Comparative analysis between retroperitoneal and transperitoneal robot-assisted partial nephrectomy for renal tumors near the collection system
-
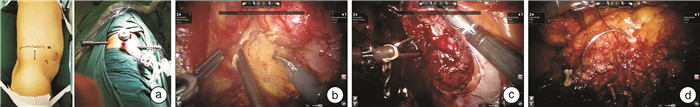
摘要: 目的 对比分析临近集合系统的肾肿瘤采取不同机器人手术入路的临床疗效及安全性。方法 回顾性收集2020年1月-2023年1月在华中科技大学同济医学院附属协和医院行腹膜后机器人辅助肾部分切除术(retroperitoneal robot-assisted partial nephrectomy, R-RAPN)和经腹入路机器人辅助肾部分切除术(transperitoneal robot-assisted partial nephrectomy, T-RAPN)的54例患者资料。分别记录R-RAPN组及T-RAPN组患者的手术时间、术中失血量、输血量、缝合方式、肾脏热缺血时间、有无转入ICU、术后拔出引流管时间、出院时间、并发症及处理措施;术前术后血红蛋白、肌酐、尿素氮、肾小球滤过率的变化,肿瘤病理分级及类型、切缘阳性率等。对围手术期及随访指标进行统计分析。结果 T-RAPN组中位手术时间为113.5(83.0,150.0) min,R-RAPN组中位手术时间为87.5(58.0,101.5) min,差异有统计学意义(P=0.039 2)。T-RAPN组中位热缺血时间为27.0(20.0,35.0) min,R-RAPN组中位热缺血时间为20.0(16.5,25.5) min,差异无统计学意义。T-RAPN组中位失血量为100.0(50.0,200.0) mL,R-RAPN组中位失血量为50.0(30.0,75.0) mL,差异无统计学意义。2组所有患者均未转入ICU。T-RAPN组患者中位拔引流管时间6.5(4.0,7.0) d,术后中位出院时间7.0(5.0,7.0) d;R-RAPN组中位拔引流管时间5.0(4.0,5.0) d,术后中位出院时间6.0(5.0,6.0) d,差异无统计学意义。所有患者术后标本均无切缘阳性,终末随访肾功能与术前几乎一致。R-RAPN组患者平均随访(24.6±2.1)个月,无一例局部复发或远处转移。T-RAPN组患者平均随访(31.9±7.3)个月,有1例局部复发。结论 临近集合系统机器人辅助肾部分切除术入路的选择可根据肿瘤偏向针对性地采用腹膜后或经腹途径。对于复杂的肾肿瘤,推荐T-RAPN以获得更大的操作空间和更广阔的视野。无论采取哪种入路方式,RAPN均能在获得良好预后的同时,能最大程度地保护肾功能。Abstract: Objective To comparatively analyze the clinical efficacy and safety of different surgical approaches for renal tumors near the collection system.Methods We have retrieved the data of patients undergoing retroperitoneal robot-assisted partial nephrectomy(R-RAPN) and transperitoneal robot-assisted partial nephrectomy (T-RAPN) approaches at Wuhan Union Hospital from January 2020 to January 2023. The operating time, intraoperative blood loss, blood transfusion volume, suture method, renal warm ischemia time, transferring to ICU or not, postoperative drainage tube withdrawal time, discharge time, complications and treatment measures were recorded in the R-RAPN group and the T-RAPN group respectively. Changes in hemoglobin, creatinine, urea nitrogen, and glomerular filtration rate before and after surgery, tumor pathological grade and type, positive rate of surgical margin, etc. were also observed. Statistical analysis was performed on perioperative and follow-up characteristics.Results The median operation time in the T-RAPN group was 113.5(83.0, 150) minutes and that in the R-RAPN group was 87.5(58.0, 101.5) minutes, with a statistical difference between the groups(P=0.039 2). The median warm ischemia time was 27.0(20.0, 35.0) minutes in the T-RAPN group and 20.0(16.5, 25.5) minutes in the R-RAPN group. There was no statistical difference between the groups. The median blood loss in the T-RAPN group was 100.0(50.0, 200.0) mL and that in the R-RAPN group was 50.0(30.0, 75.0) mL. There was no statistical difference between the groups. None of the patients in both groups were transferred to ICU. The median time for removing the drainage tube was 6.5(4.0, 7.0) days and the postoperative discharge time was 7.0(5.0, 7.0) days in the T-RAPN group. The median time for removing the drainage tube was 5.0(4.0, 5.0) days and the discharge time was 6.0(5.0, 6.0) days in the R-RAPN group. There was no statistical difference between the two groups. No surgical margin was positive in all patients' specimens after surgery, and the renal function at terminal follow-up was almost consistent with that before surgery. Patients in the R-RAPN group were followed up for an average of (24.6±2.1) months, and no local recurrence or distant metastasis was found. Patients in the T-RAPN group were followed up for an average of (31.9±7.3) months, and 1 case had local recurrence.Conclusion The selection of RAPN surgical methods for the tumor near the collection system can be targeted according to the tumor location by using retroperitoneal or transabdominal approaches. For complex renal tumors, T-RAPN is recommended to obtain greater operating space and a broader field of view. No matter which approach is used, RAPN can achieve a good prognosis while maximizing the protection of renal function.
-
Key words:
- renal cancer /
- near the collection system /
- robot /
- partial nephrectomy /
- retroperitoneal /
- transperitoneal
-

-
表 1 2组患者肾癌复杂性R.E.N.A.L.评分比较
例(%),X±S R.E.N.A.L.特征 R-RAPN组(30例) T-RAPN组(24例) P值 肿瘤直径(R) 0.2484 ≤4(1分) 18(60.0) 12(50.0) 4~7(2分) 12(40.0) 12(50.0) ≥7(3分) 0(0) 0(0) 肿瘤外凸率(E) 0.9009 ≥50%(1分) 9(30.0) 6(25.0) < 50%(2分) 18(60.0) 15(62.5) 完全内生(3分) 3(10.0) 3(12.5) 位置 < 0.0001 腹侧(A) 0(0) 18(75.0) 背侧(P) 27(90.0) 0(0) 其他(X) 3(10.0) 6(25.0) 肿瘤极性(L) 0.0769 完全在肾上/下极(1分) 12(40.0) 3(12.5) 大部分在上/下极(2分) 6(20.0) 6(25.0) >50%的肿瘤超过上/下极(3分) 12(40.0) 15(62.5) R.E.N.A.L.评分/分 8.2±1.1 8.9±1.1 0.2265 表 2 围手术期患者临床指标
例(%),M(P25,P75) 指标 R-RAPN组(30例) T-RAPN组(24例) P值 手术时间/min 87.5(58.0,101.5) 113.5(83.0,150) 0.039 2 失血量/mL 50.0(30.0,75.0) 100.0(50.0,200.0) 0.188 9 热缺血时间/min 20.0(16.5,25.5) 27.0(20.0,35.0) 0.412 8 术中缝合集合系统 12(40.0) 24(100.0) 0.007 3 拔引流管/d 5.0(4.0,5.0) 6.5(4.0,7.0) 0.738 2 术后出院/d 6.0(5.0,6.0) 7.0(5.0,7.0) 0.945 2 术后并发症 6(20.0) 0(0) 0.241 6 肿瘤病理类型 0.005 4 肾透明细胞癌 18(60.0) 12(50.0) 肾嫌色细胞癌 6(20.0) 0(0) 肾乳头状细胞癌 0(0) 6(25.0) 其他 6(20.0) 6(25.0) 病理ISUP分级 0.191 3 2/4 12(40.0) 15(62.5) 3/4 9(30.0) 3(12.5) 未分级 9(30.0) 6(25.0) 侵犯肾周脂肪 6(20.0) 0(0) 0.179 7 表 3 临床随访指标比较
X±S 指标 R-RAPN组 T-RAPN组 术前 终末随访 P值 术前 终末随访 P值 血红蛋白/(g/L) 125.9±11.0 113.4±22.8 0.1359 135.8±14.2 130.9±12.6 0.4784 肌酐/(μmol/L) 71.1±16.5 78.3±28.9 0.5049 84.5±26.4 113.0±68.0 0.2873 尿素氮/(mmol/L) 6.3±1.9 6.3±2.9 0.9674 5.2±1.2 7.0±2.6 0.0865 肾小球滤过率/(mL/min/1.73 m2) 88.3±15.1 81.7±22.4 0.4522 89.2±26.0 77.0±33.5 0.4305 -
[1] 叶孙益, 彭鼎, 景泰乐, 等. 国产单孔蛇形臂机器人辅助腹腔镜行肾部分切除术初步经验[J]. 临床泌尿外科杂志, 2022, 37(9): 661-664. https://lcmw.whuhzzs.com/article/doi/10.13201/j.issn.1001-1420.2022.09.003
[2] 孙颖浩. 中国泌尿外科和男科疾病诊断治疗指南[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2020.
[3] 韩松辰, 宋宇轩, 戴翔, 等. 热缺血时间对腹腔镜肾部分切除术后肾功能的影响[J]. 中华泌尿外科杂志, 2022, 43(5): 350-354. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112330-20220311-00110
[4] Kutikov A, Uzzo RG. The R.E.N.A.L. nephrometry score: a comprehensive standardized system for quantitating renal tumor size, location and depth[J]. J Urol, 2009, 182(3): 844-853. doi: 10.1016/j.juro.2009.05.035
[5] Moch H, Cubilla AL, Humphrey PA, et al. The 2016 WHO classification of tumours of the urinary system and male genital organs-part A: renal, penile, and testicular tumours[J]. Eur Urol, 2016, 70(1): 93-105. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2016.02.029
[6] Volpe A, Capitanio U, Falsaperla M, et al. Partial nephrectomy for renal tumors: recommendations of the Italian society of urology RCC working group[J]. Minerva Urol Nephrol, 2024, 76(1): 9-21.
[7] Mir MC, Derweesh I, Porpiglia F, et al. Partial nephrectomy versus radical nephrectomy for clinical T1b and T2 renal tumors: a systematic review and meta-analysis of comparative studies[J]. Eur Urol, 2017, 71(4): 606-617. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2016.08.060
[8] Pecoraro A, Amparore D, Manfredi M, et al. Partial vs. radical nephrectomy in non-metastatic pT3a kidney cancer patients: a population-based study[J]. Minerva Urol Nephrol, 2022, 74(4): 445-451.
[9] Stout TE, Gellhaus PT, Tracy CR, et al. Robotic partial vs radical nephrectomy for clinical T3a tumors: a narrative review[J]. J Endourol, 2023, 37(9): 978-985. doi: 10.1089/end.2023.0173
[10] Beksac AT, Okhawere KE, Abou Zeinab M, et al. Robotic partial nephrectomy for management of renal mass in patients with a solitary kidney: can we expand the indication to T2 and T3 disease?[J]. Minerva Urol Nephrol, 2022, 74(2): 203-208.
[11] Thompson RH, Lane BR, Lohse CM, et al. Renal function after partial nephrectomy: effect of warm ischemia relative to quantity and quality of preserved kidney[J]. Urology, 2012, 79(2): 356-360. doi: 10.1016/j.urology.2011.10.031
[12] Choi JE, You JH, Kim DK, et al. Comparison of perioperative outcomes between robotic and laparoscopic partial nephrectomy: a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Eur Urol, 2015, 67(5): 891-901. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2014.12.028
[13] Porpiglia F, Mari A, Amparore D, et al. Transperitoneal vs retroperitoneal minimally invasive partial nephrectomy: comparison of perioperative outcomes and functional follow-up in a large multi-institutional cohort(the RECORD 2 project)[J]. Surg Endosc, 2021, 35(8): 4295-4304. doi: 10.1007/s00464-020-07919-4
[14] Carbonara U, Crocerossa F, Campi R, et al. Retroperitoneal robot-assisted partial nephrectomy: a systematic review and pooled analysis of comparative outcomes[J]. Eur Urol Open Sci, 2022, 40: 27-37. doi: 10.1016/j.euros.2022.03.015
[15] 蒋思雄, 杨玻, 鞠红卫, 等. 弓状韧带与肾动脉关系的后腹腔镜肾切除解剖学研究[J]. 中国内镜杂志, 2016, 22(10): 90-93.
-




 下载:
下载: