Preliminary experience of female totally robot assisted radical cystectomy with the genital sparing and intracorporeal orthotopic ileal neobladder
-
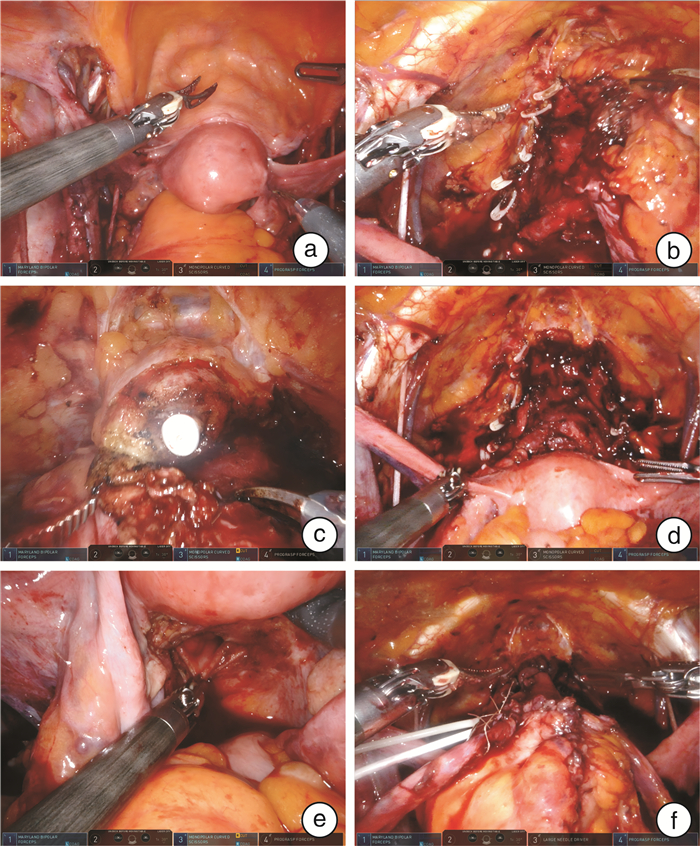
摘要: 目的 探讨女性膀胱癌患者保留生殖器官的机器人辅助根治性膀胱切除联合全腔内原位回肠新膀胱重建结合经自然腔道取标本的疗效,总结临床经验技术。方法 回顾性分析2021年7月—2023年5月陆军军医大学第一附属医院全军泌尿外科收治的8例女性膀胱尿路上皮癌患者的临床资料。患者年龄53~73岁,平均63.3岁;体重指数17.3~27.9 kg/m2,平均23.1 kg/m2;美国麻醉科医师协会评分1~3分,平均2分。均行保留生殖器官的机器人辅助根治性膀胱切除联合全腔内原位回肠新膀胱重建,并经阴道取标本。围手术期采用加速康复外科,并在术后3个月开始随访患者的肿瘤学和排尿功能学状态。结果 8例女性患者手术均顺利完成。手术时间265~451 min,平均344.8 min;术中估计出血量150~500 mL,平均281.3 mL。术后患者住院时间为14~25 d,平均16.9 d。1例患者术后第7天出现回肠新膀胱瘘,保守治疗后于术后25 d出院;另1例患者术后1个月左右复查CT提示盆腔淋巴囊肿(直径约14 cm),CT引导下穿刺引流后恢复。术后3个月左右行新膀胱尿动力学检查,新膀胱容量195.8~369.0 mL,平均249.1 mL;残余尿0~60 mL,平均24.4 mL,无患者需要间歇清洁导尿。尿失禁评估显示87.5%、12.5%和0的患者在白天被评为良好、满意和不满意,62.5%、25.0%和12.5%的患者在夜间被评为良好、满意和不满意。中位随访16.8(10~33)个月,未见肿瘤复发及转移。结论 女性膀胱癌患者行保留生殖器官的机器人辅助根治性膀胱切除联合全腔内原位回肠新膀胱重建结合经自然腔道取标本,在临床上是安全可行的,相比经典的膀胱根治性切除原位新膀胱,可能获得更好的排尿功能。
-
关键词:
- 膀胱癌 /
- 女性 /
- 机器人辅助膀胱癌根治 /
- 保留生殖器官 /
- 全腔内原位回肠新膀胱
Abstract: Objective To explore the feasibility of robot assisted radical cystectomy(RARC) with genital sparing combined with intracorporeal orthotopic neobladder(ONB) in female bladder cancer patients, combined with specimen retrieval via natural orifice, and to summarize the clinical experience and techniques.Methods Clinical data of 8 female bladder cancer patients admitted to our department from July 2021 to May 2023 were retrospectively analyzed. The patients' ages ranged from 53 to 73 years, with a mean age of 63.3 years. The body mass index(BMI) ranged from 17.3 to 27.9 kg/m2, with a mean of 23.1 kg/m2. The American Society of Anesthesiologists(ASA) scores ranged from 1 to 3, with a mean of 2. All patients underwent RARC with genital sparing plus intracorporeal ileal neobladder reconstruction, and specimen retrieval via the vagina. Enhanced recovery after surgery(ERAS) was employed postoperatively, and patients were followed up for oncological and urinary functional status starting from 3 months postoperatively.Results All operation were performed successfully. The mean operative time was 344.8 minutes(range: 265-451 minutes), with estimated blood loss ranging from 150 to 500 mL(mean: 281.3 mL). The mean length of hospital stay was 16.9 days(range: 14-25 days). One patient developed an ileal neobladder fistula on postoperative day 7, which was managed conservatively, and she was discharged after 25 days. Another patient developed a pelvic lymphocele(diameter approximately 14 cm) around 1 month postoperatively, which was managed with CT-guided drainage. Postoperative urodynamic studies conducted around 3 months postoperatively showed a mean neobladder capacity of 249.1 mL(range: 195.8-369.0 mL) and a mean residual urine volume of 24.4 mL(range: 0-60 mL), with no patients requiring intermittent clean catheterization. Urinary incontinence assessment revealed that 87.5%, 12.5%, and 0 of patients were rated as good, satisfactory, and unsatisfactory during the daytime, respectively, while 62.5%, 25%, and 12.5% were rated as good, satisfactory, and unsatisfactory during the night, respectively. The median follow-up period was 16.8 months(range: 10-33 months), and no tumor recurrence or metastasis observed.Conclusion RARC with genital sparing and intracorporeal ileal neobladder reconstruction in female bladder cancer patients, combined with specimen retrieval via natural orifice, is clinically safe and feasible. Compared to conventional radical cystectomy(RC) with ONB reconstruction, it may offer better urinary function. -

-
[1] Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2021, 71(3): 209-249. doi: 10.3322/caac.21660
[2] Leow JJ, Bedke J, Chamie K, et al. SIU-ICUD consultation on bladder cancer: treatment of muscle-invasive bladder cancer[J]. World J Urol, 2019, 37(1): 61-83. doi: 10.1007/s00345-018-2606-y
[3] Orji P, Sun H, Isali I, et al. Female sexual function evaluation and intraoperative vaginal reconstruction in bladder cancer[J]. World J Urol, 2023, 41(7): 1751-1762. doi: 10.1007/s00345-023-04502-z
[4] von Deimling M, Laukhtina E, Pradere B, et al. Radical cystectomy and urinary diversion in women: techniques, outcomes, and challenges-a narrative review[J]. Transl Androl Urol, 2022, 11(11): 1598-1610. doi: 10.21037/tau-22-463
[5] 周晓洲, 郑霁, 刘洋, 等. 机器人辅助女性根治性膀胱切除全腹腔内原位回肠W形新膀胱术的初步疗效[J]. 中华泌尿外科杂志, 2018, 39(8): 596-600. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1000-6702.2018.08.010
[6] Nakamura M, Tsuru I, Izumi T, et al. Advantages of enhanced recovery after surgery program in robot-assisted radical cystectomy[J]. Sci Rep, 2023, 13(1): 16237. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-43489-w
[7] Fasanella D, Marchioni M, Domanico L, et al. Neobladder "function": tips and tricks for surgery and postoperative management[J]. Life, 2022, 12(8): 1193. doi: 10.3390/life12081193
[8] Horwich A, Babjuk M, Bellmunt J, et al. EAU-ESMO consensus statements on the management of advanced and variant bladder cancer-an international collaborative multi-stakeholder effort: under the auspices of the EAU and ESMO Guidelines Committees[J]. Ann Oncol, 2019, 30(11): 1697-1727. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdz296
[9] Khan A, Vuppalapati JK, Sarath LR, et al. Functional outcome of robotic-assisted intracorporeal versus extracorporeal neobladder following radical cystectomy: Initial experience[J]. Urol Ann, 2021, 13(1): 9-13. doi: 10.4103/UA.UA_132_19
[10] Miao SY, He QW, Zhang YF, et al. Management of urinary incontinence after radical cystectomy and orthotopic neobladder: a scoping review of international practices[J]. Nurs Open, 2023, 10(10): 6618-6634. doi: 10.1002/nop2.1924
[11] Chen ZW, He P, Zhou XZ, et al. Preliminary functional outcome following robotic intracorporeal orthotopic ileal neobladder suspension with round ligaments in women with bladder cancer[J]. Eur Urol, 2022, 82(3): 295-302. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2021.11.012
[12] Zhou XZ, He P, Ji HX, et al. Round ligament suspending treatment in orthotopic ileal-neobladder after radical cystectomy in women: a single-centre prospective randomised trial[J]. BJU Int, 2021, 128(2): 187-195. doi: 10.1111/bju.15306
[13] Bartsch G, Daneshmand S, Skinner EC, et al. Urinary functional outcomes in female neobladder patients[J]. World J Urol, 2014, 32(1): 221-228. doi: 10.1007/s00345-013-1219-8
[14] Tuderti G, Mastroianni R, Flammia S, et al. Sex-sparing robot-assisted radical cystectomy with intracorporeal Padua ileal neobladder in female: surgical technique, perioperative, oncologic and functional outcomes[J]. J Clin Med, 2020, 9(2): 577. doi: 10.3390/jcm9020577
[15] Zahran MH, Harraz AM, Baset MA, et al. Voiding and renal function 10-years after radical cystectomy and orthotopic neobladder in women[J]. BJU Int, 2023, 132(3): 291-297. doi: 10.1111/bju.16011
[16] Salem H, El-Mazny A. A clinicopathologic study of gynecologic organ involvement at radical cystectomy for bladder cancer[J]. Int J Gynaecol Obstet, 2011, 115(2): 188-190. doi: 10.1016/j.ijgo.2011.05.026
[17] Ali-El-Dein B, Abdel-Latif M, Mosbah A, et al. Secondary malignant involvement of gynecologic organs in radical cystectomy specimens in women: is it mandatory to remove these organs routinely?[J]. J Urol, 2004, 172(3): 885-887. doi: 10.1097/01.ju.0000133986.29257.bf
[18] Veskimäe E, Neuzillet Y, Rouanne M, et al. Systematic review of the oncological and functional outcomes of pelvic organ-preserving radical cystectomy(RC)compared with standard RC in women who undergo curative surgery and orthotopic neobladder substitution for bladder cancer[J]. BJU Int, 2017, 120(1): 12-24. doi: 10.1111/bju.13819
[19] Laukhtina E, von Deimling M, Pradere B, et al. Urinary function in female patients after traditional, organ-sparing and nerve-sparing radical cystectomy for bladder cancer: a systematic review and pooled analysis[J]. BJU Int, 2024, 133(3): 246-258. doi: 10.1111/bju.16152
[20] Chahal B, Aydin A, Amin MSA, et al. The learning curves of major laparoscopic and robotic procedures in urology: a systematic review[J]. Int J Surg, 2023, 109(7): 2037-2057.
-

计量
- 文章访问数: 171
- 施引文献: 0



 下载:
下载: