Clinical data and experience of percutaneous nephrolithotomy in different positions for treatment of upper urinary stones
-
摘要: 目的 研究不同体位经皮肾镜取石术在上尿路结石的治疗效果。 方法 以2020年6月—2023年6月在广元市第一人民医院行经皮肾镜取石术的上尿路结石患者66例作为研究对象,开展回顾性分析,根据不同体位进行分组,主要有俯卧位(22例)、仰卧位(20例)、斜卧位(24例)3种体位。比较俯卧位、仰卧位、斜卧位3种体位围手术期疗效指标、血氧情况和并发症情况。 结果 俯卧位、仰卧位、斜卧位患者的手术时间、术中出血量、一次清石率差异有统计学意义(P<0.05);但是在麻醉时间、透视持续时间、建立通道时间、住院天数上差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。体位后,俯卧位、仰卧位、斜卧位患者的收缩压(SBP)、血氧饱和度(SPO2)均下降,且俯卧位患者低于仰卧位和斜卧位患者,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。 结论 斜卧位下经皮肾镜取石术用于上尿路结石相对俯卧位、仰卧位,可减少手术时间及术中出血量,提高结石清除率,对患者血液循环功能及呼吸功能影响更小。故对于上尿路结石患者的手术治疗可结合临床实际优先考虑采用斜卧位。Abstract: Objective To study the efficacy of percutaneous nephrolithotomy in different positions in the treatment of upper urinary tract calculi. Methods A total of 66 patients with upper urinary tract stones who came to Guangyuan First People's Hospital for percutaneous nephrolithotomy from June 2020 to June 2023 were selected as the study objects. A retrospective analysis was carried out according to different positions, mainly prone (n=22), supine (n=20) and oblique (n=24). The perioperative efficacy indicators, blood oxygen conditions and complications were compared among the prone, supine and oblique positions. Results There were differences in operation time, intraoperative blood loss, and one-time stone clearing rate among the three positions (P < 0.05). However, there were no significant differences in anesthesia time, fluoroscopy duration, channel establishment time and hospitalization days (P>0.05). After the patients were placed in the prone, supine or oblique position, their SBP and SPO2 decreased, and the data of patients in prone position were lower than those of patients in supine or oblique position. The difference was statistically significant (P < 0.05). Conclusion Compared with prone and supine positions, percutaneous nephrolithotomy in oblique position can reduce the operative time and intraoperative blood loss, improve the stone clearance rate, and has less influence on the blood circulation and respiratory function of patients in the treatment of upper urinary tract calculi. Therefore, oblique position can be given priority in combination with clinical practice.
-

-
表 1 3种体位患者一般资料比较
例(%),X±S 指标 俯卧位(22例) 仰卧位(20例) 斜卧位(24例) χ2/F P值 性别 0.080 0.961 男 12(54.5) 11(55.0) 14(58.3) 女 10(45.5) 9(45.0) 10(41.7) 年龄/岁 56.89±18.69 56.98±19.38 57.39±18.94 0.005 0.995 BMI/(kg/m2) 23.68±3.49 22.18±3.59 22.98±3.98 0.859 0.429 病程/年 3.36±1.59 3.59±1.49 3.68±1.59 0.253 0.777 结石直径/cm 4.31±1.11 4.58±1.13 4.33±1.08 0.391 0.678 肾积水 0.445 0.979 轻度 5(22.73) 5(25.00) 7(29.17) 中度 10(45.45) 9(45.00) 9(37.50) 重度 7(31.82) 6(30.00) 8(33.33) 表 2 3种体位患者围手术期疗效指标比较
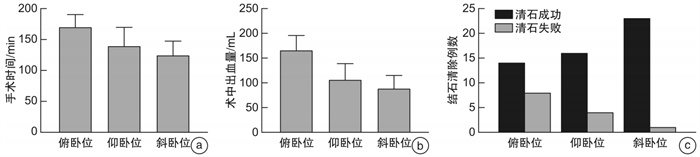
例(%),X±S 组别 麻醉时间/min 透视持续时间/min 手术时间/min 建立通道时间/min 术中出血量/mL 住院天数/d 一次清石 俯卧位(22例) 156.39±69.24 7.68±4.69 169.48±20.78 14.56±6.89 165.68±30.68 7.69±4.69 14(63.64) 仰卧位(20例) 162.39±59.48 7.98±4.26 138.98±30.781) 15.89±5.98 106.49±32.491) 7.96±4.68 16(80.00) 斜卧位(24例) 169.24±63.87 7.39±4.83 123.68±23.681)2) 14.68±6.21 88.49±26.961) 8.26±4.68 23(95.83)1) F 0.229 0.089 19.457 0.277 40.881 0.085 7.524 P值 0.796 0.915 <0.001 0.759 <0.001 0.918 0.023 与俯卧位比较,1)P<0.05;与仰卧位比较,2)P<0.05。 表 3 3种体位患者血氧情况比较
X±S 指标 俯卧位(22例) 仰卧位(20例) 斜卧位(24例) F P值 SBP/mmHg 体位前 132.56±12.68 130.68±11.49 129.8±13.68 0.279 0.758 体位后 109.58±12.75 123.68±7.351) 122.56±7.791) 14.480 <0.001 F 11.252 3.054 3.612 P值 <0.001 0.007 0.001 DBP/mmHg 体位前 82.69±12.47 81.46±10.39 81.98±11.68 0.060 0.942 体位后 71.36±8.36 77.69±10.351) 76.59±9.98 2.690 0.076 F 4.592 1.171 2.693 P值 <0.001 0.256 0.013 HR/(次/min) 体位前 86.29±10.65 85.49±9.68 84.69±10.36 0.140 0.870 体位后 85.39±9.68 84.69±10.34 85.69±9.68 0.058 0.944 F 0.487 0.344 -0.468 P值 0.632 0.735 0.644 SPO2/% 体位前 99.49±0.56 99.46±0.53 98.48±0.531)2) 25.972 <0.001 体位后 92.35±0.56 98.34±0.641) 97.68±0.751)2) 541.266 <0.001 F 83.030 8.329 7.103 P值 <0.001 <0.001 <0.001 与俯卧位比较,1)P<0.05;与仰卧位比较,2)P<0.05。 -
[1] Saluk J, Ebel J, Rose J, et al. Fellowship training in endourology: Impact on percutaneous nephrolithotomy access patterns[J]. Can Urol Assoc J, 2022, 16(2): E76-E81.
[2] 汤井源, 金振华, 张扬, 等. 完全平卧位逆行输尿管软镜碎石术治疗上尿路结石的临床研究[J]. 临床泌尿外科杂志, 2023, 38(6): 424-427. https://lcmw.whuhzzs.com/article/doi/10.13201/j.issn.1001-1420.2023.06.007
[3] Ellison JS, Lorenzo M, Beck H, et al. Comparative effectiveness of paediatric kidney stone surgery(the PKIDS trial): study protocol for a patient-centred pragmatic clinical trial[J]. BMJ Open, 2022, 12(4): e056789. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2021-056789
[4] Lin CH, Lin YC, Chiang HC, et al. Totally tubeless single access tract mini-percutaneous nephrolithotripsy in treatment of large burden>2 cm and/or complex renal stones: a case series of 62 patients[J]. BMC Urol, 2022, 22(1): 61. doi: 10.1186/s12894-022-01012-9
[5] Pillai SB, Chawla A, de la Rosette J, et al. Super-mini percutaneous nephrolithotomy(SMP)vs retrograde intrarenal surgery(RIRS)in the management of renal calculi≤2 cm: a propensity matched study[J]. World J Urol, 2022, 40(2): 553-562. doi: 10.1007/s00345-021-03860-w
[6] Kamarulzaman MN. RE: Miniaturized percutaneous nephrolithotomy versus retrograde intrarenal surgery in the treatment of renal stones with a diameter < 15 mm: a 3-year open-label prospective study[J]. Urol Ann, 2020, 12(1): 106. doi: 10.4103/UA.UA_12_19
[7] Ergani B, Ozbilen MH, Yalcın MY, et al. The effect of hydronephrosis grade on stone-free rate in retrograde intrarenal stone surgery with flexible ureterorenoscopy[J]. Am J Clin Exp Urol, 2021, 9(2): 194-201.
[8] 李彭举, 钟量, 孙杰. 儿童上尿路结石的外科治疗方式与进展[J]. 中华小儿外科杂志, 2021, 42(9): 847-852. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn421158-20200426-00294
[9] 肖莉, 汪财霞, 张小马. 血脂、血尿酸对上尿路结石最大径及数目的影响[J]. 重庆医学, 2021, 50(11): 1899-1904. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-8348.2021.11.023
[10] 堵洁, 顾鹏, 姚勇, 等. X线辅助下电磁式体外冲击波治疗上尿路结石422例[J]. 东南大学学报(医学版), 2020, 39(3): 305-308. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6264.2020.03.011
[11] 吴明震, 唐炯. 输尿管软镜下碎石术治疗上尿路结石的临床疗效及对机体应激反应的影响[J]. 山西医药杂志, 2022, 51(1): 19-23. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-9926.2022.01.004
[12] 赵文武, 唐良友, 张丽英. 上尿路结石病人临床治疗[J]. 内蒙古医科大学学报, 2020, 42(1): 51-52. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NMYX202001019.htm
[13] 段利军, 孙建明, 曾向阳. 输尿管软镜及经皮肾镜在上尿路结石中的疗效比较[J]. 中南医学科学杂志, 2020, 48(1): 88-92. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYYY202001025.htm
[14] 崔振鹏, 罗林, 刘山, 等. 缩短输尿管软镜术前双J管留置时间对直径 < 1.5 cm上尿路结石病人的疗效及预后评估[J]. 临床外科杂志, 2020, 28(2): 161-163. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-6483.2020.02.018
[15] Jamil MN, Haq FU, Islam EU, et al. Comparison between supine position versus prone position in percutaneous nephrolithotomy: a single centered analysis of 623 cases[J]. J Ayub Med Coll Abbottabad, 2022, 34(Suppl 4): S1003-S1007.
[16] Kasap Y, Senel S, Uzun E, et al. Does surgical position affect infective complications in percutaneous nephrolithotomy?[J]. Urolithiasis, 2022, 50(6): 765-771. doi: 10.1007/s00240-022-01367-6
[17] Cassell A 3rd, Jalloh M, Ndoye M, et al. Surgical management of urolithiasis of the upper tract-current trend of endourology in Africa[J]. Res Rep Urol, 2020, 12: 225-238.
[18] Choy SH, Nyanatay SA, Sothilingam S, et al. Cardiovascular risk factors, ethnicity and infection stone are independent factors associated with reduced renal function in renal stone formers[J]. PLoS One, 2022, 17(4): e0265510. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0265510
[19] Astolfi RH, Carrera R, Gattas N, et al. Current scenario of endourological treatment of kidney stones in Brazil: results of a national survey[J]. Int Braz J Urol, 2020, 46(3): 400-408.
[20] 龙金, 马重文, 刘智, 等. 半截石斜仰卧位与经典俯卧位在经皮肾镜碎石术治疗上尿路结石的对比研究[J/OL]. 现代医学与健康研究电子杂志, 2023, 7(6): 13-15.
[21] Mohd Ali DM, Mahmud MH, Mohamad NS. Pre-operative percutaneous nephrolithotripsy characterisation of kidney stones with second-generation dual-source dual-energy computed tomography[J]. Malays J Med Sci, 2020, 27(5): 43-52.
[22] Huang X, Hu ZJ, Yue X, et al. Expression of inflammatory factors in critically ill patients with urosepticemia and the imaging analysis of the severity of the disease[J]. J Healthc Eng, 2021, 2021: 6659435.
[23] Jiang T, Osadchiy V, Weinberger JM, et al. Impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on patient preferences and decision making for symptomatic urolithiasis[J]. J Endourol, 2021, 35(8): 1250-1256. doi: 10.1089/end.2020.1141
-




 下载:
下载: