Comparison of the efficacy between two neoadjuvant regimens for muscle-invasive bladder cancer: a retrospective propensity score matched study
-
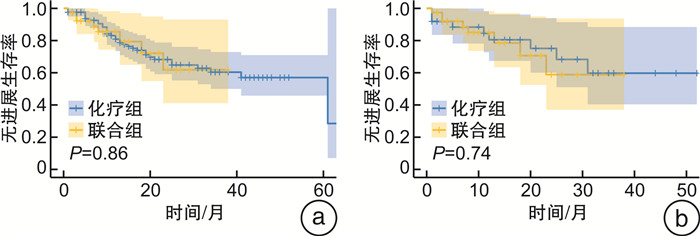
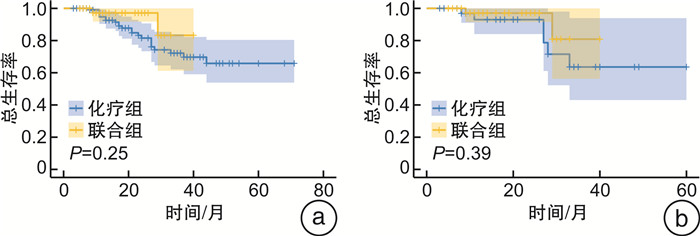
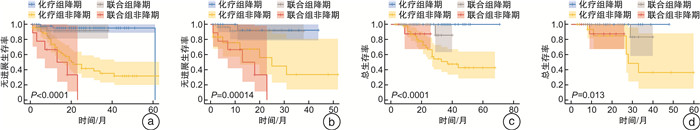
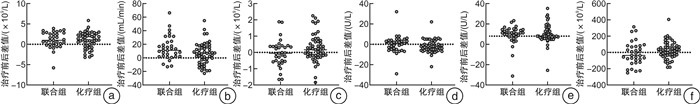
摘要: 目的 通过一项倾向性评分匹配(propensity score matching,PSM)对比研究评价新辅助化疗和化疗免疫联合治疗对肌层浸润性膀胱癌(muscle-invasive bladder cancer,MIBC)患者的无进展生存时间和病理反应,以求为MIBC患者的新辅助方案选择提供参考。方法 纳入2018年1月—2023年9月于2个医疗中心(中山大学孙逸仙纪念医院、中山大学肿瘤防治中心)接受GC(吉西他滨+顺铂)方案新辅助化疗,联合或不联合免疫治疗的MIBC患者的资料。根据新辅助治疗方案将其分为化疗组和联合组。采用PSM控制混杂因素,使用Pearson χ2检验和Fisher精确概率检验比较化疗组和联合组的基线差异,采用logistic回归评估变量与病理反应之间的关系,采用Kaplan-Meier生存曲线分析评估总生存时间和无进展生存时间。结果 在整体队列和匹配队列中联合组的病理完全缓解(pathological complete response,pCR)率和病理降期率显著优于化疗组(P < 0.001、P < 0.001和P=0.012、P=0.032)。2组在治疗前后主要的血液学指标变化方面差异无统计学意义。PSM前后的化疗组和联合组的无进展生存时间和总生存时间均差异无统计学意义。获得了pCR或病理降期的患者在生存情况上显著优于未获得pCR或病理降期的患者。结论 与单独的新辅助化疗相比,新辅助化疗联合免疫治疗获得了更高的pCR率和病理降期率,但无进展生存时间和总生存时间未显示出显著差异。Abstract: Objective To evaluate progression-free survival time and pathological response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy and chemoimmunotherapy combinations in patients with muscle-invasive bladder cancer by a propensity score matched comparative study in an attempt to inform the choice of neoadjuvant regimen for these patients.Methods Data from patients with muscle-invasive bladder cancer who received neoadjuvant chemotherapy with GC(gemcitabine, cisplatin) regimen with or without immunotherapy from January 2018 to September 2023 at two medical centers(Sun Yat-sen Memorial Hospital of Sun Yat-sen University and Sun Yat-sen University Cancer Centre) were included. They were divided into chemotherapy and combination groups according to the neoadjuvant regimen. Propensity score matching(PSM) was used to control for confounders, and Pearson chi-square test and Fisher exact probability test were used to compare baseline differences between chemotherapy and combination groups. Logistic regression was used to assess the relationship between variables and pathological response, and Kaplan-Meier analyses were used for survival analysis.Results Pathological complete response(pCR) rate and pathological downstaging rate were significantly better in the combination group than in the chemotherapy group in the overall cohort and in the matched cohort(P < 0.001, P < 0.001 and P=0.012, P=0.032). There were no significant differences between the two groups in terms of changes in major haematological parameters before and after treatment. Progression-free survival time and overall survival time were not significantly different between the chemotherapy and combination groups before and after PSM. Patients who achieved pCR or pathological downstaging were significantly better in terms of survival than those who did not.Conclusion Neoadjuvant chemotherapy combined with immunotherapy achieved higher pCR and pathological downstaging rates compared with neoadjuvant chemotherapy alone. In terms of progression-free survival time and overall survival time, the two groups did not show significant differences.
-

-
表 1 整体队列与匹配队列基线特征比较
例(%),X±S,M(Q1,Q3) 基线特征 整体队列 匹配队列 化疗组(128例) 联合组(40例) P值 化疗组(39例) 联合组(39例) P值 年龄/岁 62(54,68) 66(59,71) 0.066 64(58,67) 67(60,71) 0.258 BMI/(kg/m2) 23.5±2.9 23.0±2.7 0.389 23.3±2.3 23.1±2.7 0.795 血红蛋白/(g/L) 127±20 122±20 0.174 125±16 123±20 0.592 血小板/(×109/L) 268±70 262±70 0.938 258±71 268±70 0.514 淋巴细胞/(×109/L) 1.7±0.6 1.5±0.6 0.077 1.8±0.5 1.6±0.6 0.200 PLR 139(115,199) 172(127,212) 0.056 136(114,169) 172(127,204) 0.054 白蛋白/(g/L) 39.5±4.2 38.7±3.5 0.293 38.1±4.3 38.9±3.4 0.347 ALG/(g/L) 1.4±0.3 1.3±0.2 0.219 1.3±0.2 1.3±0.2 0.610 Ccr/(mL/min) 74.5±24.3 73.1±21.0 0.741 70.2±16.6 73.3±21.2 0.470 清扫淋巴结数/个 21(15,30) 23(16,31) 0.662 21(15,30) 23(16,31) 0.345 性别 0.783 0.498 男 111(86.72) 34(85.00) 35(89.74) 33(84.62) 女 17(13.28) 6(15.00) 4(10.26) 6(15.38) 吸烟 0.435 1.000 否 73(57.03) 20(50.00) 20(51.28) 20(51.28) 是 55(42.97) 20(50.00) 19(48.72) 19(48.72) 临床T分期 0.658 0.521 T2 63(49.22) 23(57.50) 18(46.15) 23(58.97) T3 42(32.81) 11(27.50) 14(35.90) 11(28.21) T4 23(17.97) 6(15.00) 7(17.95) 5(12.82) 临床N分期 0.964 1.000 N0 106(82.81) 33(82.50) 33(84.62) 33(84.62) N+ 22(17.19) 7(17.50) 6(15.38) 6(15.38) 分级 0.839 0.556 高级别 124(96.88) 39(97.50) 37(94.87) 38(97.44) 低级别 4(3.12) 1(2.50) 2(5.13) 1(2.56) 肾积水 0.284 0.456 否 81(63.28) 29(72.50) 26(66.67) 29(74.36) 是 47(36.72) 11(27.50) 13(33.33) 10(25.64) 辅助治疗 < 0.001 1.000 否 65(50.78) 34(85.00) 33(84.62) 33(84.62) 是 63(49.22) 6(15.00) 6(15.38) 6(15.38) 手术方式 0.753 0.234 机器人辅助手术 98(76.56) 32(80.00) 35(89.75) 31(79.49) 腹腔镜手术 15(11.72) 5(12.50) 1(2.56) 5(12.82) 开放手术 15(11.72) 3(7.50) 3(7.69) 3(7.69) 尿流改道方式 0.001 0.069 原位新膀胱 42(32.81) 26(65.00) 17(43.59) 26(66.67) 回肠通道 80(62.50) 12(30.00) 21(53.85) 11(28.20) 输尿管皮肤造口 6(4.69) 2(5.00) 1(2.56) 2(5.13) 组织学类型 0.339 1.000 尿路上皮癌 96(75.00) 33(82.50) 33(84.62) 33(84.62) 尿路上皮癌伴病理变异 24(18.75) 3(7.50) 2(5.13) 2(5.13) 尿路上皮癌伴原位癌 5(3.91) 4(10.00) 4(10.25) 4(10.25) 非尿路上皮癌 3(2.34) 0(0) 阳性淋巴结比例 0.288 0.356 0 97(75.78) 35(87.50) 29(74.36) 34(87.18) 1~25 19(14.84) 3(7.50) 6(15.38) 3(7.69) >25 12(9.38) 2(5.00) 4(10.26) 2(5.13) 切缘阳性 0.125 0.305 否 125(97.66) 37(92.50) 38(97.44) 36(92.31) 是 3(2.34) 3(7.50) 1(2.56) 3(7.69) Clavien-Dindo分级 0.109 0.113 0 72(56.25) 26(65.00) 20(51.28) 25(64.11) 1 22(17.19) 1(2.50) 7(17.95) 1(2.56) 2 26(20.31) 11(27.50) 7(17.95) 11(28.21) 3A 4(3.13) 1(2.50) 2(5.13) 1(2.56) 3B 3(2.34) 0(0) 2(5.13) 0(0) 4 0(0) 1(2.50) 0(0) 1(2.56) 5 1(0.78) 0(0) 1(2.56) 0(0) 并发症发生 0.327 0.252 否 72(56.25) 26(65.00) 20(51.28) 25(64.10) 是 56(43.75) 14(35.00) 19(48.72) 14(35.90) 表 2 整体队列与匹配队列pCR相关变量的单因素分析
因素 整体队列 匹配队列 OR 95%CI P值 OR 95%CI P值 年龄 0.997 0.957~1.039 0.886 0.993 0.944~1.045 0.796 体重指数 0.992 0.866~1.135 0.904 0.928 0.761~1.131 0.458 血红蛋白 1.011 0.992~1.032 0.245 1.004 0.977~1.032 0.752 血小板 1.002 0.998~1.006 0.423 1.004 0.996~1.012 0.276 淋巴细胞 2.002 0.977~4.103 0.058 4.411 1.463~13.298 0.008 PLR 0.999 0.995~1.003 0.545 0.995 0.987~1.003 0.166 白蛋白 0.994 0.903~1.094 0.897 0.943 0.828~1.073 0.370 ALG 1.266 0.240~6.671 0.781 1.599 0.190~13.49 0.666 Ccr 0.99 0.974~1.005 0.211 0.977 0.951~1.005 0.092 性别 男 对照 对照 女 0.787 0.268~2.312 0.662 0.333 0.086~1.294 0.112 吸烟 否 对照 对照 是 0.831 0.38~1.817 0.643 2.019 0.732~5.573 0.175 临床T分期 T2 对照 对照 T3 1.219 0.518~2.872 0.650 1.827 0.598~5.584 0.290 T4 3.828 0.833~17.59 0.084 6.346 0.743~54.168 0.091 临床N分期 N0 对照 对照 N+ 2.186 0.618~7.740 0.226 5.133 0.622~42.38 0.129 分级 高级别 对照 对照 低级别 0.902 0.097~8.362 0.928 0.778 0.067~9.031 0.841 肾积水 否 对照 对照 是 2.549 0.981~6.621 0.055 3.519 0.926~13.367 0.065 联合免疫治疗 是 对照 对照 否 0.166 0.072~0.384 0.001 0.261 0.089~0.768 0.015 OR:比值比;CI:置信区间;PLR:血小板/淋巴细胞比;ALG:白球比 表 3 整体队列与匹配队列中2种新辅助治疗方案的病理反应
例(%) 指标 整体队列 匹配队列 化疗组(128例) 联合组(40例) P值 化疗组(39例) 联合组(39例) P值 病理反应 < 0.001 0.049 完全缓解 14(10.94) 17(42.50) 6(15.38) 16(41.03) 部分缓解 45(35.15) 14(35.00) 15(38.47) 14(35.89) 疾病稳定 47(36.72) 5(12.50) 12(30.77) 5(12.82) 疾病进展 22(17.19) 4(10.00) 6(15.38) 4(10.26) pCR < 0.001 0.012 是 14(10.94) 17(42.50) 6(15.38) 16(41.03) 否 114(89.06) 23(57.50) 33(84.62) 23(58.97) 病理降期 < 0.001 0.032 是 59(46.09) 31(77.50) 21(53.85) 30(76.92) 否 69(53.91) 9(22.50) 18(46.15) 9(23.08) 疾病控制 0.273 0.498 是 106(82.81) 36(90.00) 33(84.62) 35(89.74) 否 22(17.19) 4(10.00) 6(15.38) 4(10.26) -
[1] Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2021, 71(3): 209-249. doi: 10.3322/caac.21660
[2] Stecca C, Abdeljalil O, Sridhar SS. Metastatic Urothelial Cancer: a rapidly changing treatment landscape[J]. Ther Adv Med Oncol, 2021, 13: 17588359211047352.
[3] Yin M, Joshi M, Meijer RP, et al. Neoadjuvant chemotherapy for muscle-invasive bladder cancer: a systematic review and two-step meta-analysis[J]. Oncologist, 2016, 21(6): 708-715. doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.2015-0440
[4] Grossman HB, Natale RB, Tangen CM, et al. Neoadjuvant chemotherapy plus cystectomy compared with cystectomy alone for locally advanced bladder cancer[J]. N Engl J Med, 2003, 349(9): 859-866. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa022148
[5] Advanced Bladder Cancer Meta-analysis Collaboration. Neoadjuvant chemotherapy in invasive bladder cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Lancet, 2003, 361(9373): 1927-1934. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(03)13580-5
[6] Witjes JA, Bruins HM, Cathomas R, et al. European association of urology guidelines on muscle-invasive and metastatic bladder cancer: summary of the 2020 guidelines[J]. Eur Urol, 2021, 79(1): 82-104. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2020.03.055
[7] Chang SS, Bochner BH, Chou R, et al. Treatment of non-metastatic muscle-invasive bladder cancer: AUA/ASCO/ASTRO/SUO guideline[J]. J Urol, 2017, 198(3): 552-559. doi: 10.1016/j.juro.2017.04.086
[8] Ghatalia P, Kaur J, Sonpavde G. Muscle invasive bladder cancer: where is the field headed?[J]. Expert Opin Biol Ther, 2023, 23(9): 913-927. doi: 10.1080/14712598.2023.2238607
[9] Han YY, Liu DD, Li LH. PD-1/PD-L1 pathway: current researches in cancer[J]. Am J Cancer Res, 2020, 10(3): 727-742.
[10] Pfister C, Gravis G, Fléchon A, et al. Randomized Phase Ⅲ Trial of Dose-dense Methotrexate, Vinblastine, Doxorubicin, and Cisplatin, or Gemcitabine and Cisplatin as Perioperative Chemotherapy for Patients with Muscle-invasive Bladder Cancer. Analysis of the GETUG/AFU V05 VESPER Trial Secondary Endpoints: Chemotherapy Toxicity and Pathological Responses[J]. Eur Urol, 2021, 79(2): 214-221. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2020.08.024
[11] Powles T, Csöszi T, Özgüro lu M, et al. Pembrolizumab alone or combined with chemotherapy versus chemotherapy as first-line therapy for advanced urothelial carcinoma(KEYNOTE-361): a randomised, open-label, phase 3 trial[J]. Lancet Oncol, 2021, 22(7): 931-945. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(21)00152-2
[12] Rose TL, Harrison MR, Deal AM, et al. Phase Ⅱ study of gemcitabine and split-dose cisplatin plus pembrolizumab as neoadjuvant therapy before radical cystectomy in patients with muscle-invasive bladder cancer[J]. J Clin Oncol, 2021, 39(28): 3140-3148. doi: 10.1200/JCO.21.01003
[13] Flaig TW, Tangen CM, Daneshmand S, et al. A randomized phase Ⅱ study of coexpression extrapolation(COXEN)with neoadjuvant chemotherapy for bladder cancer(SWOG S1314;NCT02177695)[J]. Clin Cancer Res, 2021, 27(9): 2435-2441. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-20-2409
[14] Cathomas R, Petrausch U, Hayoz S, et al. Perioperative chemoimmunotherapy with durvalumab(Durva)in combination with cisplatin/gemcitabine(Cis/Gem)for operable muscle-invasive urothelial carcinoma(MIUC): Preplanned interim analysis of a single-arm phase Ⅱ trial(SAKK 06/17)[J]. J Clin Oncol, 2020, 38(6_suppl): 499. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2020.38.6_suppl.499
[15] Hoimes CJ, Albany C, Hoffman-Censits J, et al. A phase Ib/Ⅱ study of neoadjuvant pembrolizumab(pembro)and chemotherapy for locally advanced urothelial cancer(UC)[J]. Ann Oncol, 2018, 29: viii726.
[16] Winquist E, Kirchner TS, Segal R, et al. Neoadjuvant chemotherapy for transitional cell carcinoma of the bladder: a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. J Urol, 2004, 171(2 pt 1): 561-569.
[17] Rosenblatt R, Sherif A, Rintala E, et al. Pathologic downstaging is a surrogate marker for efficacy and increased survival following neoadjuvant chemotherapy and radical cystectomy for muscle-invasive urothelial bladder cancer[J]. Eur Urol, 2012, 61(6): 1229-1238. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2011.12.010
[18] Xu JM, Bai YX, Xu N, et al. Tislelizumab plus chemotherapy as first-line treatment for advanced esophageal squamous cell carcinoma and gastric/gastroesophageal junction adenocarcinoma[J]. Clin Cancer Res, 2020, 26(17): 4542-4550. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-19-3561
[19] Lu S, Wang J, Yu Y, et al. Tislelizumab plus chemotherapy as first-line treatment for locally advanced or metastatic nonsquamous NSCLC(RATIONALE 304): a randomized phase 3 trial[J]. J Thorac Oncol, 2021, 16(9): 1512-1522. doi: 10.1016/j.jtho.2021.05.005
[20] Wang J, Lu S, Yu XM, et al. Tislelizumab plus chemotherapy vs chemotherapy alone as first-line treatment for advanced squamous Non-Small-Cell lung cancer: a phase 3 randomized clinical trial[J]. JAMA Oncol, 2021, 7(5): 709-717. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2021.0366
[21] Grassauer J, Schmidt J, Cowan A, et al. Downstaging and survival associated with neoadjuvant immunotherapy before radical cystectomy for muscle-invasive bladder cancer[J]. Eur Urol Oncol, 2024, 7(1): 139-146. doi: 10.1016/j.euo.2023.06.005
[22] Galsky MD, Arija JÁA, Bamias A, et al. Atezolizumab with or without chemotherapy in metastatic urothelial cancer(IMvigor130): a multicentre, randomised, placebo-controlled phase 3 trial[J]. Lancet, 2020, 395(10236): 1547-1557. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30230-0
-

计量
- 文章访问数: 295
- 施引文献: 0



 下载:
下载: