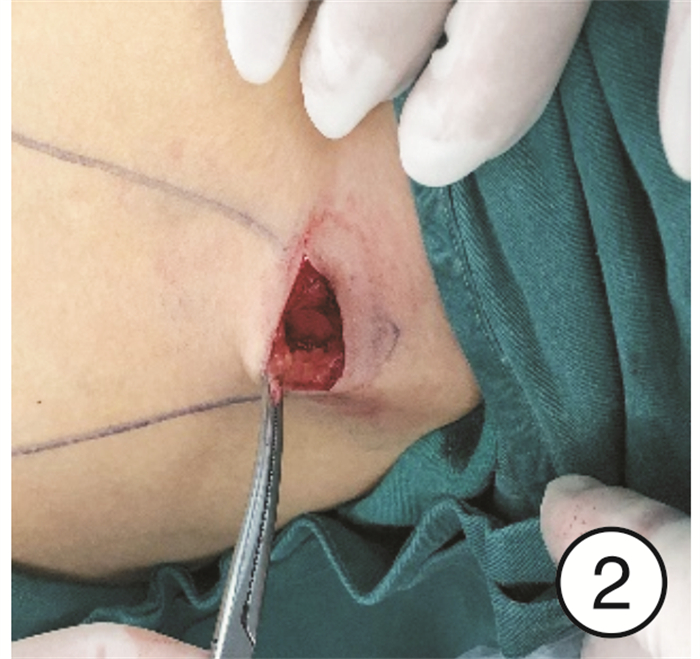
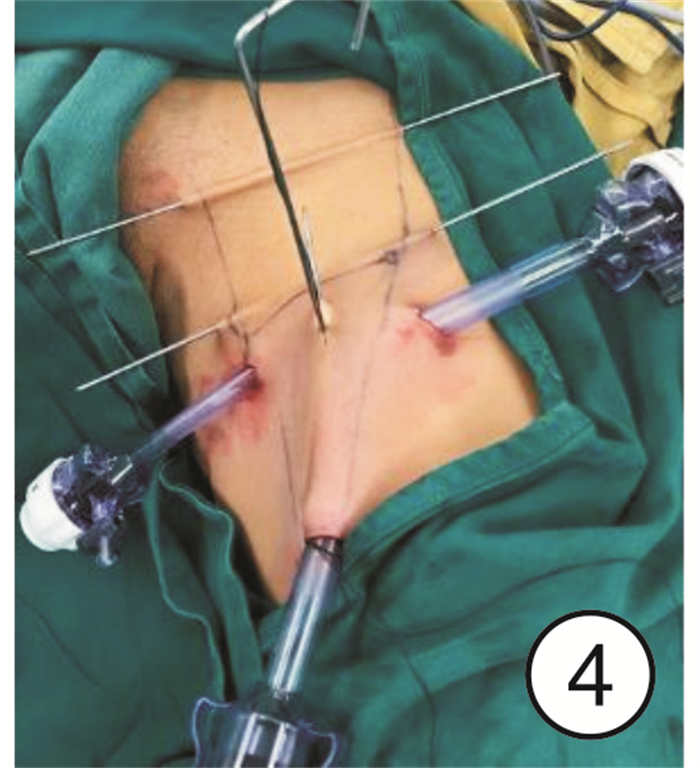
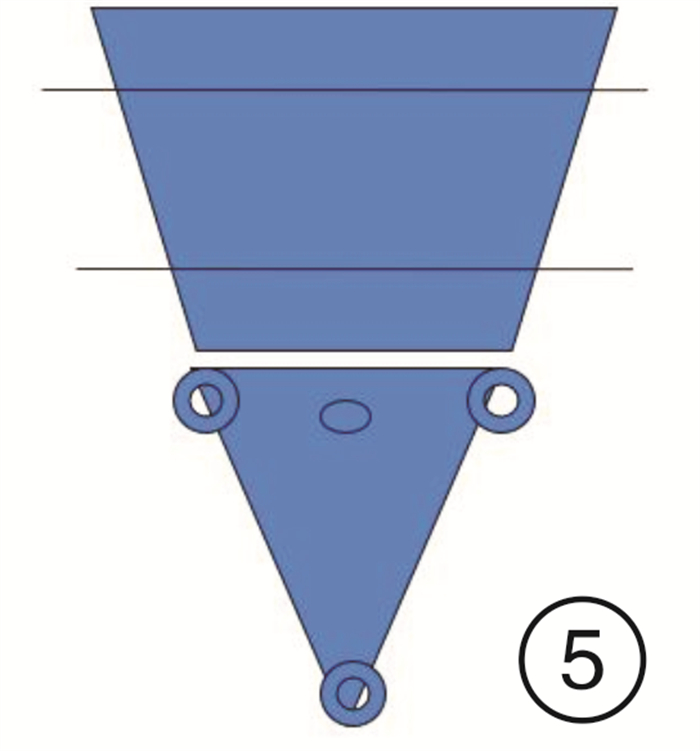
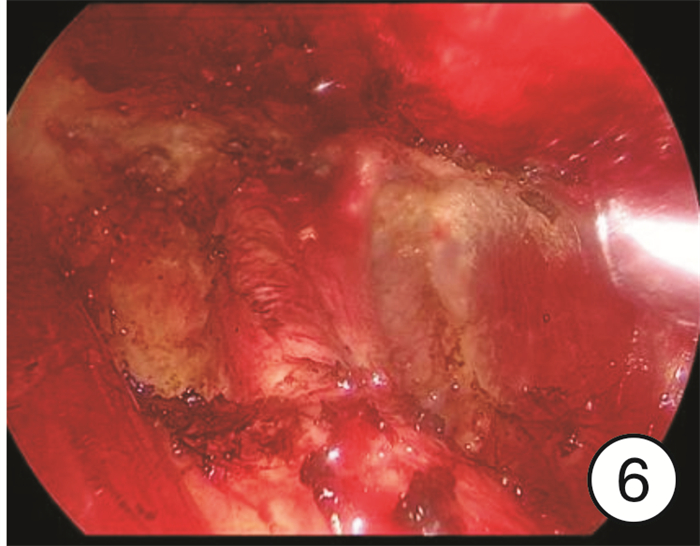
-
摘要: 目的 评估免充气自制悬吊技术实施腔镜下腹股沟淋巴结清扫术的安全性及可行性。方法 将2020年1月-2022年4月本单位拟行腹股沟淋巴结清扫手术的20例阴茎癌患者随机分为2组, 10例患者行免充气腔镜腹股沟淋巴结清扫术(免气组), 10例行常规腔镜腹股沟淋巴结清扫术(常规组)。收集分析患者年龄、体重指数(BMI)、淋巴结临床分期、住院时间、手术时间、出血量、引流管时间、淋巴结清扫数目和并发症等, 总结免充气腔镜淋巴结清扫手术临床应用的可行性及安全性。结果 2组患者年龄、BMI、临床淋巴结分期及住院时间比较差异均无统计学意义(P>0.05)。20例患者均顺利完成手术, 无中转开放手术, 免气组无改为常规腔镜手术。2组手术时间、出血量、引流管留置时间比较差异均无统计学意义(P>0.05)。免气组平均清扫淋巴结12(4~19)个, 常规组平均清扫淋巴结13(5~18)个, 差异无统计学意义。常规腔镜组有3例患者发生皮下气肿, 免气组无皮下气肿发生, 差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。常规组有1例患者出现伤口延迟愈合。免气组出现单侧下肢水肿1例, 保守治疗后缓解。术后常规组动脉血二氧化碳分压(PaCO2)高于免气组, 但差异无统计学意义。2组术后伤口疼痛评分差异无统计学意义。所有患者术中未出现大出血等严重并发症, 无皮肤感染、坏死、淋巴囊肿等并发症发生。术后随访6~24个月, 肿瘤均无复发或转移。结论 免充气腔镜腹股沟淋巴结清扫术可以获取充分的手术空间, 顺利完成手术, 治疗效果确切, 有效避免了传统腔镜手术CO2充气对身体的影响, 临床应用安全可行。
-
关键词:
- 免充气 /
- 腔镜腹股沟淋巴结清扫 /
- 阴茎癌
Abstract: Objective To evaluate the safety and feasibility of gasless video endoscopic inguinal lymphadenectomy (VEIL) with self-made suspension technology.Methods Twenty patients with penile cancer who underwent inguinal lymph node dissection in our unit from January 2020 to April 2022 were randomly divided into two groups: 10 patients underwent gasless VEIL (gasless group) and 10 patients underwent conventional VEIL (conventional group). The patients' age, BMI, clinical stage of lymph nodes, hospitalization time, operation time, bleeding volume, drainage tube retention time, number of lymph node dissection and complications were collected and analyzed to summarize the feasibility and safety of the clinical application of VEIL.Results There were no statistically significant differences in age, BMI, clinical lymph node staging or hospital stay between the two groups. All 20 patients were completed the surgery successfully without change to open surgery or no change to conventional endoscopy in the gasless group. The differences in operative time, bleeding volume, and drainage tube retention time between the two groups were not statistically significant (P>0.05). The mean number of lymph nodes cleared in the gasless group was 12(4-19), while the mean number of lymph nodes cleared in the conventional group was 13(5-18). The difference was not statistically significant. Subcutaneous emphysema occurred in three patients in the conventional group and none in the gasless group, and the difference was statistically significant (P < 0.05). One patient in the conventional group had delayed wound healing. One case of unilateral lower limb edema occurred in the gasless group, which recovered after conservative treatment. Postoperative arterial blood PaCO2 was higher in the conventional group than in the gasless group, but the difference was not statistically significant. The difference in postoperative wound pain scores between the two groups was not statistically significant. No serious complications such as hemorrhage occurred intraoperatively in all patients, and no complications such as skin infection, necrosis, or lymphatic cysts occurred. None of the tumors recurred or metastasized during the postoperative follow-up period of 6-24 months.Conclusion Gasless VEIL can obtain sufficient operation space, complete the operation smoothly, and provide a definite therapeutic effect. It effectively avoids the impact of CO2 inflation on the body in traditional laparoscopic surgery, so is safe and feasible in clinical applications.-
Key words:
- gasless /
- video endoscopic inguinal lymphadenectomy /
- penile cancer
-

-
表 1 常规组和免气组阴茎癌患者的一般情况
例(%),X±S 项目 免气组(10例) 常规组(10例) P值 年龄/岁 59.9±7.8 62.2±7.5 >0.05 BMI/(kg/m2) 25.3±4.5 24.9±6.3 >0.05 临床淋巴结分期 cN0 5(50.0) 6(60.0) >0.05 cN1 4(40.0) 3(30.0) >0.05 cN2 1(10.0) 1(10.0) >0.05 住院时间/d 13.5±4.4 14.2±3.4 >0.05 表 2 常规组和免气组的手术情况及并发症情况
例(%),X±S 项目 免气组
(10例)常规组
(10例)P值 手术时间/min 112.8±18.6 104.4±13.6 >0.05 术中出血/mL 20.2±14.1 17.2±10.9 >0.05 清扫的淋巴结数目/个 12(4~19) 13(5~18) >0.05 引流管留置时间/d 6(4~10) 7(4~12) >0.05 皮下气肿 0 3(30.0) < 0.05 伤口延迟愈合 1(10.0) 0 >0.05 下肢水肿 1(10.0) 0 >0.05 术后动脉血PaCO2/mmHg 37.8±3.5 42.2±2.4 >0.05 术后伤口疼痛评分/分 3.0±1.9 3.4±2.1 >0.05 -
[1] Leone A, Diorio GJ, Pettaway C, et al. Contemporary management of patients with penile cancer and lymph node metastasis[J]. Nat Rev Urol, 2017, 14(6): 335-347. doi: 10.1038/nrurol.2017.47
[2] Teh J, Duncan C, Qu L, et al. Inguinal lymph node dissection for penile cancer: a contemporary review[J]. Transl Androl Urol, 2020, 9(6): 3210-3218. doi: 10.21037/tau.2019.08.37
[3] 卜国峰, 修子超, 邵翠华, 等. 影响阴茎癌患者术后预后危险因素的研究[J]. 临床泌尿外科杂志, 2020, 35(6): 426-430. https://lcmw.chinajournal.net.cn/WKC/WebPublication/paperDigest.aspx?paperID=f6c91c26-9a7c-42eb-90d3-4ce053010c16
[4] Yadav SS, Tomar V, Bhattar R, et al. Video Endoscopic Inguinal Lymphadenectomy vs Open Inguinal Lymphadenectomy for Carcinoma Penis: Expanding Role and Comparison of Outcomes[J]. Urology, 2018, 113: 79-84. doi: 10.1016/j.urology.2017.11.007
[5] Tobias-Machado M, Tavares A, Ornellas AA, et al. Video endoscopic inguinal lymphadenectomy: a new minimally invasive procedure for radical management of inguinal nodes in patients with penile squamous cell carcinoma[J]. J Urol, 2007, 177(3): 953-957;discussion 958. doi: 10.1016/j.juro.2006.10.075
[6] 李升, 吴铁林, 许建挺, 等. 阴茎癌腹腔镜与开放术式腹股沟淋巴结清扫的效果比较[J]. 浙江医学, 2020, 42(24): 2675-2677. doi: 10.12056/j.issn.1006-2785.2020.42.24.2020-2349
[7] Kumar V, Sethia KK. Prospective study comparing video-endoscopic radical inguinal lymph node dissection(VEILND)with open radical ILND(OILND)for penile cancer over an 8-year period[J]. BJU Int, 2017, 119(4): 530-534. doi: 10.1111/bju.13660
[8] 杨勇飞, 梁朝朝. 腹腔镜手术腹腔内与腹膜后二氧化碳充气对机体影响[J]. 国际泌尿系统杂志, 2007, 27(3): 375-378. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1673-4416.2007.03.025
[9] 戴君勇, 唐显力, 刘南, 等. 低气压腔镜腹股沟淋巴结清扫术在阴茎癌治疗中的应用[J]. 临床泌尿外科杂志, 2021, 36(5): 362-365, 370. https://lcmw.chinajournal.net.cn/WKC/WebPublication/paperDigest.aspx?paperID=101b5add-e9e3-4bb6-8a22-13aa1e3e01dc
[10] 张昊, 姜元军, 刘涛. 顺行性腹腔镜下腹股沟淋巴结清扫术14例经验总结[J/OL]. 中华腔镜泌尿外科杂志(电子版), 2021, 15(4): 317-320.
[11] O'Brien JS, Perera M, Manning T, et al. Penile Cancer: Contemporary Lymph Node Management[J]. J Urol, 2017, 197(6): 1387-1395. doi: 10.1016/j.juro.2017.01.059
[12] 时佳子, 贲亮亮, 房晓, 等. 单术者腹腔镜保留大隐静脉的腹股沟淋巴结清扫术经验总结[J]. 中国男科学杂志, 2020, 34(2): 50-52. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NXXX202002010.htm
-

| 引用本文: | 陈金虎, 颜雷, 骆广跃, 等. 免充气腔镜下腹股沟淋巴结清扫术的临床应用[J]. 临床泌尿外科杂志, 2023, 38(7): 483-486. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.1001-1420.2023.07.001 |
| Citation: | CHEN Jinhu, YAN Lei, LUO Guangyue, et al. Clinical application of gasless video endoscopic inguinal lymphadenectomy[J]. J Clin Urol, 2023, 38(7): 483-486. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.1001-1420.2023.07.001 |
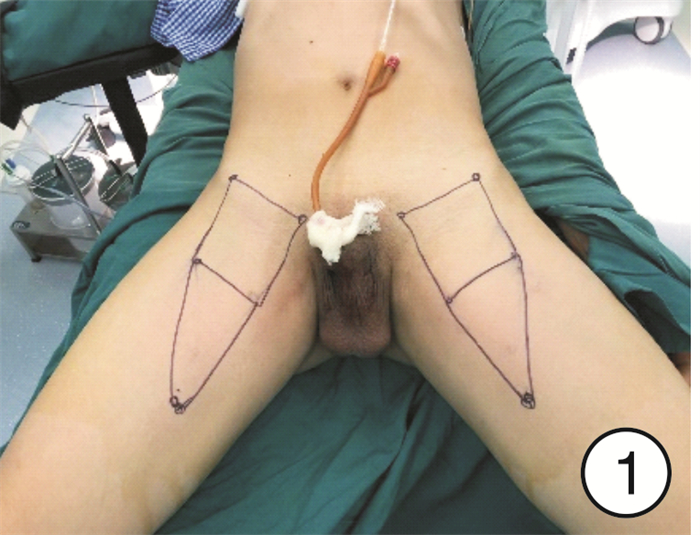
- Figure 1.
- Figure 2.
- Figure 3.
- Figure 4.
- Figure 5.
- Figure 6.



 下载:
下载: