Predictive value of neutrophil/lymphocyte ratio for intravesical recurrence after upper urinary tract urothelial carcinoma surgery
-
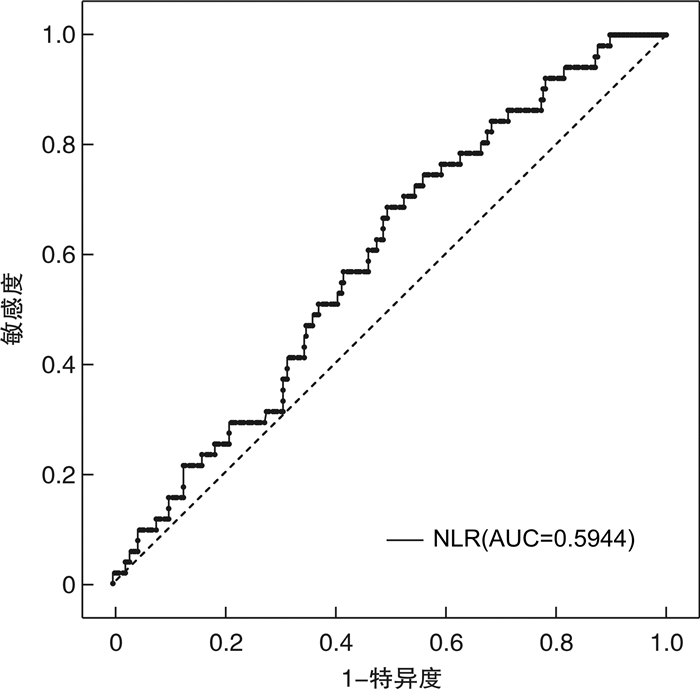
摘要: 目的 探讨术前中性粒细胞与淋巴细胞比值(NLR)对上尿路尿路上皮癌(UTUC)患者术后出现膀胱内复发(IVR)的预测价值。方法 回顾性分析青岛大学附属医院于2011年1月—2017年7月收治317例UTUC患者的临床资料,采用受试者工作特征(ROC)曲线分析NLR最佳截断值,将患者分为低NLR组及高NLR组;利用单因素分析对可能导致UTUC术后出现IVR的危险因素进行分析,将其有意义的因素纳入二元logistics回归分析,筛选出独立危险因素。结果 ROC曲线显示NLR最佳截断值为1.877,单因素分析示BMI < 18.5 kg/m2或≥24 kg/m2、肿瘤分期、术前行输尿管镜检查、既往或合并膀胱癌、高NLR是UTUC术后出现IVR的危险因素(P < 0.05),二元logistic回归分析以上各项均为独立危险因素。结论 NLR的获取简易经济,高NLR水平对UTUC患者术后出现IVR具有独立的预测价值。
-
关键词:
- 上尿路尿路上皮癌 /
- 中性粒细胞与淋巴细胞比值 /
- 膀胱内复发
Abstract: Objective To investigate the predictive value of preoperative neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio (NLR) for postoperative intravesical recurrence (IVR) in patients with upper urinary tract urothelial carcinoma (UTUC).Methods The clinical data of 317 patients with UTUC admitted to Affiliated Hospital of Qingdao University from January 2011 to July 2017 were retrospectively analyzed. The best cut-off value of NLR was analyzed by receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve. The patients were divided into low NLR group and high NLR group. Univariate analysis was used to analyze the risk factors that may lead to postoperative IVR, and the meaningful factors were included in the binary logistic regression analysis to screen out the independent risk factors.Results ROC curve showed that the best cut-off value of NLR was 1.877. Univariate analysis showed that BMI < 18.5 kg/m2 or ≥ 24 kg/m2, tumor stage, preoperative ureteroscopy, previous or combined bladder cancer, and high NLR were the risk factors for postoperative IVR in patients with UTUC.Conclusion The acquisition of NLR is simple and economical. High NLR level has independent predictive value for postoperative IVR in patients with UTUC. -

-
表 1 NLR与UTUC患者的临床病理资料比较
例(%) 临床资料 高NLR组(167组) 低NLR组(150组) χ2值 P值 性别 0.337 0.562 男 105(62.9) 99(66.0) 女 62(37.1) 51(34.0) 年龄 0.038 0.846 < 65岁 63(37.7) 55(36.7) ≥65岁 104(62.3) 95(63.3) BMI 0.003 0.959 < 18.5或≥24 kg/m2 94(56.3) 84(56.0) 18.5≤BMI < 24 kg/m2 73(43.7) 66(44.0) 抽烟史 4.620 0.032 抽烟 56(33.5) 68(45.3) 不抽烟 111(66.5) 82(54.7) 肿瘤大小 0.122 0.727 >3 cm 89(53.3) 77(51.3) ≤3 cm 78(46.7) 73(48.7) 肿瘤分期 11.835 0.001 T3~T4 98(58.7) 59(39.3) Ta~T2 69(41.3) 91(60.7) 肿瘤分级 1.530 0.216 高级别 54(32.3) 39(26.0) 低级别 113(67.7) 111(74.0) 表 2 UTUC患者RNU术后膀胱内复发的单因素分析
例(%) 临床资料 膀胱内复发(51例) 膀胱内未复发(266例) χ2值 P值 性别 2.733 0.098 男 38(74.5) 166(62.4) 女 13(25.5) 100(37.6) 年龄 3.619 0.057 < 65岁 25(49.0) 93(35.0) ≥65岁 26(51.0) 173(65.0) BMI 5.145 0.023 < 18.5或≥24 kg/m2 36(70.6) 142(53.4) 18.5≤BMI < 24 kg/m2 15(29.4) 124(46.6) 抽烟史 0.108 0.742 抽烟 21(41.2) 103(38.7) 不抽烟 30(58.8) 163(61.3) 高血压史 0.682 0.409 高血压 17(33.3) 105(39.5) 无高血压 34(66.7) 161(60.5) 糖尿病史 0.166 0.684 糖尿病 8(15.7) 36(13.5) 无糖尿病 43(84.3) 230(86.5) 血尿史 0.655 0.418 血尿 36(70.6) 202(75.9) 无血尿 15(29.4) 64(24.1) 腰痛史 0.717 0.397 腰痛 20(39.2) 88(33.1) 无腰痛 31(60.8) 178(66.9) 术前肾积水 0.106 0.745 肾积水 25(49.0) 137(51.5) 无肾积水 26(51.0) 129(48.5) 输尿管镜检查 8.252 0.004 行镜检 22(43.1) 63(23.7) 未行镜检 29(56.9) 203(76.3) 肿瘤侧别 2.511 0.113 左侧 23(45.1) 152(57.1) 右侧 28(54.9) 114(42.9) 肿瘤位置 0.000 1.000 肾盂或输尿管 48(94.1) 251(94.4) 肾盂及输尿管 3(5.9) 15(5.6) 肿瘤大小 0.157 0.692 >3 cm 23(45.1) 128(48.1) ≤3 cm 28(54.9) 138(51.9) 肿瘤分期 14.047 0.000 T3~T4 13(25.5) 144(54.1) Ta~T2 38(74.5) 122(45.9) 肿瘤分级 0.000 0.990 高级别 36(70.6) 188(70.7) 低级别 15(29.4) 78(29.3) 合并膀胱癌 8.000 0.005 合并膀胱癌 10(19.6) 19(7.1) 未合并膀胱癌 41(80.4) 247(92.9) NLR分组 6.200 0.013 高 NLR 35(68.6) 132(49.6) 低 NLR 16(31.4) 134(50.4) 表 3 UTUC术后出现膀胱复发的二元logistics回归分析
变量 B SE Wald Exp(B) P 95%CI BMI 0.712 0.353 4.073 2.037 0.044 1.021~4.066 输尿管镜检查 0.882 0.345 6.516 2.415 0.011 1.227~4.751 肿瘤分期 -1.198 0.362 10.963 0.302 0.001 0.149~0.613 合并膀胱癌 1.465 0.467 9.824 4.326 0.002 1.731~10.810 NLR分组 0.916 0.350 6.868 2.500 0.009 1.260~4.961 -
[1] Rouprêt M, Babjuk M, Burger M, et al. European association of urology guidelines on upper urinary tract urothelial carcinoma: 2020 update[J]. Eur Urol, 2021, 79(1): 62-79. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2020.05.042
[2] Seisen T, Granger B, Colin P, et al. A Systematic review and meta-analysis of clinicopathologic factors linked to intravesical recurrence after radical nephroureterectomy to treat upper tract urothelial carcinoma[J]. Eur Urol, 2015, 67(6): 1122-1133. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2014.11.035
[3] 袁易初. 诊断性输尿管镜检查对上尿路尿路上皮癌术后膀胱内复发的影响: 双中心958例回顾性研究[J]. 临床泌尿外科杂志, 2021, 36(1): 18-23. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCMW202101004.htm
[4] Kim SH, Song MK, Joung JY, et al. Significant clinicopathologic prognostic factors for bladder recurrence, progression, and cancer-specific survival after surgery among patients with upper urinary tract urothelial carcinoma[J]. Investig Clin Urol, 2019, 60(6): 432-442. doi: 10.4111/icu.2019.60.6.432
[5] Greten FR, Grivennikov SI. Inflammation and cancer: triggers, mechanisms, and consequences[J]. Immunity, 2019, 51(1): 27-41. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2019.06.025
[6] 王鹏桥, 谢喜, 杨雷, 等. 血清炎性因子白介素-35与前列腺癌发生发展的相关性研究[J]. 临床泌尿外科杂志, 2020, 35(3): 176-179. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.1001-1420.2020.03.002
[7] Grivennikov SI, Greten FR, Karin M. Immunity, inflammation, and cancer[J]. Cell, 2010, 140(6): 883-899. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2010.01.025
[8] Lu C, Gao P, Yang Y, et al. Prognostic evaluation of platelet to lymphocyte ratio in patients with colorectal cancer[J]. Oncotarget, 2017, 8(49): 86287-86295. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.21141
[9] Luo H, Ge H, Cui Y, et al. Systemic inflammation biomarkers predict survival in patients of early stage non-small cell lung cancer treated with stereotactic ablative radiotherapy-a single center experience[J]. J Cancer, 2018, 9(1): 182-188. doi: 10.7150/jca.21703
[10] Hsu JT, Liao CK, Le PH, et al. Prognostic value of the preoperative neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio in resectable gastric cancer[J]. Medicine(Baltimore), 2015, 94(39): e1589.
[11] Guo W, Lu X, Liu Q, et al. Prognostic value of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio and platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio for breast cancer patients: An updated meta-analysis of 17079 individuals[J]. Cancer Med, 2019, 8(9): 4135-4148. doi: 10.1002/cam4.2281
[12] 刘涛, 王辉, 王杰, 等. 术前中性粒细胞与淋巴细胞比值和血小板与淋巴细胞比值对肾透明细胞癌的预后评估价值[J]. 临床泌尿外科杂志, 2021, 36(1): 7-11, 17. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.1001-1420.2021.01.002
[13] Vartolomei MD, Mathieu R, Margulis V, et al. Promising role of preoperative neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio in patients treated with radical nephroureterectomy[J]. World J Urol, 2017, 35(1): 121-130. doi: 10.1007/s00345-016-1848-9
[14] Chien TM, Li CC, Lu YM, et al. The predictive value of systemic immune-inflammation index on bladder recurrence on upper tract urothelial carcinoma outcomes after radical nephroureterectomy[J]. J Clin Med, 2021, 10(22): 111.
[15] Kishimoto N, Takao T, Kuribayashi S, et al. The neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio as a predictor of intravesical recurrence in patients with upper urinary tract urothelial carcinoma treated with radical nephroureterectomy[J]. Int J Clin Oncol, 2017, 22(1): 153-158.
[16] Hanahan D, Weinberg RA. Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation[J]. Cell, 2011, 144(5): 646-674.
[17] Lu H, Ouyang W, Huang C. Inflammation, a key event in cancer development[J]. Mol Cancer Res, 2006, 4(4): 221-233.
[18] Mantovani A, Cassatella MA, Costantini C, et al. Neutrophils in the activation and regulation of innate and adaptive immunity[J]. Nat Rev Immunol, 2011, 11(8): 519-531.
[19] Zhao J, Huang W, Wu Y, et al. Prognostic role of pretreatment blood lymphocyte count in patients with solid tumors: a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Cancer Cell Int, 2020, 20: 15.
[20] Iyengar NM, Gucalp A, Dannenberg AJ, et al. Obesity and cancer mechanisms: tumor microenvironment and inflammation[J]. J Clin Oncol, 2016, 34(35): 4270-4276.
-




 下载:
下载: