Optimizing tip-flexible ureteral access sheath parameters with intelligent pressure control in stone-clearing mode: an in vitro study
-
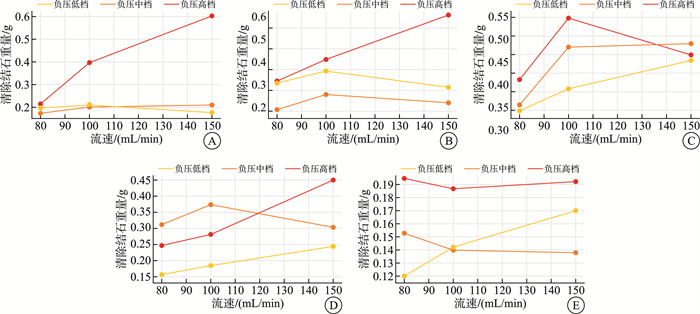
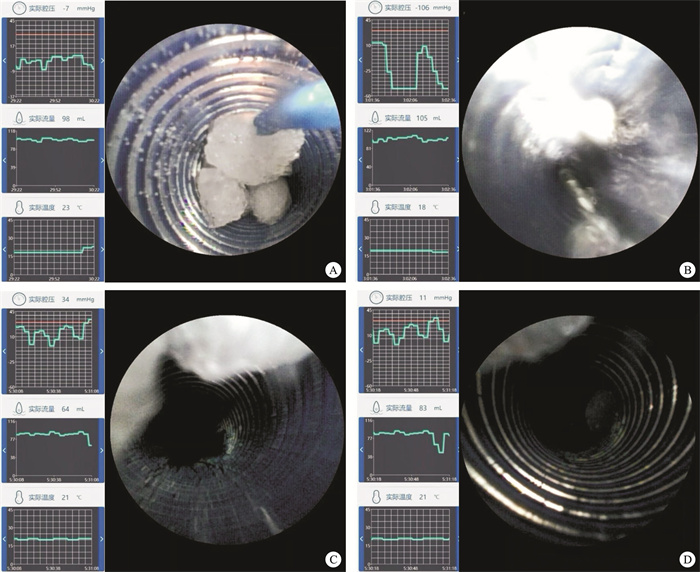
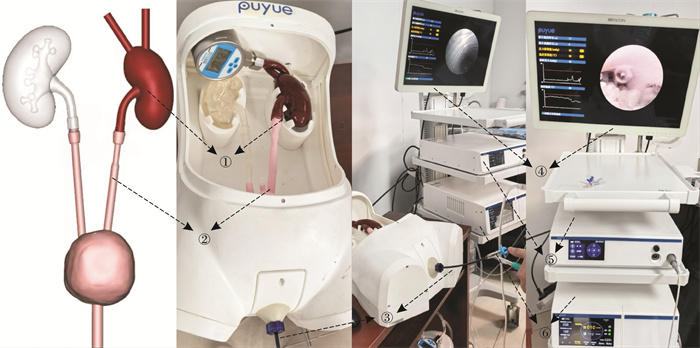
摘要: 目的 模拟术中不同体位、灌流流速与负压吸引水平的条件组合,探讨清石过程中的最佳参数,评估智能控压软镜系统的效果。方法 分别设置灌注流速(80、100、150 mL/min)与负压吸引水平(低、中、高),形成9种不同的清石模式,同时调整模型体位为平卧、头高脚低(15°和30°)及头低脚高(15°和30°)。每组实验测量5 min内清除的结石重量并评估不同条件对清石效率的影响。结果 单因素分析显示,体位(P < 0.001)和负压水平(P=0.018)对结石清除有显著影响。多因素分析进一步表明,与平卧位相比,头高脚低30°显著提高了清石效率(P=0.001);头低脚高15°同样对结石清除具有正向作用(P=0.035),但头低脚高30°却显著降低了清石效率(P=0.002)。此外,负压高档相较于中档和低档能显著提高清石效率(P < 0.001)。虽然灌流流速的单因素影响差异无统计学意义(P=0.073),但在与体位和负压的配合下,其作用显现出差异有统计学意义(P=0.006)。结论 在保证肾盂内压安全的前提下,利用负压吸引结石时,可以采用头高脚低体位,并配合较高的灌流流速和较高的负压吸引水平,有助于结石的清除。Abstract: Objective To simulate the combinations of intraoperative positions, irrigation flow rates, and negative pressure suction levels to explore the optimal parameter for stone clearance and to evaluate the performance of an intelligent pressure-controlled flexible ureteroscope system.Methods Irrigation flow rates(80, 100, 150 mL/min) and negative pressure suction levels(low, medium, high) were set to form nine different stone clearance modes, while the model's positions were adjusted to supine, head-up(15°and 30°), and head-down(15°and 30°) tilt angles. The weight of stones cleared within 5 minutes was measured for each group, and the effects of different conditions on stone clearance efficiency were assessed.Results The univariate analysis showed that body position(P < 0.001) and negative pressure level(P=0.018) had a significant impact on stone clearance. Multivariate analysis further revealed that, compared to the supine position, a 30° head-up, feet-down position significantly improved the clearance efficiency(P=0.001); a 15° head-down, feet-up position also had a positive effect on stone clearance(P=0.035), but a 30° head-down, feet-up position significantly reduced the clearance efficiency(P=0.002). Additionally, a high negative pressure level significantly improved the clearance efficiency compared to the medium and low levels(P < 0.001). Although the univariate effect of perfusion flow rate was not significant(P=0.073), its effect became statistically significant when combined with body position and negative pressure(P=0.006).Conclusion Under the premise of ensuring the safety of renal pelvis pressure, when using negative pressure suction to remove stones, a head-up, feet-down position can be adopted, along with a higher perfusion flow rate and higher negative pressure suction level. This helps in the clearance of the stones.
-

-
表 1 结石清石情况的单因素分析
影响因素 效应量 F P值 体位 0.886 7.801 < 0.001 灌流流速 0.772 3.378 0.073 负压 0.816 4.444 0.018 表 2 不同因素对结石清石情况的多因素分析
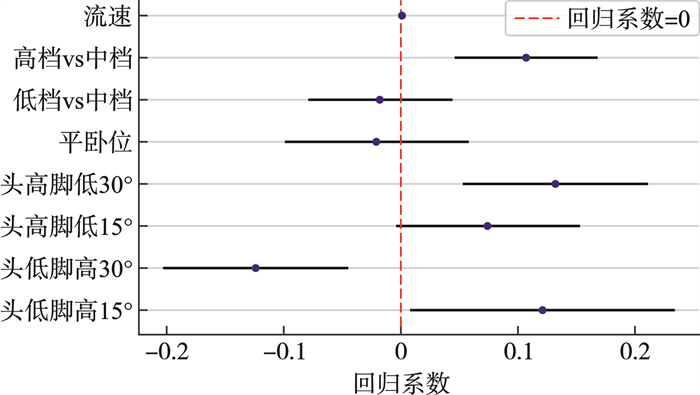
影响因素 回归系数 OR t P值 95%置信区间 下限 上限 头低脚高15° 0.121 1.128 2.183 0.035 0.009 0.233 头低脚高30° -0.124 0.883 -3.236 0.002 -0.202 -0.046 头高脚低15° 0.074 1.077 1.939 0.060 -0.003 0.152 头高脚低30° 0.132 1.141 3.433 0.001 0.054 0.210 平卧位 -0.021 0.979 -0.538 0.594 -0.098 0.057 低档vs中档 -0.018 0.982 -0.594 0.556 -0.078 0.043 高档vs中档 0.107 1.113 2.928 < 0.001 0.047 0.167 流速 0.001 1.001 2.928 0.006 < 0.001 0.002 -
[1] He M, Dong YH, Cai WS, et al. Recent advances in the treatment of renal stones using flexible ureteroscopys[J]. Int J Surg, 2024, 110(7): 4320-4328.
[2] Papatsoris A, Alba AB, Llopis JAG, et al. Management of urinary stones: state of the art and future perspectives by experts in stone disease[J]. Arch Ital Urol Androl, 2024, 96(2): 12703.
[3] Geavlete P, Multescu R, Mares C, et al. Retrograde intrarenal surgery for lithiasis using suctioning devices: a shift in paradigm?[J]. J Clin Med, 2024, 13(9): 2493. doi: 10.3390/jcm13092493
[4] 厉晓伟, 袁杰, 沈大渝, 等. 输尿管软镜联合负压吸引鞘治疗复杂肾结石的疗效和安全性[J]. 江苏大学学报(医学版), 2024, 34(4): 317-320.
[5] Wang LJ, Zhou ZJ, Gao P, et al. Comparison of traditional and suctioning ureteral access sheath during retrograde intrarenal surgery in the treatment of renal calculi[J]. Langenbecks Arch Surg, 2024, 409(1): 81. doi: 10.1007/s00423-024-03275-2
[6] Panthier F, Pauchard F, Traxer O. Retrograde intra renal surgery and safety: pressure and temperature. A systematic review[J]. Curr Opin Urol, 2023, 33(4): 308-317. doi: 10.1097/MOU.0000000000001102
[7] Tzelves L, Geraghty R, Juliebø-Jones P, et al. Suction use in ureterorenoscopy: a systematic review and meta-analysis of comparative studies[J]. BJUI Compass, 2024, 5(10): 895-912.
[8] 高坪, 吕桥, 李松波, 等. 智能控压输尿管软镜取石术治疗多囊肾合并结石的临床分析[J]. 暨南大学学报(自然科学与医学版), 2024, 45(5): 488-492.
[9] 陈海潮, 胡鹏程, 姚家涛, 等. 输尿管软镜结合可弯曲负压吸引鞘治疗感染性结石的效果[J]. 中华医院感染学杂志, 2024, 34(20): 3098-3101.
[10] Bai JJ, Shangguan T, Zou GY, et al. Efficacy and intrarenal pressure analysis of flexible and navigable suction ureteral access sheaths with flexible ureteroscopy in modified surgical positions for 2-6 cm upper urinary tract stones: a multicenter retrospective study[J]. Front Med(Lausanne), 2024, 11: 1501464.
[11] Gauhar V, Yuen SKK, Traxer O, et al. Can suction technology be a potential game changer that reshapes pediatric endourological interventions? Results from a scoping review[J]. World J Urol, 2024, 42(1): 645. doi: 10.1007/s00345-024-05353-y
[12] Cui DH, Ma QH, Zhang QY, et al. Analysis of postoperative infection factors of retrograde intrarenal surgery combined with negative pressure equipment for renal stones[J]. Sci Rep, 2024, 14(1): 22945. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-75073-1
[13] Gauhar V, Madarriaga YQ, Somani B, et al. Is flexible and navigable suction ureteral access sheath(FANS-UAS)the next best development for retrograde intrarenal surgery in children? Results of a prospective multicentre study[J]. World J Urol, 2024, 42(1): 627. doi: 10.1007/s00345-024-05337-y
[14] Chen H, Xiao JS, Ge JQ, et al. Clinical efficacy analysis of tip-flexible suctioning ureteral access sheath combined with disposable flexible ureteroscope to treat 2-4 cm renal stones[J]. Int Urol Nephrol, 2024, 56(10): 3193-3199.
[15] Chen D, Chen CS, Xie YR, et al. Suctioning versus traditional access sheath in mini-percutaneous nephrolithotomy: a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Urol J, 2021, 19(1): 1-8.
[16] Corrales M, Panthier F, Solano C, et al. Laser safety, warnings, and limits in retrograde intrarenal surgery[J]. Actas Urol Esp(Engl Ed), 2024, 48(1): 19-24.
[17] Zhong YM, Xie DH, Luo CX, et al. Clinical application of flexible ureteroscopic sheath with controllable intraluminal pressure in treating ureteral stones[J]. Asian J Urol, 2023, 10(2): 166-171.
[18] 中华医学会泌尿外科学分会结石学组, 中国泌尿系结石联盟. 负压技术在输尿管镜治疗上尿路结石应用的中国专家共识(2023年)[J]. 临床泌尿外科杂志, 2023, 38(8): 565-568.
[19] Jahrreiss V, Nedbal C, Castellani D, et al. Is suction the future of endourology?overview from EAU section of urolithiasis[J]. Ther Adv Urol, 2024, 16: 17562872241232275. doi: 10.1177/17562872241232275
[20] Shi JY, Huang T, Song BY, et al. The optimal ratio of endoscope-sheath diameter with negative-pressure ureteral access sheath: an in vitro research[J]. World J Urol, 2024, 42(1): 122.
[21] Lazarus J, Wisniewski P, Kaestner L. Beware the bolus size: understanding intrarenal pressure during ureteroscopic fluid administration[J]. S Afr J Surg, 2020, 58(4): 220.
[22] Giulioni C, Castellani D, Traxer O, et al. Experimental and clinical applications and outcomes of using different forms of suction in retrograde intrarenal surgery. Results from a systematic review[J]. Actas Urol Esp(Engl Ed), 2024, 48(1): 57-70.
-

计量
- 文章访问数: 365
- 施引文献: 0



 下载:
下载: