Clinical study on plasma bipolar electric loop in minimally invasive percutaneous nephrolithotomy for channel electrocoagulation and hemostasis
-
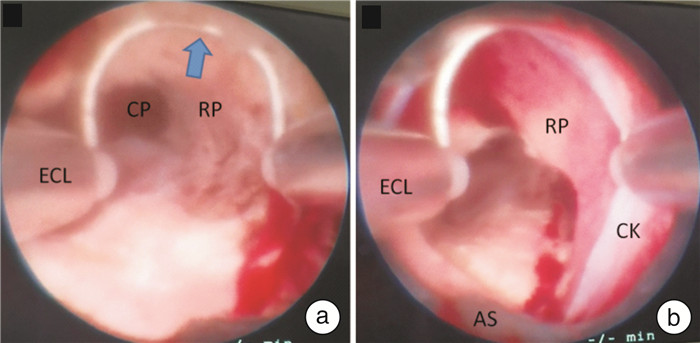
摘要: 目的 探讨等离子双极电切环在微创经皮肾镜取石术(minimally invasive percutaneous nephrolithotomy,mPCNL)中通道电凝止血的有效性与安全性。方法 回顾性分析2019年2月—2023年7月在南昌大学附属第一医院行mPCNL术中输尿管镜直视下发现通道出血的21例患者临床资料,其中男13例,女8例;年龄20~65岁,平均42.7岁。术中使用18Fr撕开鞘建立工作通道,碎石结束后,将输尿管镜与等离子双极电切环同时置入18Fr撕开鞘内,再缓慢退鞘将等离子双极电切环顶住暴露的出血点通过电凝(功率120 W)实现快速止血。结果 21例患者均止血成功,无急诊行选择性肾动脉造影加栓塞术止血或中转开放手术。手术时间20~90 min,平均(49.0±15.1) min;止血时间2~10 min,平均(3±2) min;无术中、术后输血,所有患者均实现了无管化。术后复查腹部平片或泌尿系统彩超,16例患者取净结石无结石残留;5例患者有结石残留于平行肾盏,术后行输尿管软镜激光碎石取石术或体外冲击波碎石术后排出碎石。结论 等离子双极电切环应用于mPCNL术中通道的电凝止血是一种安全有效的止血方法。Abstract: Objective To evaluate the efficacy and safety of plasma bipolar electrotomy in minimally invasive percutaneous nephrolithotomy(mPCNL).Methods A retrospective analysis was performed on 21 patients with channel bleeding found under direct ureteroscope during mPCNL in First Affiliated Hospital of Nanchang University from February 2019 to July 2023, including 13 males and 8 females, aged 20 to 65 years, with an average age of 42.7 years. During the operation, 18Fr channel sheath was used to establish a working channel. After the completion of lithotripsis, the ureteroscope and plasma bipolar electric incision ring were placed into the 18Fr channel sheath at the same time, then the plasma bipolar electric incision ring was slowly removed from the sheath to support the exposed bleeding points through electric coagulation(power 120 W) to achieve rapid hemostasis.Results All the 21 patients had successful hemostasis without DSA embolization or conversion to open surgery. The operation time was 20-90 min, with an average of (49.0±15.1) min. The hemostasis time was 2-10 min, with an average of(3±2) min, without intraoperative or postoperative blood transfusion, and all patients achieved tubeless. KUB radiograph or color ultrasonography of urinary system were reexamined after operation, and no stone remained in 16 patients. Five patients with residual calculi in parallel calices were removed after flexible ureteroscopic laser lithotripsy or extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy(ESWL).Conclusion Plasma bipolar electrotomy ring is a safe and effective method for hemostasis in mPCNL.
-

-
[1] 郑亮亮, 匡仁锐, 邓君, 等. 刺激性利尿局麻微创经皮肾镜取石术在上尿路结石中的应用[J]. 微创泌尿外科杂志, 2020, 9(4): 240-244.
[2] Aghamir SMK, Elmimehr R, Modaresi SS, et al. Comparing bleeding complications of double and single access totally tubeless PCNL: is it safe to obtain more accesses?[J]. Urol Int, 2016, 96(1): 73-76. doi: 10.1159/000381988
[3] Kyriazis I, Panagopoulos V, Kallidonis P, et al. Complications in percutaneous nephrolithotomy[J]. World J Urol, 2015, 33(8): 1069-1077. doi: 10.1007/s00345-014-1400-8
[4] 宁坷平, 祖雄兵, 齐琳, 等. 微创经皮肾镜碎石术并发大出血原因及临床处理分析[J]. 中国内镜杂志, 2009, 15(9): 975-977.
[5] 梁卓寅, 梁志雄, 陈琇萌, 等. 微创经皮肾穿刺取石术并发出血的治疗体会[J]. 中国医师进修杂志, 2006, 29(11): 9-10, 13.
[6] Hong Y, Xiong LL, Ye HY, et al. Outcome of selective renal artery embolization in managing severe bleeding after percutaneous nephrolithotomy[J]. Urol Int, 2020, 104(9-10): 797-802.
[7] Merinov DS, Gurbanov SS, Artemov AV, et al. Prevention of bleeding during tubeless percutaneous nephrolithotomy[J]. Urologiia, 2019(4): 38-43.
[8] Fornazari VAV, Santos RFT, Nunes TF, et al. Hemorrhagic complications after percutaneous nephrolithotomy: angiographic diagnosis and management by transcatheter arterial embolization[J]. Radiol Bras, 2020, 53(6): 390-396. doi: 10.1590/0100-3984.2019.0130
[9] Du N, Ma JQ, Luo JJ, et al. The efficacy and safety of transcatheter arterial embolization to treat renal hemorrhage after percutaneous nephrolithotomy[J]. Biomed Res Int, 2019, 2019: 6265183.
[10] Jou YC, Cheng MC, Sheen JH, et al. Cauterization of access tract for nephrostomy tube-free percutaneous nephrolithotomy[J]. J Endourol, 2004, 18(6): 547-549.
[11] 陶维雄, 魏世平, 李辉明, 等. 等离子双极电切电凝系统在经皮肾镜碎石术中的直接止血作用[J]. 中国微创外科杂志, 2020, 20(5): 424-426. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6604.2020.05.011
[12] Zhang HH, Xu HF, Fei KL, et al. The safety and efficiency of a 1470nm laser in obtaining tract hemostasis in tubeless percutaneous nephrolithotomy: a retrospective cross-sectional study[J]. BMC Urol, 2022, 22(1): 94.
[13] Noller MW, Baughman SM, Morey AF, et al. Fibrin sealant enables tubeless percutaneous stone surgery[J]. J Urol, 2004, 172(1): 166-169.
-




 下载:
下载: