Analysis on relationship between serum Cor, Cys-C and acute renal injury in patients with renal calculi after ESWL based on decision curve
-
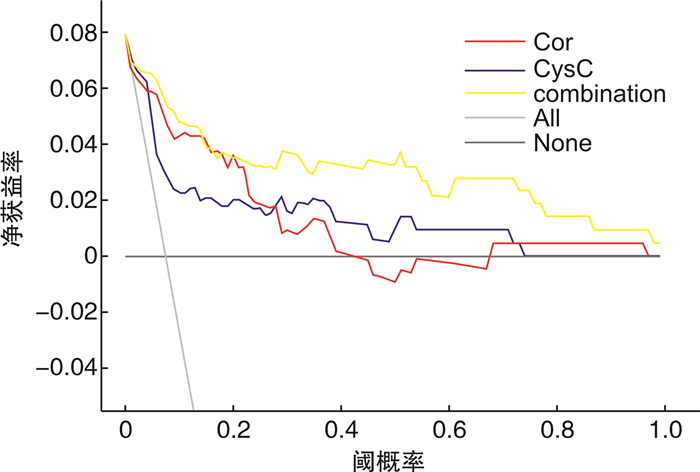
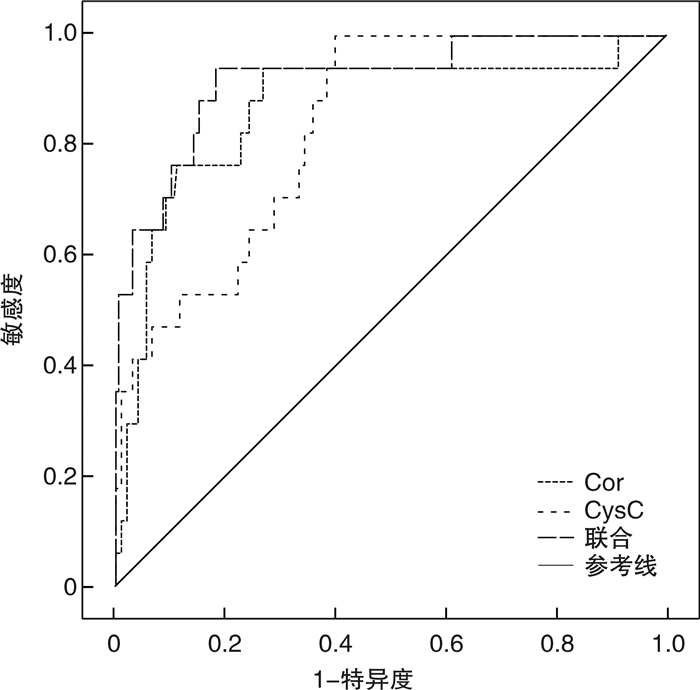
摘要: 目的观察肾结石患者血清皮质醇(Cor)、胱抑素C(Cys-C)表达及其体外冲击波碎石术(ESWL)术后肾损伤发生情况,并基于决策曲线分析血清指标与术后急性肾损伤发生的关系。方法选取2018年8月—2021年8月于新疆医科大学第一附属医院接受ESWL治疗的215例肾结石患者,术后随访7 d并评估患者急性肾损伤发生情况,由研究者设计基线资料调查表,详细统计发生组和未发生组基线资料,分析ESWL术前血清Cor、Cys-C水平与术后急性肾损伤发生的关系,并基于受试者工作特征(ROC)曲线及决策曲线分析术前血清Cor、Cys-C水平预测肾结石患者术后发生急性肾损伤的价值。结果215例肾结石患者术后随访7 d,发生急性肾损伤17例,占比7.91%;发生组血肌酐(Scr)、Cor、Cys-C水平高于未发生组,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05);组间性别、年龄、体重指数、结石直径、结石位置、手术时间、结石手术史、长期饮酒史、甘油三酯(TG)、总胆固醇(TC)、血红蛋白(HGB)比较,差异无统计学意义;回归分析结果显示,Scr、Cor、Cys-C过高表达均是肾结石患者术后急性肾损伤发生的危险因子(OR>1,P < 0.05);绘制ROC曲线,结果显示,血清Cor、Cys-C水平预测肾结石患者术后急性肾损伤发生风险的曲线下面积(AUC)均>0.7,具有一定的预测价值,且联合预测价值较高;绘制决策曲线,结果显示,在阈值0.06~0.15及0.21~1.00范围内,血清Cor、Cys-C水平联合的预测模型预测肾结石患者术后急性肾损伤发生的净收益率高于血清Cor、Cys-C单独检测。结论血清Cor、Cys-C水平与肾结石患者术后急性肾损伤发生有关,检测血清Cor、Cys-C水平可预测肾结石患者术后急性肾损伤发生风险,且二者联合预测收益率更高。Abstract: ObjectiveTo observe the expression of serum cortisol (Cor), cystatin-C (Cys-C) and the occurrence of renal injury after extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy (ESWL) in patients with renal calculi, and to analyze the relationship between serum indexes and postoperative acute renal injury based on decision curve.MethodsFrom August 2018 to August 2021, 215 patients with renal calculi who underwent ESWL in First Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University were selected. The patients were followed up for 7 days and the occurrence of acute renal injury of patients was evaluated. The baseline data questionnaire was designed by the researcher, and the baseline data of the occurrence group and non occurrence group were counted in detail. The relationship between serum Cor and Cys-C levels before ESWL and postoperative acute renal injury was analyzed, and the value of preoperative serum Cor and Cys-C levels in predicting postoperative acute renal injury in patients with renal calculi was analyzed based on receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve and decision curve.ResultsTwo hundred and fifteen patients with renal calculi were followed up for 7 days. Seventeen cases had acute renal injury, accounting for 7.91%. The levels of serum creatinine (Scr), Cor and Cys-C in the occurrence group were significantly higher than those in the non occurrence group, and the difference was statistically significant (P < 0.05). However, there was no statistical significant difference in gender, age, body mass index, calculi diameter, calculi location, operation time, calculi operation history, long-term drinking history, triglyceride (TG), total cholesterol (TC) or hemoglobin (HGB). The results of regression analysis showed that the overexpression of Scr, Cor and Cys-C were the risk factors of postoperative acute renal injury in patients with renal calculi (OR > 1, P < 0.05). The ROC curve was drawn, and the results showed that the area under the curve (AUC) of serum Cor and Cys-C levels in predicting the risk of postoperative acute renal injury in patients with renal calculi were > 0.7, which had certain predictive value, and the combined predictive value was higher. The decision curve was drawn, and the results showed that in the threshold range of 0.06-0.15 and 0.21-1.00, the net benefit rate of the combined prediction model of serum Cor and Cys-C levels in predicting postoperative acute renal injury in patients with renal calculi was higher than that detected by serum Cor and Cys-C alone.ConclusionThe levels of serum Cor and Cys-C are related to the occurrence of postoperative acute renal injury in patients with renal calculi, so detection of serum Cor and Cys-C levels can predict the risk of postoperative acute renal injury in patients with renal calculi, especially the joint prediction of the two indexes.
-
Key words:
- renal calculi /
- acute renal injury /
- extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy /
- cortisol /
- cystatin-C
-

-
表 1 发生组与未发生组基线资料比较
例(%),X±S 项目 发生组(17例) 未发生组(198例) χ2/t P 性别 0.053 0.819 男 12(70.59) 147(74.24) 女 5(29.41) 51(25.76) 年龄/岁 41.75±5.29 41.20±5.07 0.428 0.669 BMI/(kg·m-2) 22.04±2.58 21.85±2.17 0.341 0.733 结石直径/cm 1.33±0.11 1.31±0.09 0.863 0.389 结石位置 1.279 0.734 肾盂 6(35.29) 68(34.34) 肾上盏 9(52.94) 89(44.95) 肾中盏 3(17.65) 32(16.16) 肾下盏 1(5.88) 9(4.55) 手术时间/min 33.74±4.23 34.52±5.07 0.616 0.539 结石手术史 0.075 0.785 有 4(23.53) 35(17.68) 无 13(76.47) 163(82.32) 长期饮酒史 0.170 0.680 有 5(29.41) 68(34.34) 无 12(70.59) 130(65.66) TG/(mmol·L-1) 4.23±0.49 4.37±0.53 1.051 0.295 TC/(mmol·L-1) 4.34±0.51 4.51±0.57 1.189 0.236 Scr/(μmol·L-1) 67.35±7.23 59.81±6.14 4.790 < 0.001 Cor/(μg·L-1) 107.36±10.28 93.54±8.85 6.099 < 0.001 Cys-C/(μg·L-1) 572.21±51.34 503.67±47.52 5.672 < 0.001 HGB/(g·L-1) 112.57±11.63 117.72±12.74 1.610 0.109 表 2 血清指标与肾结石患者术后急性肾损伤发生关系的回归分析结果
指标 B SE Wald P OR 95%CI 常量 -38.221 8.685 19.368 < 0.001 - - Scr 0.140 0.057 6.021 0.014 1.151 1.029~1.287 Cor 0.155 0.048 10.524 0.001 1.167 1.063~1.282 Cys-C 0.025 0.007 11.596 0.001 1.025 1.011~1.040 HGB -0.017 0.035 0.246 0.620 0.983 0.918~1.052 表 3 血清Cor、Cys-C水平联合预测肾结石患者术后急性肾损伤发生的价值分析结果
指标 AUC AUC的95%CI P 截点值/(μg·L-1) 特异度 敏感度 约登指数 Cor 0.869 0.765~0.972 < 0.001 100.415 0.824 0.773 0.597 Cys-C 0.835 0.754~0.915 < 0.001 530.235 0.712 0.706 0.418 联合 0.921 0.849~0.992 < 0.001 - 0.941 0.818 0.759 -
[1] 王建喜, 李信, 李明亮, 等. 3D打印技术联合PCNL对肾结石患者清除率及并发症的影响[J]. 临床泌尿外科杂志, 2021, 36(8): 593-597. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCMW202108001.htm
[2] Ng CF, Yee CH, Teoh JYC, et al. Effect of Stepwise Voltage Escalation on Treatment Outcomes following Extracorporeal Shock Wave Lithotripsy of Renal Calculi: A Prospective Randomized Study[J]. J Urol, 2019, 202(5): 986-993. doi: 10.1097/JU.0000000000000344
[3] Slominski AT, Bro yna AA, Tuckey RC. Cutaneous Glucocorticoidogenesis and Cortisol Signaling Are Defective in Psoriasis[J]. J Invest Dermatol, 2017, 137(8): 1609-1611. doi: 10.1016/j.jid.2017.04.004
[4] 艾合买提·艾买尔, 雷鹏, 塔来提·塔依尔, 等. 血清皮质醇和促肾上腺皮质激素水平与肾结石患者输尿管软镜碎石术后早期肾损伤的相关性[J]. 中华实用诊断与治疗杂志, 2021, 35(2): 151-155. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HNZD202102011.htm
[5] Garcia-Garcia P, Castejon R, Tutor-Ureta P, et al. Serum cystatin C is associated with kidney function but not with cardiovascular risk factors or subclinical atherosclerosis in patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus[J]. Clin Rheumatol, 2017, 36(12): 2709-2717. doi: 10.1007/s10067-017-3837-9
[6] 武道荣, 方磊, 李睿, 等. APACHEⅡ评分联合血清RBP和Cys-C在ICU脓毒症性急性肾损伤患者中的评估价值[J]. 临床急诊杂志, 2021, 22(8): 563-568. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZZLC202108012.htm
[7] 葛均波, 徐永健. 内科学[M]. 第8版. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2013: 520-521.
[8] Junbo L, Yugen L, Guo J, et al. Retrograde Intrarenal Surgery vs. Percutaneous Nephrolithotomy vs. Extracorporeal Shock Wave Lithotripsy for Lower Pole Renal Stones 10-20 mm: A Meta-analysis and Systematic Review[J]. Urol J, 2019, 16(2): 97-106.
[9] Drosos G, Ampatzidou F, Sarafidis P, et al. Serum Creatinine and Chronic Kidney Disease-Epidemiology Estimated Glomerular Filtration Rate: Independent Predictors of Renal Replacement Therapy following Cardiac Surgery[J]. Am J Nephrol, 2018, 48(2): 108-117. doi: 10.1159/000492182
[10] Wada H, Kanda J, Akahoshi Y, et al. Impact of estimated glomerular filtration rate based on plasma Cystatin-C and serum creatinine levels before allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation[J]. Hematology, 2018, 23(5): 271-276. doi: 10.1080/10245332.2017.1396026
[11] 杜昌国, 叶明宝, 燕群峰, 等. 体外震波碎石术治疗肾结石后氧化应激与急性肾损伤的关系[J]. 中国临床研究, 2018, 31(3): 343-346. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGCK201803013.htm
[12] Paragliola RM, Corsello A, Troiani E, et al. Cortisol circadian rhythm and jet-lag syndrome: evaluation of salivary cortisol rhythm in a group of eastward travelers[J]. Endocrine, 2021, 73(2): 424-430.
[13] 陆怀志, 曾博文. FURL联合SMP治疗上尿路结石患者的疗效及安全性评估[J]. 河北医药, 2020, 42(11): 1657-1660, 1664. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HBYZ202011013.htm
[14] Bevc S, Hojs N, Knehtl M, et al. Cystatin-C as a predictor of mortality in elderly patients with chronic kidney disease[J]. Aging Male, 2019, 22(1): 62-67.
[15] 魏天祥, 崔世红, 陈娟, 等. 血清胱抑素C、尿β2-微球蛋白及随机尿微量白蛋白与肌酐比在妊娠期高血压疾病早期肾损伤中的临床应用[J]. 现代妇产科进展, 2018, 27(10): 766-768. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDFC201810011.htm
[16] 朱烨, 张芃子, 毕艳. 血促肾上腺皮质激素、皮质醇水平及其节律与糖尿病肾病关系的研究[J]. 中华糖尿病杂志, 2021, 13(6): 597-602.
[17] 袁晓红, 李鹏, 李雯, 等. 清热解毒化瘀汤联合前列腺素E对脓毒症致急性肾损伤患者机体氧化应激及血清相关细胞因子水平的影响[J]. 现代中西医结合杂志, 2019, 28(36): 4042-4046. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDJH201936014.htm
[18] Qiu X, Liu C, Ye Y, et al. The diagnostic value of serum creatinine and Cystatin-C in evaluating glomerular filtration rate in patients with chronic kidney disease: a systematic literature review and meta-analysis[J]. Oncotarget, 2017, 8(42): 72985-72999.
[19] Andrade López AC, Bande Fernández JJ, Díaz Corte C. Cystatin-C in estimation of renal function in liver transplantation candidates[J]. Med Clin(Barc), 2020, 155(9): 419-420.
-




 下载:
下载: