-
摘要: 目的 探讨原发性肾上腺淋巴瘤(PAL)临床特征及预后分析。方法 回顾性分析郑州大学第一附属医院2010年5月—2018年9月收治的28例PAL患者的相关资料,采用Kaplan-Meier曲线进行生存分析,并总结影响预后的临床因素。结果 男15例,女13例,男女比例1.15︰1.00;年龄23~77岁,中位年龄60岁;肿瘤最大层面17~175 mm,中位肿瘤最大层面61 mm;出现肾上腺皮质功能减低17例,出现B症状16例。总随访时间2~75个月,中位随访时间33个月;1年总生存率为53.6%,3年总生存率为46.4%;单因素分析治疗方法(P=0.019)、肾上腺皮质功能减低(P=0.018)、疗效是否完全缓解(CR)(P<0.001)、是否进行化疗(P=0.007)、B症状(P=0.031),是影响PAL患者生存时间的因素。结论 PAL是一种非常罕见的实体恶性肿瘤,进展快,Cox多因素分析结果显示化疗(OR=0.101,P=0.008)、疗效CR(OR=0.198,P=0.020)是影响PAL患者生存时间的独立因素。Abstract: Objective To investigate the clinical features and prognosis of primary adrenal lymphoma (PAL).Methods We retrospectively analyzed the relevant data of 28 PAL patients admitted to First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University from May 2010 to September 2018. The Kaplan-Meier method was used for survival analysis, and the clinical factors affecting the prognosis were analyzed.Results There were 15 males and 13 females. The male-to-female ratio was 1.15∶1.00, aged 23-77 years old, with a median age of 60 years. The largest tumor size was 17-175 mm, and the median tumor largest size was 61 mm. The adrenal cortex function decreased in some cases. Of 17 cases, 16 cases had B symptoms. The total follow-up time was 2-75 months, and the median follow-up time was 33 months. The 1-year overall survival rate was 53.6%, and the 3-year overall survival rate was 46.4%. Univariate analysis showed treatment method (P=0.019), adrenal cortex function reduction (P=0.018), complete response (CR) or not (P < 0.001), receiving chemotherapy or not (P=0.007), and B symptoms (P=0.031) were factors that affect the survival time of patients with PAL.Conclusion PAL is a very rare solid malignant tumor with rapid progress. Cox multivariate analysis showed that chemotherapy (OR=0.101, P=0.008) and therapeutic effect of CR (OR=0.198, P=0.020) are the influence independent factors for survival time of PAL patients.
-
Key words:
- primary adrenal lymphoma /
- clinical features /
- survival analysis /
- prognosis
-

-
表 1 PAL患者临床特征及预后单因素分析
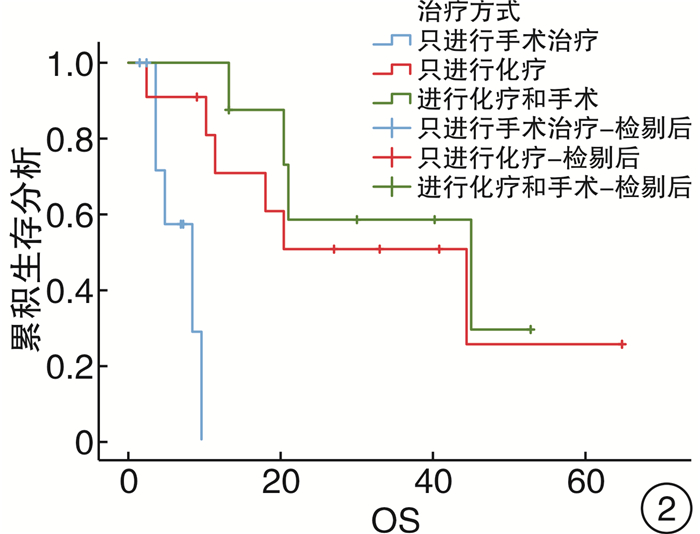
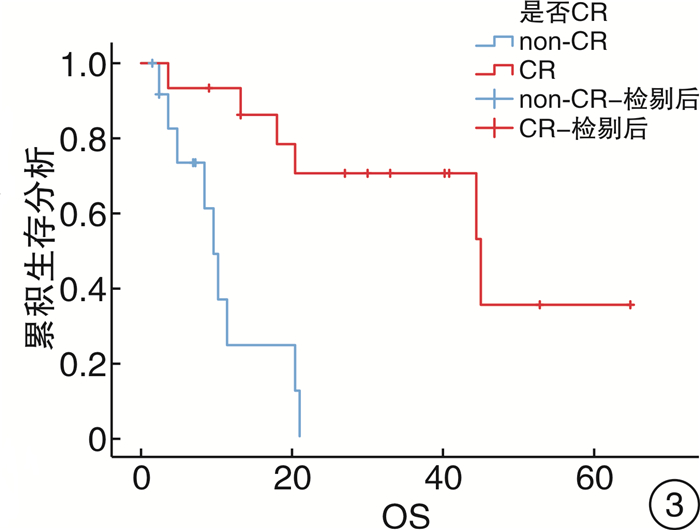
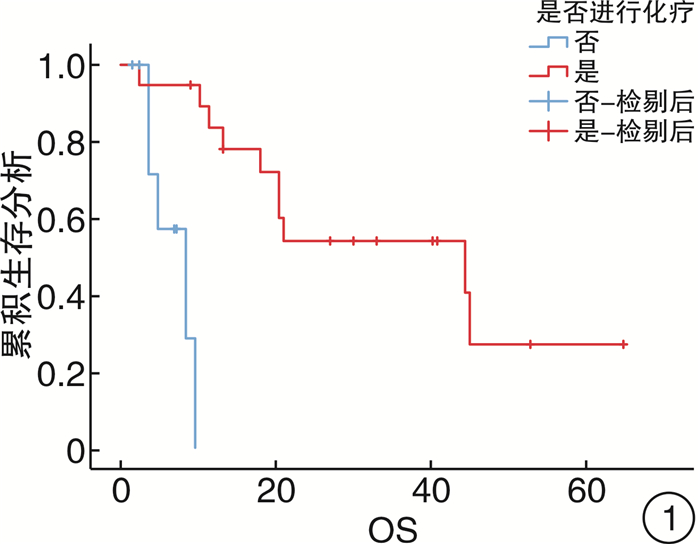
项目 例数 百分率/% χ2 P值 95%CI 性别 0.080 0.778 (0.260~5.886) 男 15 53.6 女 13 46.4 年龄 1.673 0.196 (0.051~1.904) ≤60岁 10 35.7 >60岁 18 64.3 确诊方式 2.489 0.115 (0.703~19.120) 穿刺 11 39.3 手术 17 60.7 是否有高血压 0.033 0.856 (0.220~1.199) 否 19 67.9 是 9 32.1 病灶 0.562 0.453 (0.104~2.765) 单侧 11 39.3 双侧 17 60.7 是否生发中心来源a) 2.424 0.119 (0.038~1.514) 否 14 63.6 是 8 36.4 乳酸脱氢酶 4.489 0.175 (0.503~25.120) 否 14 50.0 是 14 50.0 是否出现AI 6.152 0.018 (1.419~47.016) 否 11 39.3 是 17 60.7 病理类型 4.836 0.305 - 间变性大细胞淋巴瘤 1 3.6 弥漫大B细胞淋巴瘤 22 78.6 小B细胞淋巴瘤 1 3.6 间变性大细胞淋巴瘤(ALK阴性) 1 3.6 NK/T细胞淋巴瘤 3 10.7 疗效是否CR 13.481 <0.001 (0.004~0.430) non-CR 13 46.4 CR 15 53.6 是否进行化疗 7.368 0.007 (0.004~0.264) 否 9 32.1 是 19 67.9 治疗方式 7.955 0.019 - 只进行手术治疗 9 32.1 只进行化疗 11 39.3 进行化疗和手术 8 28.6 肾上腺占位大小 0.56 0.454 (0.080~3.127) <6 cm 8 28.6 ≥6 cm 20 71.4 B症状 4.680 0.031 (1.107~33.238) 否 12 42.9 是 16 57.1 注:a)根据病理结果将22例弥漫大B细胞淋巴瘤分为是否生发中心来源。 表 2 PAL患者预后影响因素Cox模型分析
预后 OR P值 95%CI 是否CR 0.198 0.020 0.051~0.773 是否进行化疗 0.101 0.008 0.019~0.549 -
[1] Wang Y, Ren Y, Ma L, et al. Clinical Features of 50 Patients With Primary Adrenal Lymphoma[J]. Front Endocrinol(Lausanne), 2020, 11: 595. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2020.00595
[2] Rashidi A, Fisher SI. Primary adrenal lymphoma: a systematic review[J]. Ann Hematol, 2013, 92(12): 1583-1593. doi: 10.1007/s00277-013-1812-3
[3] Younes A, Hilden P, Coiffier B, et al. International Working Group consensus response evaluation criteria in lymphoma(RECIL 2017)[J]. Ann Oncol, 2017, 28(7): 1436-1447. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdx097
[4] Zhang J, Sun J, Feng J, et al. Primary adrenal diffuse large B cell lymphoma: a clinicopathological and molecular study from China[J]. Virchows Arch, 2018, 473(1): 95-103. doi: 10.1007/s00428-018-2378-1
[5] Tomoyose T, Nagasaki A, Uchihara JN, et al. Primary adrenal adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma: a case report and review of the literature[J]. Am J Hematol, 2007, 82(8): 748-752. doi: 10.1002/ajh.20856
[6] Harada K, Kimura K, Iwamuro M, et al. The Clinical and Hormonal Characteristics of Primary Adrenal Lymphomas: The Necessity of Early Detection of Adrenal Insufficiency[J]. Intern Med, 2017, 56(17): 2261-2269. doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.8216-16
[7] 那彦群. 中国泌尿外科疾病诊断治疗指南手册(2014版)[M]. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2013: 525, 563.
[8] Kumar R, Xiu Y, Mavi A, et al. FDG-PET imaging in primary bilateral adrenal lymphoma: a case report and review of the literature[J]. Clin Nucl Med, 2005, 30(4): 222-230. doi: 10.1097/01.rlu.0000155983.46815.1c
[9] Li Y, Sun H, Gao S, et al. Primary bilateral adrenal lymphoma: 2 case reports[J]. J Comput Assist Tomogr, 2006, 30(5): 791-793. doi: 10.1097/01.rct.0000216112.15564.0c
[10] Falchook FS, Allard JC. CT of primary adrenal lymphoma[J]. J Comput Assist Tomogr, 1991, 15(6): 1048-1050. doi: 10.1097/00004728-199111000-00030
[11] Zhang HM, Perrier ND, Grubbs EG, et al. CT features and quantification of the characteristics of adrenocortical carcinomas on unenhanced and contrast-enhanced studies[J]. Clin Radiol, 2012, 67(1): 38-46. doi: 10.1016/j.crad.2011.03.023
[12] Wang F, Liu J, Zhang R, et al. CT and MRI of adrenal gland pathologies[J]. Quant Imaging Med Surg, 2018, 8(8): 853-875. doi: 10.21037/qims.2018.09.13
[13] Ide M, Fukushima N, Hisatomi T, et al. Non-germinal cell phenotype and bcl-2 expression in primary adrenal diffuse large B-cell lymphoma[J]. Leuk Lymphoma, 2007, 48: 2244-2246. doi: 10.1080/10428190701636450
[14] Kim YR, Kim JS, Min YH, et al. Prognostic factors in primary diffuse large B-cell lymphoma of adrenal gland treated with rituximab-CHOP chemotherapy from the Consortium for Improving Survival of Lymphoma(CISL)[J]. J Hematol Oncol, 2012, 5: 49. doi: 10.1186/1756-8722-5-49
[15] Ichikawa S, Fukuhara N, Inoue A, et al. Clinicopathological analysis of primary adrenal diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: effectiveness of rituximab-containing chemotherapy including central nervous system prophylaxis[J]. Exp Hematol Oncol, 2013, 2(1): 19. doi: 10.1186/2162-3619-2-19
[16] Illuminati G, Nardi P, Fratini C, et al. Outcome of Surgical Resection and Chemotherapy Versus Chemotherapy Alone for the Treatment of Isolated Primary Adrenal Lymphoma: A Retrospective Cohort Study of 16 Consecutive Patients[J]. Anticancer Res, 2021, 41(5): 2647-2652. doi: 10.21873/anticanres.15045
[17] 祝宇, 吴瑜璇, 张翀宇, 等. 原发性肾上腺恶性淋巴瘤3例报告[J]. 临床泌尿外科杂志, 2007, 22(10): 752-754. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1420.2007.10.012 http://lcmw.cbpt.cnki.net/WKC/WebPublication/paperDigest.aspx?paperID=b1e76a4a-aceb-4dae-b8dc-42de7630f3e3
[18] 宫进龙, 崔喆. 原发性肾上腺淋巴瘤的诊断和治疗[J]. 临床泌尿外科杂志, 2015, 30(9): 807-810. http://lcmw.cbpt.cnki.net/WKC/WebPublication/paperDigest.aspx?paperID=70fc0028-eae4-4812-93ae-69249ceb36a6
[19] Laurent C, Casasnovas O, Martin L, et al. Adrenal lymphoma: presentation, management and prognosis[J]. QJM, 2017, 110(2): 103-109.
[20] Mermershtain W, Liel Y, Zirkin HJ, et al. Primary bilateral adrenal lymphoma relapsing as a solid cerebral mass after complete clinical remission: a case report[J]. Am J Clin Oncol, 2001, 24(6): 583-585. doi: 10.1097/00000421-200112000-00011
[21] Cheah CY, Herbert KE, O'Rourke K, et al. A multicentre retrospective comparison of central nervous system prophylaxis strategies among patients with high-risk diffuse large B-cell lymphoma[J]. Br J Cancer, 2014, 111(6): 1072-1079. doi: 10.1038/bjc.2014.405
-

| 引用本文: | 刘宇, 张龙, 贾占奎. 原发性肾上腺淋巴瘤临床特征及预后相关因素分析[J]. 临床泌尿外科杂志, 2022, 37(6): 452-456. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.1001-1420.2022.06.010 |
| Citation: | LIU Yu, ZHANG Long, JIA Zhankui. Analysis of clinical features and prognostic factors of primary adrenal lymphoma[J]. J Clin Urol, 2022, 37(6): 452-456. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.1001-1420.2022.06.010 |
- Figure 1.
- Figure 2.
- Figure 3.



 下载:
下载: