-
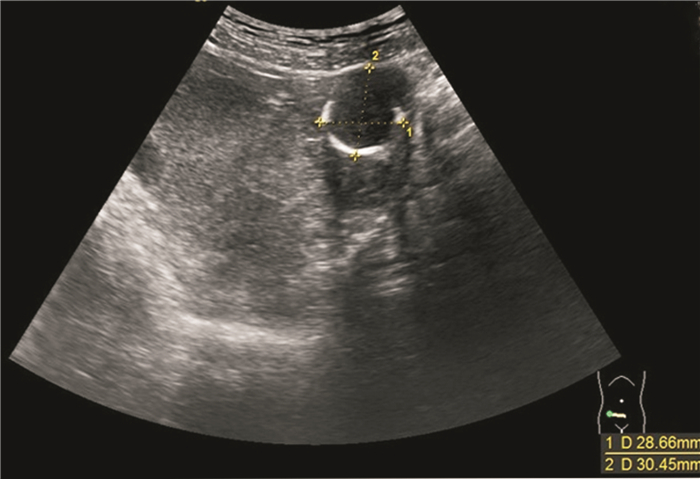
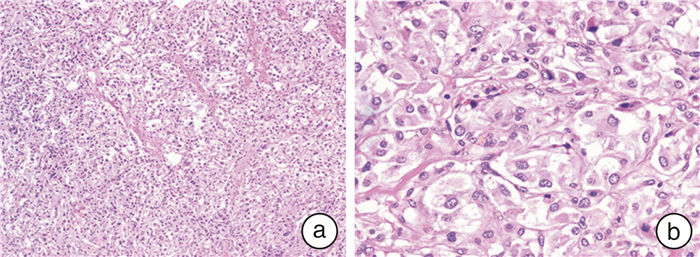
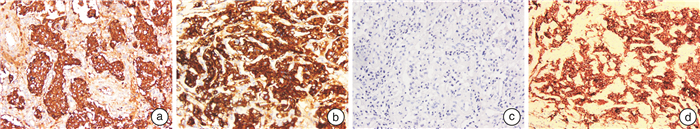
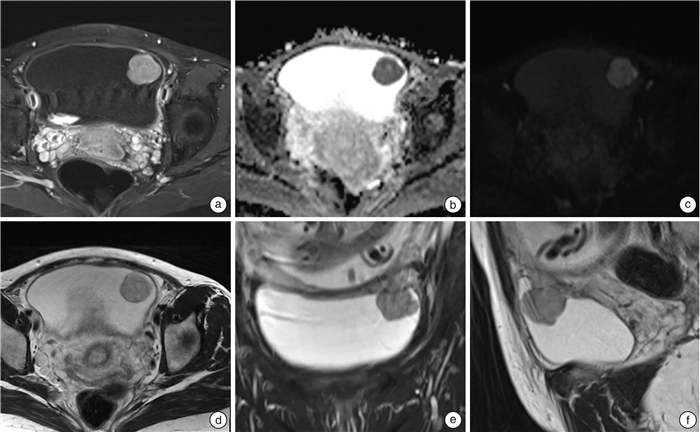
摘要: 膀胱副神经节瘤是一种罕见的肿瘤疾病,因多位于黏膜下层和肌层之间,且具有潜在恶性,故极易误诊为膀胱尿路上皮癌。本例报道1例27岁女性膀胱副神经节瘤患者。该患者因“大量血尿”入院,彩超、CT、MRI均提示膀胱占位。全身麻醉下行经尿道膀胱肿瘤电切手术,术后组织病理及免疫组织化学提示副神经节瘤。出院后2周再次发生无痛性肉眼血尿,全身麻醉下行膀胱部分切除术,术后痊愈出院。正确地诊断膀胱副神经节瘤具有重要的临床价值,尤其是影像学检查对诊断至关重要。手术是膀胱副神经节瘤最有效的治疗方法,而膀胱部分切除术是膀胱副神经节瘤的主要手术方式。Abstract: Paraganglioma of urinary bladder (PUB) is a rare tumor. As PUB mostly lies between submucosa and muscularis and has potential malignancy, it is very easy to be misdiagnosed as bladder urothelial carcinoma. This is the case report of a twenty-seven female patient with PUB. The patient was admitted due to 'massive hematuria'. Ultrasound, CT and MRI all showed space occupying lesion of bladder. The patient underwent transurethral resection of bladder tumor (TURBT). Paraganglioma was revealed by histopathology and immunohistochemistry. Painless hematuria occurred again 2 weeks after leaving hospital. Hence, the patient underwent partial cystectomy (PC) and be cured. It is important to diagnosis of PUB correctly, in particular for radiology. Surgery is the most effective treatment for PUB, and PC is the dominant surgical method for PUB.
-
Key words:
- paraganglioma /
- urinary bladder /
- partial cystectomy
-

-
[1] 黄健. 中国泌尿外科和男科疾病诊断治疗指南[M]. 科学出版社, 2020.
[2] Williams P, Siref L, Feloney M. Pheochromocytoma of the urinary bladder[J]. N Engl J Med, 1953, 249(1): 25-26. doi: 10.1056/NEJM195307022490106
[3] Yuan Y, Su Z, Zhu R, et al. Bladder paraganglioma: three cases report and literature review[J]. Int Med Case Rep J, 2021, 14: 765-771. doi: 10.2147/IMCRJ.S336659
[4] 汪群锋, 梁朝朝, 朱劲松, 等. 膀胱嗜铬细胞瘤1例诊治并文献复习[J]. 现代泌尿生殖肿瘤杂志, 2017, 9(5): 278-280. doi: 10.3870/j.issn.1674-4624.2017.05.007
[5] Tu X, Zhang N, Zhuang X, et al. Incidental diagnosis of nonfunctional bladder paraganglioma: a case report and literature review[J]. BMC Urol, 2021, 21(1): 98. doi: 10.1186/s12894-021-00863-y
[6] Priyadarshi V, Pal DK. Paraganglioma of urinary bladder[J]. Urol Ann, 2015, 7(3): 402-404. doi: 10.4103/0974-7796.152058
[7] Wang S, Zhang A, Huang S, et al. Non functioning paraganglioma in the urinary bladder: a case report[J]. Urol J, 2020, 17(4): 426-428.
[8] 牛琳, 荣璐璐, 蒋涛. 膀胱副神经节瘤的多层螺旋CT诊断价值[J]. 实用放射学杂志, 2021, 37(6): 965-967, 988. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XYXZ201410034.htm
[9] Deng JH, Li HZ, Zhang YS, et al. Functional paragangliomas of the urinary bladder: a report of 9 cases[J]. Chin J Cancer, 2010, 29(8): 729-734. doi: 10.5732/cjc.009.10703
[10] Quist EE, Javadzadeh BM, Johannesen E, et al. Malignant paraganglioma of the bladder: a case report and review of the literature[J]. Pathol Res Pract, 2015, 211(2): 183-188. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2014.10.009
[11] Frantellizzi V, Pontico M, Letizia C, et al. Bladder wall paraganglioma located using(123) I-mIBG SPECT and CT imaging[J]. Rev Esp Med Nucl Imagen Mol, 2018, 37(4): 253-254.
[12] Degrieck B, De Visschere P, Lapauw B. Bladder Paraganglioma[J]. J Belg Soc Radiol, 2020, 104(1): 25. doi: 10.5334/jbsr.2064
[13] Panebianco V, Narumi Y, Altun E, et al. Multiparametric magnetic resonance imaging for bladder cancer: development of Ⅵ-RADS(vesical imaging-reporting and data system)[J]. Eur Urol, 2018, 74(3): 294-306. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2018.04.029
[14] 范大铬, 吴春林, 黄海建, 等. 膀胱副神经节瘤23例临床病理学分析[J]. 中华病理学杂志, 2020, 49(4): 311-316. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112151-20190928-00535
[15] 王乾, 任翠萍, 李莹, 等. 膀胱副神经节瘤一例[J]. 临床放射学杂志, 2017, 36(5): 662-663. doi: 10.13437/j.cnki.jcr.2017.05.016
[16] Beilan JA, Lawton A, Hajdenberg J, et al. Pheochromocytoma of the urinary bladder: a systematic review of the contemporary literature[J]. BMC Urol, 2013, 13: 22. doi: 10.1186/1471-2490-13-22
[17] Tsai CC, Wu WJ, Chueh KS, et al. Paraganglioma of the urinary bladder first presented by bladder bloody tamponade: two case reports and review of the literatures[J]. Kaohsiung J Med Sci, 2011, 27(3): 108-113. doi: 10.1016/j.kjms.2010.05.005
[18] Das S, Bulusu NV, Lowe P. Primary vesical pheochromocytoma[J]. Urology, 1983, 21(1): 20-25. doi: 10.1016/0090-4295(83)90116-4
[19] Ahn SG, Jang H, Han DS, et al. Transurethral resection of bladder tumour (TURBT) as an optional treatment method on pheochromocytoma of the urinary bladder[J]. Can Urol Assoc J, 2013, 7(1-2): E130-E134. doi: 10.5489/cuaj.255
[20] Grossman A, Pacak K, Sawka A, et al. Biochemical diagnosis and localization of pheochromocytoma: can we reach a consensus?[J]. Ann N Y Acad Sci, 2006, 1073: 332-347. doi: 10.1196/annals.1353.038
[21] 金从军, 邵玉军, 曾正陪, 等. 131I-间位碘代苄胍治疗恶性嗜铬细胞瘤/副神经节瘤的临床疗效分析[J]. 中华泌尿外科杂志, 2015, 36(1): 24-28.
[22] Kotecka-Blicharz A, Hasse-Lazar K, Handkiewicz-Junak D, et al. 131-I MIBG therapy of malignant pheochromocytoma and paraganglioma tumours-a single-centre study[J]. Endokrynol Pol, 2018, 69(3): 246-251. doi: 10.5603/EP.a2018.0024
[23] You D, Ren R, Chen E, et al. Radiotherapy for urinary bladder pheochromocytoma with invasion of the prostate: A case report and literature review[J]. Mol Clin Oncol, 2016, 4(6): 1060-1062. doi: 10.3892/mco.2016.820
[24] Sisson JC, Shapiro B, Shulkin BL, et al. Treatment of malignant pheochromocytomas with 131-I metaiodobenzylguanidine and chemotherapy[J]. Am J Clin Oncol, 1999, 22(4): 364-370. doi: 10.1097/00000421-199908000-00008
[25] Joshua AM, Ezzat S, Asa SL, et al. Rationale and evidence for sunitinib in the treatment of malignant paraganglioma/pheochromocytoma[J]. J Clin Endocrinol Metab, 2009, 94(1): 5-9. doi: 10.1210/jc.2008-1836
[26] Ilanchezhian M, Jha A, Pacak K, et al. Emerging treatments for advanced/metastatic pheochromocytoma and paraganglioma[J]. Curr Treat Options Oncol, 2020, 21(11): 85. doi: 10.1007/s11864-020-00787-z
[27] Naing A, Meric-Bernstam F, Stephen B, et al. Phase 2 study of pembrolizumab in patients with advanced rare cancers[J]. J Immunother Cancer, 2020, 8(1): e000347.
-

| 引用本文: | 刘沛昆, 杨潇, 曹强, 等. 膀胱副神经节瘤1例[J]. 临床泌尿外科杂志, 2022, 37(11): 885-888. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.1001-1420.2022.11.018 |
| Citation: | LIU Peikun, YANG Xiao, CAO Qiang, et al. Paraganglioma of urinary bladder: a case report[J]. J Clin Urol, 2022, 37(11): 885-888. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.1001-1420.2022.11.018 |
- Figure 1.
- Figure 2.
- Figure 3.
- Figure 4.



 下载:
下载: