Analysis of risk factors for urinary tract infection after flexible ureteroscopic lithotripsy and construction of predictive model
-
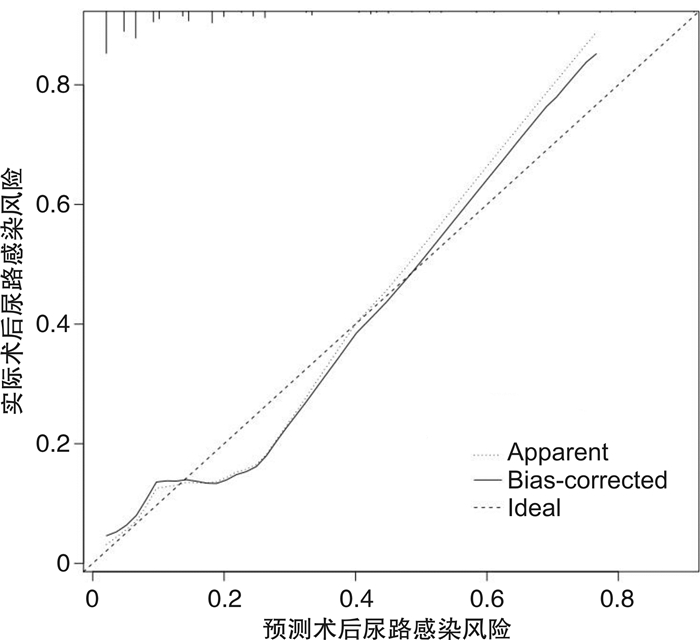
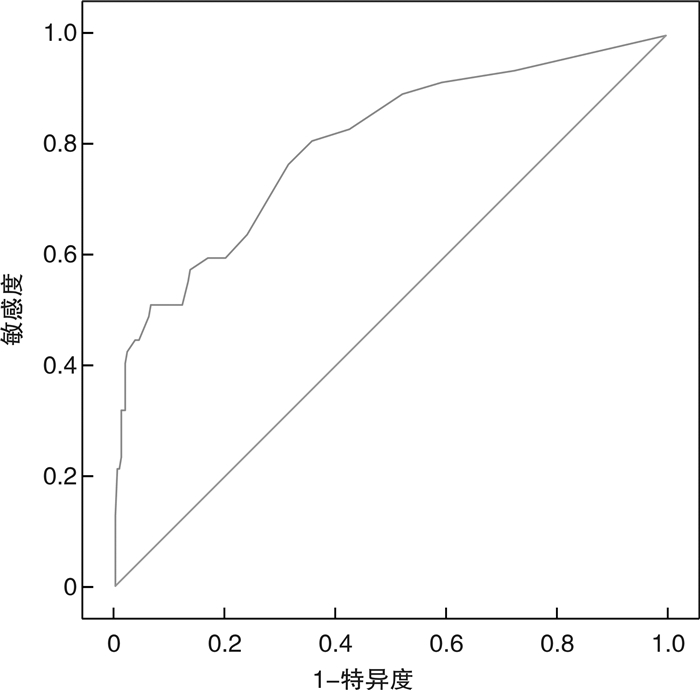
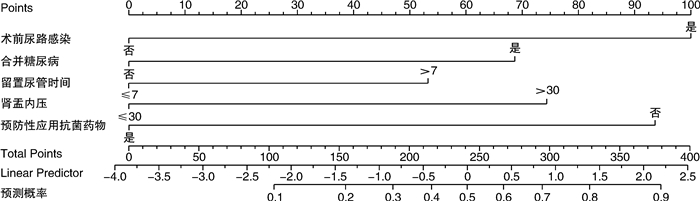
摘要: 目的 分析影响输尿管软镜碎石术后尿路感染的危险因素,建立列线图预测模型。方法 采用便利抽样法,选取2019年4月—2021年7月阜南县人民医院收治的327例行输尿管软镜碎石术患者为研究对象,根据术后30 d内是否发生尿路感染分为感染组与未感染组,采用多因素logistics回归模型筛选术后尿路感染的独立影响因素,基于独立影响因素建立列线图预测模型,并评估模型的区分度与准确度。结果 输尿管软镜碎石术患者术后尿路感染发生率为14.37%(47/327);多因素logistic回归分析显示,术前尿路感染、合并糖尿病、留置尿管时间>7 d、肾盂内压>30 mmHg为影响术后尿路感染的独立危险因素(P < 0.05),预防性应用抗菌药物为保护性因素(P < 0.05);基于输尿管软镜碎石术后尿路感染的独立影响因素建立列线图预测模型,内部验证结果显示列线图模型的校准曲线预测值与实际值基本一致,Hosmer-Lemeshow拟合优度检验χ2=8.199,P=0.315,ROC曲线下面积为0.805(95%CI:0.729~0.877),DCA曲线分析阈值范围为0.05~0.85,模型具有正的净收益。结论 输尿管软镜碎石术后尿路感染的列线图预测模型具有良好的预测效能与临床实用价值,能够帮助医护人员尽早将尿路感染的高危人群筛选出来,从而制定针对性的防治措施。Abstract: Objective To analyze the risk factors of urinary tract infection after flexible ureteroscopic lithotripsy and to establish a nomogram prediction model.Methods Using convenience sampling method, 327 patients treated with flexible ureteroscopic lithotripsy admitted to our hospital from April 2019 to Jul 2021 were selected as the research objects. According to whether urinary tract infection occurred within 30 days after operation, they were divided into infection group and non-infection group. The independent influencing factors of postoperative urinary tract infection were screened by a multivariate logistics regression model, a nomogram prediction model was established based on independent influencing factors, and the discrimination and accuracy of the model were evaluated.Results The incidence of postoperative urinary tract infection in patients undergoing flexible ureteroscopic lithotripsy was 14.37% (47/327). Multivariate logistic regression analysis showed that preoperative urinary tract infection, diabetes mellitus, indwelling catheter time > 7 days, intrapelvic pressure > 30 mmHg were independent risk factors affecting postoperative urinary tract infection (P < 0.05), and preventive use of antibiotics was a protective factor (P < 0.05). Then, a nomogram prediction model was established based on the independent influencing factors of urinary tract infection after flexible ureteroscopic lithotripsy. The internal verification results showed that the predicted value of the calibration curve of the nomogram model was basically consistent with the actual value, Hosmer-Lemeshow goodness of fit test showed χ2=8.199, P=0.315, and the area under the ROC curve was 0.805 (95CI: 0.729-0.877). The DCA curve analysis threshold range was between 0.05 and 0.85. The model has a positive net income.Conclusion The nomogram prediction model of urinary tract infection after flexible ureteroscopic lithotripsy has good predictive performance and clinical practical value, and can help medical staff to screen out high-risk groups of urinary tract infections as soon as possible, so as to formulate targeted prevention and treatment measures.
-

-
表 1 影响输尿管软镜碎石术后尿路感染单因素分析
例(%) 组别 例数 感染组(n=47) 未感染组(n=280) t/χ2 P值 性别 0.556 0.456 男 197 26(55.32) 171(61.07) 女 130 21(44.68) 109(38.93) 年龄/岁 2.877 0.099 ≤60 190 22(46.81) 168(60.00) >60 137 25(53.19) 112(40.00) BMI/(kg·m-2) 2.609 0.106 < 24 132 24(51.06) 108(38.57) ≥24 195 23(48.94) 172(61.43) 结石部位 0.083 0.773 肾结石 126 19(40.43) 107(38.21) 输尿管结石 201 28(59.57) 173(61.79) 结石位置 0.340 0.560 左侧 113 18(38.30) 95(33.93) 右侧 214 29(61.70) 185(66.07) 术前尿路感染 17.050 < 0.001 否 261 27(57.45) 234(83.57) 是 66 20(42.55) 46(16.43) 结石直径/cm 1.304 0.254 ≤1 185 23(48.94) 162(57.86) >1 142 24(51.06) 118(42.14) 感染性结石 2.746 0.097 否 222 27(57.45) 195(69.64) 是 105 20(42.55) 85(30.36) 合并高血压 1.115 0.291 否 243 32(68.09) 211(75.36) 是 84 15(31.91) 69(24.64) 合并糖尿病 6.975 0.008 否 251 29(61.70) 222(79.29) 是 76 18(38.30) 58(20.71) 留置尿管时间/d 4.563 0.033 ≤7 212 24(51.06) 188(67.14) >7 115 23(48.94) 92(32.86) 手术时间/min 2.641 0.104 ≤60 147 16(34.04) 131(46.79) >60 180 31(65.96) 149(53.21) 肾盂内压/mmHg 14.797 < 0.001 ≤30 219 20(42.55) 199(71.07) >30 108 27(57.45) 81(28.93) 预防性应用抗菌药物 9.024 0.003 否 60 16(34.04) 44(15.71) 是 267 31(65.96) 236(84.29) 广谱抗生素种类 1.606 0.658 青霉素 82 7(22.58) 75(31.78) 头孢菌素 73 11(35.48) 62(26.27) 氨基糖苷类 69 8(25.81) 61(25.85) 其他 43 5(16.13) 38(16.10) 术后抗感染时间/h 1.268 0.260 ≤48 120 11(35.48) 109(46.19) >48 147 20(64.52) 127(53.81) 住院时间/d 2.767 0.096 ≤10 196 23(48.94) 173(61.79) >10 131 24(51.06) 107(38.21) 表 2 影响输尿管软镜碎石术后尿路感染多因素logistic回归分析
因素 β SE Wald(χ2) P值 OR 95%CI 下限 上限 术前尿路感染 1.596 0.377 17.954 < 0.001 4.931 2.357 10.315 合并糖尿病 1.098 0.380 8.343 0.004 2.997 1.423 6.312 留置尿管时间 0.851 0.363 5.510 0.019 2.343 1.151 4.768 肾盂内压 1.187 0.366 10.524 0.001 3.277 1.600 6.713 预防性应用抗菌药物 -1.494 0.403 13.723 < 0.001 0.224 0.102 0.495 常量 -2.356 0.436 29.164 < 0.001 0.095 -
[1] 张微雯, 计安东, 段超杰, 等. 辽宁地区尿路结石患者结石成分及相关因素分析[J]. 现代预防医学, 2020, 47(7): 178-182. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDYF202007044.htm
[2] Rodger F, Roditi G, Aboumarzouk OM. Diagnostic Accuracy of Low and Ultra-Low Dose CT for Identification of Urinary Tract Stones: A Systematic Review[J]. Urol Int, 2018, 100(4): 375-385. doi: 10.1159/000488062
[3] 高让, 廖邦华, 陈云天, 等. 输尿管软镜钬激光碎石取石术治疗大于2 cm上尿路结石的疗效及安全性分析[J]. 重庆医科大学学报, 2018, 43(4): 57-61. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYK201804012.htm
[4] Zhong F, Alberto G, Chen G, et al. Endourologic strategies for a minimally invasive management of urinary tract stones in patients with urinary diversion[J]. Int Braz J Urol, 2018, 44(1): 75-80. doi: 10.1590/s1677-5538.ibju.2017.0431
[5] 杨超, 姚俊, 张双洋. 上尿路结石患者行输尿管软镜钬激光碎石术后院内感染发生的相关因素分析[J]. 河北医学, 2019, 25(5): 816-820. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6233.2019.05.26
[6] 徐建华, 杨元强, 李巍, 等. 肾结石输尿管软镜碎石术后尿路感染病原菌分布特点及危险因素分析[J]. 疑难病杂志, 2020, 19(12): 34-37, 41. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YNBZ202012008.htm
[7] 尿路感染诊断与治疗中国专家共识编写组. 尿路感染诊断与治疗中国专家共识(2015版)-复杂性尿路感染[J]. 中华泌尿外科杂志, 2015, 36(4): 241-242.
[8] 杨嗣星, 郑府, 柯芹, 等. 软性输尿管镜碎石术中肾盂内压力监测方法及意义[J]. 中华泌尿外科杂志, 2014, 35(8): 575-578. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1000-6702.2014.08.004
[9] 陈亮, 刘勇, 刘强, 等. 输尿管软镜治疗输尿管结石患者术后感染高危因素分析[J]. 中国性科学, 2020, 29(10): 118-121. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XKXZ202010032.htm
[10] Zheng J, Wang Y, Chen B, et al. Risk factors for ureteroscopic lithotripsy: a case-control study and analysis of 385 cases of holmium laser ureterolithotripsy[J]. Wideochir Inne Tech Maloinwazyjne, 2020, 15(1): 185-191.
[11] Baboudjian M, Gondran-Tellier B, Abdallah R, et al. Predictive risk factors of urinary tract infection following flexible ureteroscopy despite preoperative precautions to avoid infectious complications[J]. World J Urol, 2020, 38(5): 1253-1259. doi: 10.1007/s00345-019-02891-8
[12] 焦志灵, 徐国良, 李路鹏, 等. 经尿道输尿管镜钬激光碎石术后尿路感染调查及其对预后的影响[J]. 临床泌尿外科杂志, 2020, 35(5): 344-348. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCMW202005003.htm
[13] Yamashita S, Kohjimoto Y, Higuchi M, et al. Postoperative Progress after Stone Removal Following Treatment for Obstructive Acute Pyelonephritis Associated with Urinary Tract Calculi: A Retrospective Study[J]. Urol J, 2020, 17(2): 118-123.
[14] Kaygısız O, Satar N, Güneş A, et al. Factors predicting postoperative febrile urinary tract infection following percutaneous nephrolithotomy in prepubertal children[J]. J Pediatr Urol, 2018, 14(5): 448. e1-448. e7.
[15] 李天, 朱柏珍, 李逊, 等. 上尿路结石患者输尿管软镜钬激光碎石术后感染状况研究[J]. 中华医院感染学杂志, 2018, 28(3): 432-436. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHYY201803030.htm
[16] Bai T, Yu X, Qin C, et al. Identification of Factors Associated with Postoperative Urosepsis after Ureteroscopy with Holmium: Yttrium-Aluminum-Garnet Laser Lithotripsy[J]. Urol In, 2019, 103(3): 311-317.
[17] Kazan HO, Cakici MC, Efiloglu O, et al Clinical characteristics of postoperative febrile urinary tract infections after ureteroscopic lithotripsy in diabetics: Impact of glycemic control[J]. Arch Esp Urol, 2020, 73(7): 634-642.
[18] 孙莹, 江娟, 王钰, 等. 输尿管软镜碎石术后尿路感染的危险因素及血清IL-8、TNF-α、CD4+CD8+T细胞研究[J]. 中华医院感染学杂志, 2020, 30(7): 1086-1090. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHYY202007028.htm
[19] 钱冲, 党博文, 谭宝飞, 等. 输尿管软镜术肾盂内压的测定与术后发热的关系[J]. 局解手术学杂志, 2018, 27(5): 342-346. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JJXZ201805008.htm
[20] 季健, 普超, 朱元全, 等. 低压重力滴注法与灌注泵灌注法在经皮肾镜取石术中肾盂输尿管内压及感染相关指标的对比[J]. 昆明医科大学学报, 2018, 39(2): 104-107. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KMYX201802023.htm
[21] 程传宇, 郝建伟, 武玉东, 等. HIV感染肾结石患者行输尿管软镜钬激光碎石术后发生尿路感染的危险因素分析[J]. 中华泌尿外科杂志, 2019, 40(9): 690-694.
-




 下载:
下载: