The mechanism of metformin inhibiting the proliferation, apoptosis, invasion and metastasis of prostate cancer cells by regulating PKM2
-
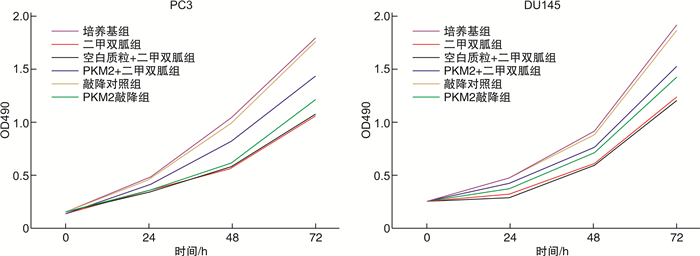
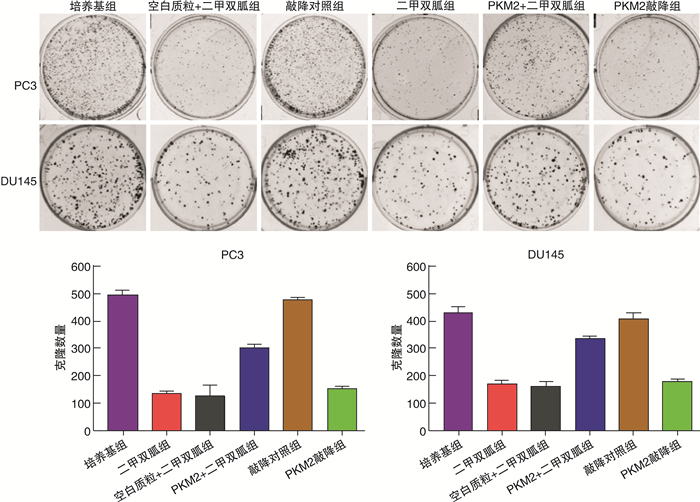
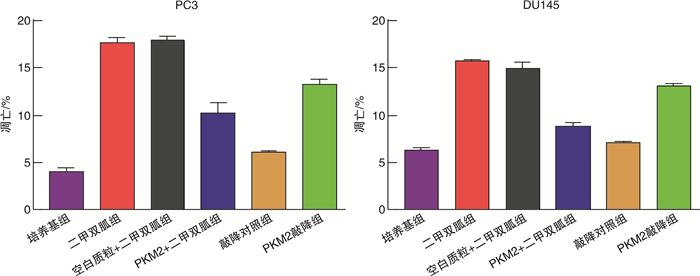
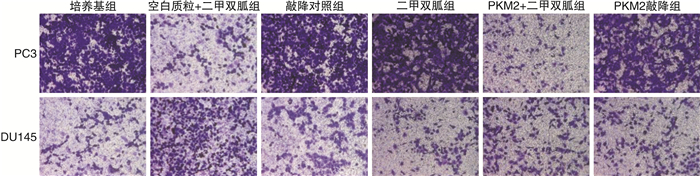
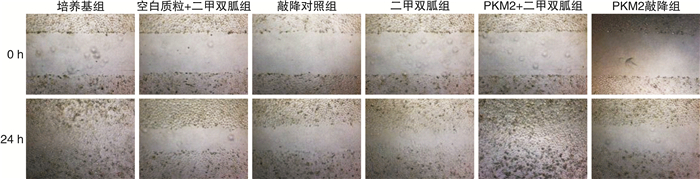
摘要: 目的探讨M2型丙酮酸激酶(PKM2)在二甲双胍的作用下调控肿瘤细胞增殖与凋亡影响前列腺癌浸润和转移的相关机制。方法以前列腺癌PC3/DU145细胞为模型,根据处理或转染方式将细胞分别分为培养基组、二甲双胍组、空白质粒+二甲双胍组、PKM2+二甲双胍组、敲降对照组和PKM2敲降组,转染24 h后收集细胞用于实验。采用Western Blot和荧光定量PCR法检测PKM2蛋白和mRNA的表达水平;采用CCK-8法检测细胞的活性;采用流式细胞术检测细胞凋亡和周期;采用Transwell和划痕实验法检测细胞的侵袭和迁移情况。结果PC3和DU145前列腺癌细胞qPCR及Western Blot结果显示,前列腺癌细胞在二甲双胍作用后PKM2的mRNA及蛋白表达水平用药组(二甲双胍组)明显低于对照组(培养基组),表明二甲双胍有效抑制了PKM2的mRNA与蛋白的表达;在非用药物组分别转染空载质粒sh-NC(敲降对照组)和敲降质粒PKM2-shRNA(PKM2敲降组),在二甲双胍处理的前列腺癌细胞中转染PKM2过表达质粒PKM2-OE(PKM2+二甲双胍组)及空白质粒(空白质粒+二甲双胍组),表明回补PKM2可以显著抑制二甲双胍对PKM2的mRNA与蛋白表达水平的下调作用。CCK-8和流式细胞实验表明,二甲双胍用药组显著抑制前列腺癌细胞增殖和促进细胞凋亡,回补PKM2能显著阻止该作用。进一步的细胞功能实验显示,二甲双胍用药组显著抑制前列腺癌细胞的迁移和浸润,回补PKM2能显著阻止该作用。结论二甲双胍通过下调PKM2从而抑制肿瘤细胞增殖、凋亡进而影响前列腺癌的浸润和转移,相关机制的阐明为前列腺癌早期诊断与治疗提供了理论依据和技术支持。Abstract: ObjectiveTo explore the mechanism of M2-type pyruvate kinase (PKM2) regulating tumor cell proliferation and apoptosis under the action of metformin and affecting the invasion and metastasis of prostate cancer.MethodsPC3/DU145 cells of prostate cancer were used as the model. Cells were divided into culture medium group, metformin group, blank plasmid+metformin group, PKM2+metformin group, knockdown control group and PKM2 knockdown group according to the treatment or transfection methods. Cells were collected for the experiment after 24 hours of transfection. Western Blot and fluorescent quantitative PCR were used to detect the expression level of PKM2 protein and mRNA; The cell activity was detected by CCK-8 method; Apoptosis and cell cycle were detected by flow cytometry; Detection of cell invasion and migration by Transwell and scratch test.ResultsThe qPCR and Western Blot results of PC3 and DU145 prostate cancer cells treated with metformin showed that the mRNA and protein expression levels of PKM2 were significantly downregulated treated with metformin, indicating that metformin effectively inhibited the mRNA and protein expressions of PKM2 in PC3 and DU145 cells. In addition, the non-medicated group was transfected with empty vector sh-NC and knockdown plasmid PKM2-shRNA and the metformin-treated prostate cancer cells were transfected with PKM2 overexpression plasmid PKM2-OE, the results indicated that PKM2 supplementation significantly inhibited the down-regulation of PKM2 mRNA and protein expression by metformin. CCK-8 and flow cytometry experiments showed that the metformin could significantly inhibit the proliferation of prostate cancer cells and induce cell apoptosis, the supplementation of PKM2 can significantly inhibit the down-regulation. Further cell function experiments showed that the metformin significantly inhibited the migration and infiltration of prostate cancer cells, and the supplementation of PKM2 could significantly prevent this effect.ConclusionMetformin inhibits the proliferation, apoptosis, invasion and metastasis of prostate cancer cells by downregulating PKM2. The elucidation of the relevant mechanism provides theoretical basis and technical support for the early diagnosis and treatment of prostate cancer.
-
Key words:
- PKM2 /
- metformin /
- prostate cancer /
- infiltration /
- metastasis
-

-
[1] Talkar SS, Patravale VB. Gene therapy for prostate cancer: a review[J]. Endocr Metab Immune Disord Drug Targets, 2021, 21(3): 385-963. doi: 10.2174/1871530320666200531141455
[2] Ha Chung B, Horie S, Chiong E. The incidence, mortality, and risk factors of prostate cancer in Asian men[J]. Prostate Int, 2019, 7(1): 1-8. doi: 10.1016/j.prnil.2018.11.001
[3] Kaiser A, Haskins C, Siddiqui MM, et al. The evolving role of diet in prostate cancer risk and progression[J]. Curr Opin Oncol, 2019, 31(3): 222-229. doi: 10.1097/CCO.0000000000000519
[4] Freedman LS, Agay N, Farmer R, et al. Metformin treatment among men with diabetes and the risk of prostate cancer: a population-based historical cohort study[J]. Am J Epidemiol, 2022, 191(4): 626-635. doi: 10.1093/aje/kwab287
[5] Zhu S, Guo Y, Zhang X, et al. Pyruvate kinase M2 (PKM2) in cancer and cancer therapeutics[J]. Cancer Lett, 2021, 503: 240-248. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2020.11.018
[6] Di Sebastiano KM, Pinthus JH, Duivenvoorden WCM, et al. Glucose impairments and insulin resistance in prostate cancer: the role of obesity, nutrition and exercise[J]. Obes Rev, 2018, 19(7): 1008-1016. doi: 10.1111/obr.12674
[7] Lee YHA, Hui JMH, Chan JSK, et al. Metformin use and mortality in Asian, diabetic patients with prostate cancer on androgen deprivation therapy: A population-based study[J]. Prostate, 2022. doi: 10.1002/pros.24443
[8] Wilson BE, Armstrong AJ, de Bono J, et al. Effects of metformin and statins on outcomes in men with castration-resistant metastatic prostate cancer: Secondary analysis of COU-AA-301 and COU-AA-302[J]. Eur J Cancer, 2022, 170: 296-304. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2022.03.042
[9] Li H, Xu H, Xing R, et al. Pyruvate kinase M2 contributes to cell growth in gastric cancer via aerobic glycolysis[J]. Pathol Res Pract, 2019, 215(6): 152409. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2019.04.001
[10] Zhang H, Feng C, Zhang M, et al. miR-625-5p/PKM2 negatively regulates melanoma glycolysis state[J]. J Cell Biochem, 2019, 120(3): 2964-2972. doi: 10.1002/jcb.26917
[11] 赵晓莹. 联合检测血浆中PKM2和CEA在人结肠癌中的临床价值[J]. 中国现代药物应用, 2018, 12(12): 31-23. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZWYY201812015.htm
[12] Huang Q, Zhang X. Emerging roles and research tools of atypical ubiquitination[J]. Proteomics, 2020, 20(9): e1900100. doi: 10.1002/pmic.201900100
[13] Morale MG, Tamura RE, Rubio IGS. Metformin and Cancer Hallmarks: Molecular Mechanisms in Thyroid, Prostate and Head and Neck Cancer Models[J]. Biomolecules, 2022, 12(3): 357. doi: 10.3390/biom12030357
[14] Skuli SJ, Alomari S, Gaitsch H, et al. Metformin and Cancer, an Ambiguanidous Relationship[J]. Pharmaceuticals (Basel), 2022, 15(5): 626. doi: 10.3390/ph15050626
[15] Chow E, Yang A, Chung CHL, et al. A clinical perspective of the multifaceted mechanism of metformin in diabetes, infections, cognitive dysfunction, and cancer[J]. Pharmaceuticals(Basel), 2022, 15(4): 442. doi: 10.3390/ph15040442
[16] Ma T, Tian X, Zhang B, et al. Low-dose metformin targets the lysosomal AMPK pathway through PEN2[J]. Nature, 2022, 603(7899): 159-165. doi: 10.1038/s41586-022-04431-8
-





 下载:
下载: