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-PLHY201723098.htm
[33] 张福霖, 刘百川, 杨国胜. 小体积良性前列腺增生激光治疗研究进展[J]. 现代泌尿生殖肿瘤杂志, 2020, 12(1): 57-60. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-PXDM202001021.htm
[34] 刘宁, 陈恕求, 许斌, 等. 经尿道前列腺电切+膀胱颈电切术治疗小体积前列腺增生的疗效观察[J]. 中华男科学杂志, 2016, 22(5): 474-476. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NKXB201605020.htm
[35] 马圣君, 李静, 张爱珍. 小体积前列腺增生经尿道电切术后膀胱颈挛缩的防治[J]. 中国实用医刊, 2014(24): 108-109.
[36] 成龙, 杨伟忠, 石崇军. 保留膀胱颈完整性的钬激光小前列腺剜除对术后膀胱颈挛缩及性功能影响[J]. 临床泌尿外科杂志, 2021, 36(3): 191-196. https://lcmw.whuhzzs.com/article/doi/10.13201/j.issn.1001-1420.2021.03.006
[37] Al-Singary W, Arya M, Patel HRH. Bladder neck stenosis after transurethral resection of prostate: does size matter?[J]. Urol Int, 2004, 73(3): 262-265.
[38] Cakiroglu B, Hazar AI, Sinanoglu O, et al. Comparison of transurethral incision of the prostate and silodosin in patients having benign prostatic obstruction in terms of retrograde ejaculation[J]. Arch Ital Urol Androl, 2017, 89(1): 31-33.
[39] Taylor BL, Jaffe WI. Electrosurgical transurethral resection of the prostate and transurethral incision of the prostate(monopolar techniques)[J]. Can J Urol, 2015, 22(Suppl 1): 24-29.
-




 下载:
下载: