Retzius-sparing robot-assisted radical prostatectomyin 12 cases of prostate cancer with prominent median lobe
-
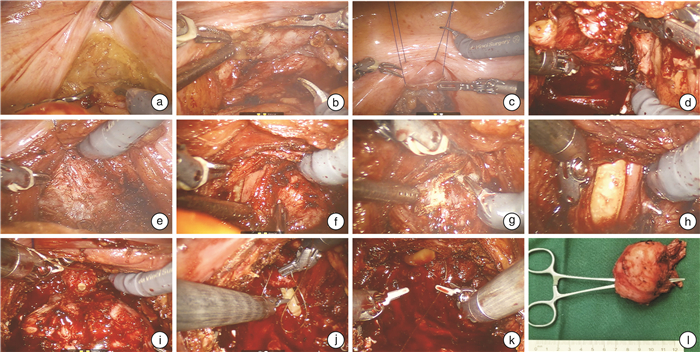
摘要: 目的 探讨前列腺中叶突出的前列腺癌患者行机器人辅助保留Retzius间隙前列腺根治术(Retzius-sparing robot-assisted radical prostatectomy,RsRARP)的安全性及可行性,分析围手术期结果。方法 回顾性分析2023年1月—2023年6月在解放军总医院第三医学中心行RsRARP的患者资料,通过术前影像学资料筛选出中叶突入膀胱≥2.0 cm的患者共12例,进行为期3个月的随访。患者中位年龄为68岁,中位体重指数(body mass index,BMI)为24.9 kg/m2。术前总前列腺特异性抗原(total prostate specific antigen,tPSA)中位数为9.0 μg/L,游离PSA(free postate specific antigen, fPSA)中位数为1.375 μg/L。穿刺总阳性针数中位数为2.5针,活检Gleason评分6分2例,8分2例,9分4例。临床TNM分期cT1c期2例,cT2a期8例,cT3b期2例。所有患者术前控尿均正常,国际勃起功能指数问卷表-5(International Index of Erectile Function5,IIEF-5)评分均小于7分。术后6周开始复查血清PSA,之后每3个月复查1次,记录术后1、2、3个月时控尿及勃起功能情况。结果 12例手术均顺利完成,无中转开放患者,无输血患者,无严重术中、术后并发症发生。所有患者均采用未保留勃起神经的筋膜外技术,2例术前活检提示9分的患者在术中进行了淋巴结清扫,中位手术时长(从建立气腹到缝合皮肤切口)为125.0 min,中位出血量为50 mL。术后病理示无包膜外及淋巴结转移,切缘阳性率为16.7%,pT2a期4例,pT2b期2例,pT2c期6例。Gleason评分3+4=7分2例,4+3=7分6例,4+5=9分4例。所有患者术后均成功拔除尿管,拔除时长中位数为14 d,术后3个月tPSA中位数为0.009 μg/L,且所有患者均小于0.060 μg/L,未观察到生化复发。所有患者术后3个月均无勃起功能。术后1个月尿控率为33.3%,2个月尿控率为66.7%,3个月尿控率为83.3%。结论 对于熟练掌握RsRARP的术者来说,RsRARP在治疗中叶突出的pT2期及以下前列腺癌患者时,对肿瘤控制和术后尿控相关解剖结构的保护效果较为理想,无严重并发症,出血量和手术时长较为可控。然而,仍需要进行大样本、长期随访研究以进一步探索和验证。
-
关键词:
- 机器人辅助保留Retzius间隙前列腺根治术 /
- 前列腺癌 /
- 前列腺中叶突出
Abstract: Objective To investigate the safety and feasibility of Retzius-sparing robot-assisted radical prostatectomy (RsRARP) for prostate cancer patients with prominent median lobe, and to analyze the perioperative outcomes.Methods A retrospective analysis was conducted on patients who underwent RsRARP at our center from January 2023 to June 2023. A total of 12 patients with median lobe protrusion into the bladder ≥2.0 cm were selected through preoperative imaging data andthree-month follow-up. The median age of the patients was 68 years, and the median body mass index(BMI)was 24.9 kg/m2. The median preoperative total prostate specific antigen(tPSA) was 9.0 μg/L, and the median free postate specific antigen(fPSA) was 1.375 μg/L. The median number of positive biopsy cores was 2.5. The Gleason score was 6 in 2 cases, 8 in 2 cases, and 9 in 4 cases. The clinical TNM stage was cT1c in 2 cases, cT2a in 8 cases, and cT3b in 2 cases. All patients had normal preoperative urinary continence and an International Index of Erectile Function5(IIEF-5) score of less than 7. Serum PSA was reviewed starting at 6 weeks postoperatively and then every three months. Urinary continence and erectile function were recorded at 1, 2, and 3 months postoperatively.Results All 12 surgeries were successfully completed without conversion to open surgery, blood transfusion, or serious intraoperative and postoperative complications. All patients underwent extrafascial technique without preserving erectile nerves. Lymph node dissection was performed in 2 cases with a preoperative biopsy suggesting a Gleason score of 9. The median operative time(from skin to skin) was 125.0 minutes, and the median blood loss was 50 mL. Postoperative pathology showed no extracapsular or lymph node metastasis. The positive margin rate was 16.7%. According to the pT stage, there were 4 cases of pT2a, 2 cases of pT2b, and 6 cases of pT2c. The Gleason score was 3+4=7 in 2 cases, 4+3=7 in 6 cases, and 4+5=9 in 4 cases. All patients successfully had their urinary catheters removed postoperatively, with a median removal time of 14 days. The median tPSA at three months postoperatively was 0.009 μg/L, and all patients had a value less than 0.060 μg/L, indicating no biochemical recurrence. No patients had erectile function at three months postoperatively. The urinary continence rate was 33.3% at one month, 66.7% at two months, and 83.3% at three months postoperatively.Conclusion For surgeons proficient in RsRARP, this technique demonstrates ideal tumor control and protection of urinary continence-related anatomical structures when treating pT2 or lower-grade prostate cancer patients with prominent median lobe. It is associated with low complication rates and controllable blood loss and operative time. However, further exploration and validation through large-sample, long-term follow-up studies are still warranted. -

-
[1] Pasticier G, Rietbergen JB, Guillonneau B, et al. Robotically assisted laparoscopic radical prostatectomy: feasibility study in men[J]. Eur Urol, 2001, 40(1): 70-74. doi: 10.1159/000049751
[2] Menon M, Tewari A, Peabody J, et al. Vattikuti Institute prostatectomy: technique[J]. J Urol, 2003, 169(6): 2289-2292. doi: 10.1097/01.ju.0000067464.53313.dd
[3] Galfano A, Ascione A, Grimaldi S, et al. A new anatomic approach for robot-assisted laparoscopic prostatectomy: a feasibility study for completely intrafascial surgery[J]. Eur Urol, 2010, 58(3): 457-461. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2010.06.008
[4] Barakat B, Othman H, Gauger U, et al. Retzius Sparing Radical Prostatectomy Versus Robot-assisted Radical Prostatectomy: Which Technique Is More Beneficial for Prostate Cancer Patients(MASTER Study)? A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis[J]. Eur Urol Focus, 2022, 8(4): 1060-1071. doi: 10.1016/j.euf.2021.08.003
[5] 黄双, 马鑫, 朱捷, 等. 保留Retzius间隙的机器人辅助根治性前列腺切除术治疗局限性前列腺癌8例报告[J]. 微创泌尿外科杂志, 2017, 6(4): 198-201.
[6] Patel SR, Kaplon DM, Jarrard D. A technique for the management of a large median lobe in robot-assisted laparoscopic radical prostatectomy[J]. J Endourol, 2010, 24(12): 1899-1901. doi: 10.1089/end.2010.0074
[7] 黄恒前, 付杰新, 谢光宇, 等. 良性前列腺中叶增生患者临床尿动力学特点分析[J]. 现代医药卫生, 2008, 24(19): 2873-2874.
[8] Lee LS, Sim HG, Lim KB, et al. Intravesical prostatic protrusion predicts clinical progression of benign prostatic enlargement in patients receiving medical treatment[J]. Int J Urol, 2010, 17(1): 69-74. doi: 10.1111/j.1442-2042.2009.02409.x
[9] Bantis A, Zissimopoulos A, Kalaytzis C, et al. Correlation of serum prostate specific antigen, the volume and the intravesical prostatic protrusion for diagnosing bladder outlet obstruction in patients with benign prostate hyperplasia[J]. Hell J Nucl Med, 2007, 10(2): 138-143.
[10] Lieber MM, Jacobson DJ, McGree ME, et al. Intravesical prostatic protrusion in men in Olmsted County, Minnesota[J]. J Urol, 2009, 182(6): 2819-2824. doi: 10.1016/j.juro.2009.08.086
[11] Stolzenburg JU, Kallidonis P, Hicks J, et al. Effect of bladder neck preservation during endoscopic extraperitoneal radical prostatectomy on urinary continence[J]. Urol Int, 2010, 85(2): 135-138. doi: 10.1159/000314842
[12] 王荣, 范明, 章小平. 经尿道前列腺中叶剜除术治疗高危前列腺中叶增生[J/OL]. 中华腔镜外科杂志(电子版), 2013, 6(1): 38-42.
[13] Cadeddu JA. Re: A Pragmatic Randomized Controlled Trial Examining the Impact of the Retzius-Sparing Approach on Early Urinary Continence Recovery after Robot-Assisted Radical Prostatectomy[J]. J Urol, 2018, 199(4): 875-876.
[14] Clark R, Vesprini D, Narod SA. The Effect of Age on Prostate Cancer Survival[J]. Cancers(Basel), 2022, 14(17): 4149.
[15] Du Y, Long Q, Guan B, et al. Robot-Assisted Radical Prostatectomy Is More Beneficial for Prostate Cancer Patients: A System Review and Meta-Analysis[J]. Med Sci Monit, 2018, 24: 272-287. doi: 10.12659/MSM.907092
[16] Santok GD, Abdel Raheem A, Kim LH, et al. Perioperative and short-term outcomes of Retzius-sparing robot-assisted laparoscopic radical prostatectomy stratified by gland size[J]. BJU Int, 2017, 119(1): 135-141. doi: 10.1111/bju.13632
[17] 周晓晨, 胡兵, 傅斌, 等. 3种机器人辅助腹腔镜根治性前列腺切除术手术入路对比研究: 前入路、后入路及经膀胱入路[J]. 临床泌尿外科杂志, 2019, 34(7): 501-506. https://lcmw.whuhzzs.com/article/doi/10.13201/j.issn.1001-1420.2019.07.001
[18] Takayanagi A, Takahashi A, Yorozuya W, et al. Predictive Factor of Urinary Continence after Robot-Assisted Laparoscopic Radical Prostatectomy[J]. Hinyokika Kiyo, 2019, 65(11): 451-454.
[19] Lim SK, Kim KH, Shin TY, et al. Retzius-sparing robot-assisted laparoscopic radical prostatectomy: combining the best of retropubic and perineal approaches[J]. BJU Int, 2014, 114(2): 236-344. doi: 10.1111/bju.12705
[20] Galfano A, Secco S, Bocciardi AM. Will Retzius-sparing Prostatectomy Be the Future of Prostate Cancer Surgery?[J]. Eur Urol, 2017, 72(5): 686-688. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2017.06.023
[21] 胡兵. 机器人辅助腹腔镜经膀胱入路与后入路根治性前列腺切除术临床疗效对比研究[D]. 南昌: 南昌大学, 2020.
[22] Ugwumba FO, Ozoemena OF, Okoh AD, et al. Transvesical prostatectomy in the management of benign prostatic hyperplasia in a developing country[J]. Niger J Clin Pract, 2014, 17(6): 797-801. doi: 10.4103/1119-3077.144402
[23] Dalela D, Jeong W, Prasad MA, et al. A Pragmatic Randomized Controlled Trial Examining the Impact of the Retzius-sparing Approach on Early Urinary Continence Recovery After Robot-assisted Radical Prostatectomy[J]. Eur Urol, 2017, 72(5): 677-685. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2017.04.029
[24] Jeong CW, Lee S, Oh JJ, et al. Quantification of median lobe protrusion and its impact on the base surgical margin status during robot-assisted laparoscopic prostatectomy[J]. World J Urol, 2014, 32(2): 419-423. doi: 10.1007/s00345-013-1118-z
[25] 张帆, 肖春雷, 张树栋, 等. 前列腺体积及前列腺突入膀胱长度与腹腔镜前列腺癌根治术后控尿功能恢复的相关性[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2018, 50(4): 621-625.
-




 下载:
下载: