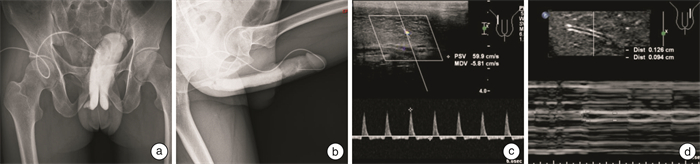
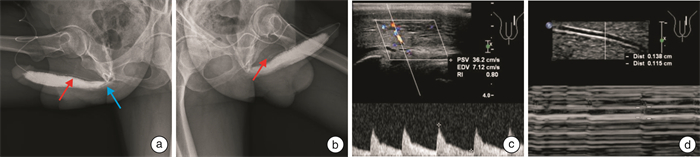
Application of diastolic contraction ratio of cavernous artery in ultrasonic diagnosis of arterial penile erectile dysfunction
-
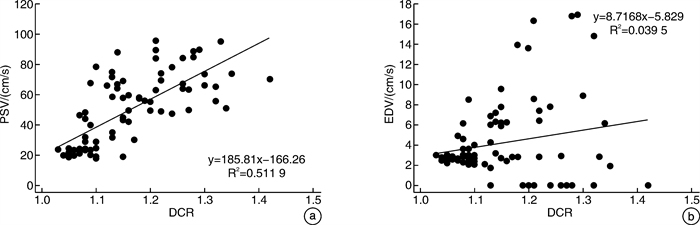
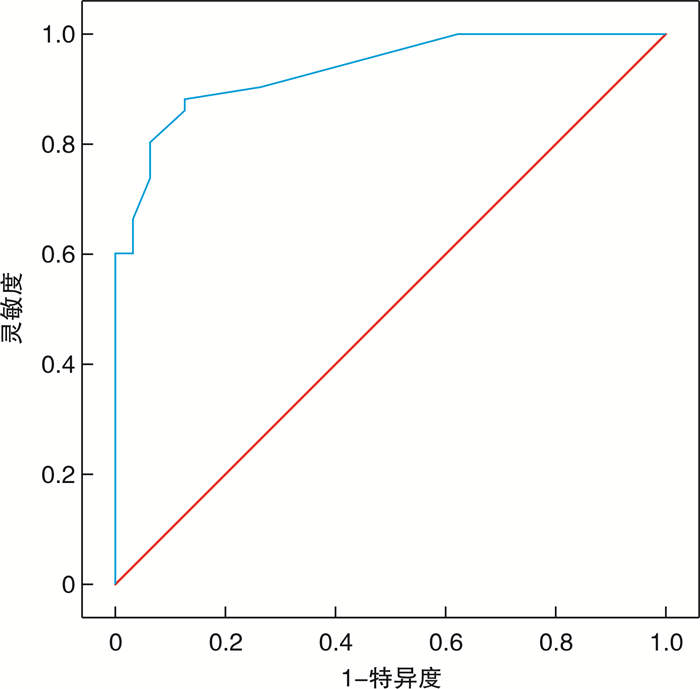
摘要: 目的 探讨阴茎双功能多普勒超声(penile duplex doppler ultrasound, PDDU)新指标海绵体动脉管径舒缩比值(diastolic contraction ratio, DCR)在动脉型阴茎勃起功能障碍(erectile dysfunction, ED)分型诊断中的价值。方法 将2018年7月-2021年12月来我院行PDDU检查并经阴茎海绵体动脉或静脉造影确诊分型的ED患者, 分为动脉型组(32例)、静脉型组(25例)和非血管性组(25例)。注射药物后在阴茎达到最大硬度时测量双侧阴茎海绵体动脉收缩期管径(a)、舒张期管径(b)、b/a(DCR)和收缩期峰速(PSV)、舒张末期峰速(EDV)、阻力指数(RI)等参数, 探讨各组DCR差异性及DCR在动脉型ED中的诊断界值及准确率。结果 应用PDDU传统标准正确诊断动脉型ED 27例和静脉型ED 21例, 血管性ED分型诊断的灵敏度、特异度和准确率分别为77.1%、89.4%和84.4%。动脉型组DCR值显著低于静脉型组和非血管型组(均P < 0.05), 而静脉型组与非血管型组间DCR值差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。DCR值与PSV呈正相关(r=0.51, P < 0.05)。将DCR≤1.11作为诊断阴茎海绵体动脉功能不良的标准时, 诊断灵敏度、特异度分别为88.0%和87.5%(AUC=0.934), 与传统PDDU诊断标准比较, 灵敏度更高(P < 0.05), 特异度无明显差异(P>0.05)。结论 DCR可作为ED患者PDDU分型诊断的新参数, DCR≤1.1作为动脉型ED的诊断标准, 其诊断准确率高于PDDU诊断。
-
关键词:
- 勃起功能障碍 /
- 阴茎双功能多普勒超声 /
- 阴茎海绵体注射血管活性药物试验 /
- 动脉硬化
Abstract: Objective To investigate the value of the new index of penile duplex doppler ultrasound(PDDU), cavernous artery diameter diastolic contraction ratio(DCR), in the diagnosis of arterial erectile dysfunction(ED).Methods ED patients who came to our hospital from July 2018 to December 2021 for PDDU examination and were confirmed by penile cavernous artery or venography were divided into arterial group(n=32), venous group(n=25) and non-vascular group(n=25). Systolic tube diameter(A), diastolic tube diameter(B), B/A(DCR), systolic peak velocity(PSV), end diastolic peak velocity(EDV), resistance index(RI) and other parameters of bilateral penile cavernous artery were measured when the penis reached the maximum hardness after injection. The differences of DCR in each group and the diagnostic cutoff value and accuracy of DCR in arterial ED were investigated.Results Twenty-seven cases of arterial ED and 21 cases of venous ED were correctly diagnosed by PDDU. The sensitivity, specificity and accuracy of vascular ED were 77.1%, 89.4% and 84.4%, respectively. The DCR value of patients with arterial ED was significantly lower than that of the venous group and the non-vascular group(P < 0.05), but there was no statistical significance in the DCR value between the venous group and the non-vascular group(P>0.05). DCR value was positively correlated with PSV(r=0.51, P < 0.05). When DCR≤1.11 was used as the standard for diagnosis of penile cavernous artery dysfunction, the sensitivity and specificity were 88.0% and 87.5%(AUC=0.934). Compared with the traditional diagnostic criteria of PDDU, the sensitivity was higher(P < 0.05), and the specificity was not significantly different(P>0.05).Conclusion DCR can be used as a new parameter for the classification and diagnosis of PDDU in ED patients. DCR≤1.11 is a diagnostic criterion for arterial ED, and its diagnostic accuracy is higher than that of PDDU. -

-
表 1 各组患者临床指标测量结果
例(%),X±S 指标 动脉型组
(32例)静脉型组
(25例)非血管型组
(25例)年龄/岁 31.8±9.8 25.2±6.1 27.4±8.6 病程/周 35.6±11.7 28.7±10.6 20.4±6.3 IIEF-5评分/分 12±2 15±4 17±5 ICI最大硬度 Ⅰ~Ⅲ Ⅱ~Ⅳ Ⅱ~Ⅳ IBM/(kg/m2) 25.1±5.7 22.3±4.8 22.6±4.1 糖尿病 5(15.6) 3(12.0) 2(8.0) 高血压 9(28.1) 6(24.0) 4(16.0) 服用PDE5Is 14(43.8) 8(32.0) 9(36.0) 表 2 各组患者PDDU测量结果
X±S 指标 动脉型组
(32例)静脉型组
(25例)非血管型组
(25例)PSV/(cm/s) 23.4±4.2 63.5±14.1 66.2±16.3 EDV/(cm/s) 2.8±0.8 8.4±3.9 1.5±1.8 RI 0.87±0.03 0.86±0.07 0.98±0.03 a/mm 0.95±0.13 1.06±0.10 1.05±0.14 b/mm 1.02±0.11 1.28±0.16 1.26±0.17 DCR 1.08±0.03 1.20±0.08 1.21±0.09 表 3 应用PDDU传统标准的诊断结果
例 组别 传统PDDU分型诊断 合计 动脉型 可疑动脉型 静脉型 可疑静脉型 非血管型 动脉型组 27 3 1 1 0 32 静脉型组 0 0 21 2 2 25 非血管型组 0 0 2 2 21 25 合计 27 3 24 5 23 82 -
[1] Salonia A, Bettocchi C, Boeri L, et al. European Association of Urology Guidelines on Sexual and Reproductive Health-2021 update: Male sexual dysfunction[J]. Eur Urol, 2021, 80(3): 333-357. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2021.06.007
[2] Capogrosso P, Ventimiglia E, Boeri L, et al. Age at First Presentation for Erectile Dysfunction: Analysis of Changes over a 12-yr Period[J]. Eur Urol Focus, 2019, 5(5): 899-905. doi: 10.1016/j.euf.2018.02.006
[3] Guo LQ, Liu YQ, Sun WD, et al. Significance of platelet distribution width as a severity marker of erectile dysfunction[J]. Andrologia, 2017, 49(3): e12628. doi: 10.1111/and.12628
[4] McCabe MP, Sharlip ID, Lewis R, et al. Incidence and prevalence of sexual dysfunction in women and men: a consensus statement from the Fourth International Consultation on Sexual Medicine 2015[J]. J Sex Med, 2016, 13(2): 144-152. doi: 10.1016/j.jsxm.2015.12.034
[5] Speel TGW, van Langen H, Wijkstra H, et al. Penile duplex pharmaco-ultrasonography revisited: Revalidation of the parameters of the cavernous arterial response[J]. J Urol, 2003, 169(1): 216-220. doi: 10.1016/S0022-5347(05)64071-2
[6] 贾慧军, 庞雪芹, 宋悦, 等. 药物性阴茎双功能超声在诊断双干背深静脉漏中的价值2019[J]. 临床泌尿外科杂志, 2019, 34(10): 782-790. https://lcmw.chinajournal.net.cn/WKC/WebPublication/paperDigest.aspx?paperID=c42b2fa0-e627-4930-b898-9a6a716a0664
[7] Aversa A, Crafa A, Greco EA, et al. The penile duplex ultrasound: How and when to perform it?[J]. Andrology, 2021, 9(5): 1457-1466. doi: 10.1111/andr.13029
[8] Sikka SC, Hellstrom WJ, Brock G, el a1. Standardization of vascular assessment of erectile dysfunction: Standardoperating procedures for duplex ultrasound[J]. J Sex Med, 2013, 10(1): 120-129. doi: 10.1111/j.1743-6109.2012.02825.x
[9] Nascimento B, Miranda EP, Terrier JE, et al. A Critical Analysis of Methodology Pitfalls in Duplex Doppler Ultrasound in the Evaluation of Patients With Erectile Dysfunction: Technical and Interpretation Deficiencies[J]. J Sex Med, 2020, 17(8): 1416-1422. doi: 10.1016/j.jsxm.2020.05.023
[10] 石臣坤, 智二磊, 陈慧兴, 等. 可膨胀性人工海绵体植入术储水囊放置方法改良30例报告2022[J]. 临床泌尿外科杂志, 2022, 37(5): 359-363. https://lcmw.chinajournal.net.cn/WKC/WebPublication/paperDigest.aspx?paperID=679effb0-d815-46ae-96ad-e6b4a52a3e50
[11] Arthur L Burnett. Commentary RE: The international index of erectile function(ⅡEF): a multidimensional scale for assessment of erectile dysfunction[J]. Urology, 2020, 11(145): 308-309.
[12] Pagano MJ, Stahl PJ. Variation in Penile Hemodynamics by Anatomic Location of Cavernosal Artery Imaging in Penile Duplex Doppler Ultrasound[J]. J Sex Med, 2015, 12(9): 1911-1919. doi: 10.1111/jsm.12958
[13] Wang J, Wang J, Liu Q, et al. Time-effect of Penile Color Duplex Doppler Ultrasound for Diagnosing Vascular Erectile Dysfunction, 2020[J]. Med Ultrason, 2020, 22(1): 37-42.
[14] Bassiem MA, Ismail IY, Salem TA, et al. Effect of Intracavernosal Injection of Prostaglandin E1 on Duration and Rigidity of Erection in Patients With Vasculogenic Erectile Dysfunction: Is It Dose Dependent?[J]. Urology, 2021, 148: 173-178. doi: 10.1016/j.urology.2020.09.030
[15] Sikka SC, Hellstrom WJG, Brock G, et al. Standardization of Vascular Assessment of Erectile Dysfunction Standard Operating Procedures for Duplex Ultrasound[J]. J Sex Med, 2013, 10(1): 120-129. doi: 10.1111/j.1743-6109.2012.02825.x
[16] Dean RC, Lue TF. Physiology of penile erection and pathophysiology of erectile dysfunction, 2005[J]. Urol Clin North Am, 2005, 32(4): 379-395. doi: 10.1016/j.ucl.2005.08.007
[17] Clement P, Giuliano F. Anatomy and physiology of genital organs-men[J]. Handb Clin Neurol, 2015, 130: 19-37.
[18] Gandaglia G, Briganti A, Montorsi P, et al. Diagnostic and therapeutic implications of erectile dysfunction in patients with cardiovascular disease, 2016[J]. Eur Urol, 2016, 70(2): 219-222. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2016.01.054
[19] Uddin SMI, Mirbolouk M, Dardari Z, et al. Erectile Dysfunction as an Independent Predictor of Future Cardiovascular Events: The Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis[J]. Circulation, 2018, 138(5): 540-542. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.118.033990
[20] Azab SS, El Din Hosni H, El Far TA, et al. The Predictive Value of Arteriogenic Erectile Dysfunction for Coronary Artery Disease in Men[J]. J Sex Med, 2018, 15(6): 880-887. doi: 10.1016/j.jsxm.2018.04.639
[21] Li M, Ma Z, Zhang XL, et al. Significance of blood lipid parameters as effective markers for arteriogenic erectile dysfunction[J]. Andrology, 2020, 8(5): 1086-1094. doi: 10.1111/andr.12776
[22] Wang XS, Guo LQ, Xiao ZY, et al. Mean platelet volume might be an effective indicator of arterial erectile dysfunction[J]. Asian J Androl, 2018, 21(1): 62-66.
[23] Caretta N, De Rocco Ponce M, Minicuci N, et al. Penile doppler ultrasound predicts cardiovascular events in men with erectile dysfunction[J]. Andrology, 2019, 7(1): 82-87. doi: 10.1111/andr.12561
[24] Lue TF, Hricak H, Marich KW, et al. Vasculogenic impotence evaluated by hig-resolution ultrasonography and pulsed Doppler spectrum analysis[J]. Radiology, 1985, 155(3): 777-781. doi: 10.1148/radiology.155.3.3890009
[25] Aversa A, Crafa A, Greco EA, et al. The penile duplex ultrasound: How and when to perform it?[J]. Andrology, 2021, 9(5): 1457-1466. doi: 10.1111/andr.13029
[26] Chiou RK, Pomeroy BD, Chen WS, et al. Hemodynamic patterns ofpharmacologically induced erection: evaluation bycolor Doppler sonography[J]. J Urol, 1998, 159(1): 109-112. doi: 10.1016/S0022-5347(01)64028-X
[27] Bertolotto M, Campo I, Sachs C, et al. Sonography of the penis/erectile dysfunction[J]. Abdom Radiol(NY), 2020, 45(7): 1973-1989. doi: 10.1007/s00261-020-02529-z
[28] Yildirim D, BozkurT IH, Gurses B. A new parameter in the diagnosis of vascular erectile dysfunction with penile Doppler ultrasound: cavernous artery ondulation index[J]. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci, 2013, 17(10): 1382-1388.
[29] Del Corso L, Moruzzo D, Conte B. Tortuosity, kinking, and coiling of the carotid artery: expression of atherosclerosis or aging?[J]. Angiology, 1998, 49(5): 361-371. doi: 10.1177/000331979804900505
[30] Zhang JS, Zhou W, Zhang YY, et al. A Novel Methodsto Quantify Penile Arterial Blood Supply Using Shear Wave Elastography During Penile Duplex Ultrasound in Men with Erectile Dysfunction[J]. Med Sci Monit, 2022, 28: e935232.
[31] 邓京平, 白文俊, 毛迅. 血管性勃起功能障碍患者阴茎血流动力学的变化2005[J]. 中国男科学杂志, 2005, 19(2): 42-44. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NXXX200608013.htm
-




 下载:
下载: