Initial experience of extraperitoneal radical prostatectomy and total anatomical reconstruction with domestic endoscopic surgical robot system
-
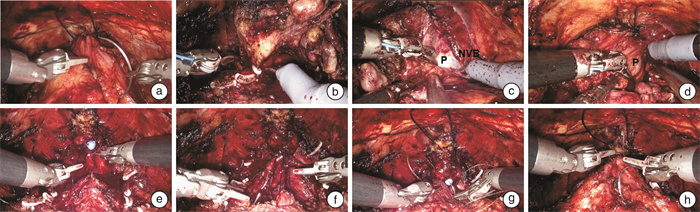
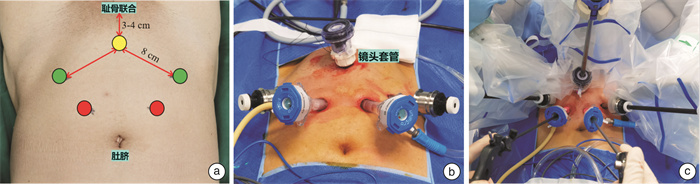
摘要: 目的 总结采用国产康多内窥镜手术机器人系统行经腹膜外根治性前列腺切除及尿道周围全重建术的临床应用经验,初步评价其安全性和有效性。方法 前瞻性收集2021年5月20日—2021年6月20日于本中心接受康多内窥镜手术机器人经腹膜外根治性前列腺切除及尿道周围全重建术的患者的临床资料。描述手术过程,观察记录手术时间、出血量、住院天数、围术期并发症、术后病理、术后血清前列腺特异性抗原(PSA)及拔除尿管后控尿情况,将24 h使用尿垫≤1片或24 h漏尿量≤20 g定义为完全自主控尿。结果 本研究纳入6例患者,平均年龄为65(58~72)岁,平均体重指数为25.3(20.8~28.0) kg/m2,平均前列腺体积为47.3(27.0~86.0) mL。术前平均前列腺特异性抗原(PSA)为10.51(6.50~17.98) ng/mL。穿刺病理示:Gleason评分6分1例,7分5例。临床分期:T2b期2例,T2c期4例。既往有腹盆部手术史者2例(均为阑尾切除术)。6例手术均由单一术者完成,术中无并发症或器械相关不良事件发生。平均手术时间138(120~154) min,平均机械臂对接时间5.7(2.5~9.8) min,平均机械臂腔内操作时间为96(82~116) min,平均膀胱颈与尿道吻合时间为15.9(12.2~25.7) min,平均术中出血量为85(10~200) mL。术后平均住院时间为6(4~10) d,所有患者均无Clavien-DindoⅡ~Ⅴ级并发症出现。术后组织病理示:Gleason评分7分者5例,9分者1例,病理分期T2a、T2c和T3a期各2例,切缘阳性1例。术后1个月平均PSA为0.014(0.007~0.033) ng/mL。所有患者尿管均留置2周,拔除尿管后48 h,3例患者完全自主控尿;拔管后1周,所有患者控尿能力较前增强,3例患者自主控尿;拔管后1个月,所有患者均完全自主控尿。结论 国产康多内窥镜手术机器人系统用于施行经腹膜外根治性前列腺切除及尿道周围全重建术具有良好的安全性和有效性,术后短期随访手术效果满意。Abstract: Objective To present the initial experience of extraperitoneal radical prostatectomy and total anatomical reconstruction with Kangduo endoscopic surgical robot system, and evaluate its safety and effectiveness.Methods From May 20 2021 to June 20 2021, the clinical data of patients who underwent extraperitoneal radical prostatectomy and total anatomical reconstruction with Kangduo surgical robot system in our institute were collected prospectively. The operation process was described. The key indicators to be investigated include, operation time, blood loss, length of hospital stay, perioperative complications, postoperative pathology, serum prostate specific antigen (PSA) one month after surgery, and urinary continence after catheter removal. The patient was defined as continent if no more than one diaper pad was needed per day, or no more than 20-gram urine leakage on the 24 h pad weight test.Results This study included 6 patients with a mean age of 65 (58-72) years, a mean body mass index of 25.3 (20.8-28.0) kg/m2, a mean prostate volume of 47.3 (27.0-86.0) mL. The mean preoperative PSA was 10.51 (6.50-17.98) ng/mL. Biopsy showed that one case with Gleason score 6 and 5 cases with Gleason score 7. Clinical stage showed that T2b in 2 cases and T2c in 4 cases. There were 2 cases with a history of abdominal and pelvic surgery (both were appendectomy). All operations were implemented successfully without intraoperative complications or any other adverse events associated with the instrument. The mean operation time was 138 (120-154) min, mean docking time was 5.7 (2.5-9.8) min, mean operative time for robotic arm was 96 (82-116) min, mean time for vesico-urethral anastomosis was 15.9 (12.2-25.7) min, and the mean estimated blood loss was 85 (10-200) mL. The mean postoperative hospital stay was 6 (4-10) days, and all patients had no Clavien-Dindo Ⅱ-Ⅴ complications within one month after surgery. Postoperative pathology: five cases with Gleason score 7 and one case with Gleason score 9, stage pT2a in 2 cases, stage pT2c in 2 cases, and stage pT3a in 2 cases, positive margin in one case. The mean PSA one month after surgery was 0.014 (0.007-0.033) ng/mL. Three patients recover urinary continence, 48 hours after the catheter removal. The ability of urinary continence of all patients were improved, one week after the catheter removal. All patients recover urinary continence, one month after the catheter removal.Conclusion Kangduo endoscopic surgical robot system has good safety and effectiveness for extraperitoneal radical prostatectomy and total anatomical reconstruction. The outcomes were satisfactory in short-term follow-up.
-

-
表 1 患者一般资料
编号 年龄/岁 BMI/ (kg·m-2) 前列腺体积/ mL 腹盆部手术史 术前PSA/ (ng·mL-1) 穿刺病理Gleason评分/分 临床分期 1 65 28.0 63 无 17.98 3+4 T2c 2 67 26.2 45 无 8.00 3+4 T2b 3 72 23.1 86 无 11.90 3+4 T2c 4 60 20.8 28 阑尾切除术 12.10 3+3 T2b 5 58 25.8 35 无 6.61 4+3 T2c 6 66 27.7 27 阑尾切除术 6.50 3+4 T2c 表 2 手术参数和术后相关信息
编号 对接用时/min 手术总时长/min 机械臂操作时长/min 尿道吻合用时/min 出血量/mL 神经保留 术后住院天数/d 组织病理Gleason评分/分 病理分期 切缘 术后1个月PSA /(ng· mL-1) 1 5.3 154 109 25.7 50 是 8 3+4 T2a 阴性 0.033 2 3.8 149 116 12.9 200 是 6 3+4 T2a 阳性 0.008 3 6.5 126 87 16.8 50 否 4 3+4 T2c 阴性 0.015 4 9.8 140 96 12.2 10 是 4 3+4 T2c 阴性 0.009 5 2.5 120 86 12.8 100 否 10 4+3 T3a 阴性 0.012 6 6.5 140 82 14.9 100 否 5 4+5 T3a 阴性 0.007 表 3 术后短期内控尿随访信息
编号 拔除尿管后48 h 拔除尿管后1周 拔除尿管后1个月 漏尿克数/g 24 h使用尿垫个数 漏尿克数/g 24 h使用尿垫个数 漏尿克数/g 24 h使用尿垫个数 1 430 2 90 2 3 1 2 1000 4 400 2 250 1 3 20 1 0 0 0 0 4 30 1 10 1 0 1 5 50 1 4 1 0 0 6 180 4 150 3 15 1 -
[1] von Eyben FE. Re: Philip Cornford, Roderick C.N. van den Bergh, Erik Briers, et al. EAU-ESTRO-ESUR-SIOG Guidelines on Prostate Cancer. Part Ⅱ-2020 Update: Treatment of Relapsing and Metastatic Prostate Cancer. Eur Urol, 2021, 79: 263-282[J]. Eur Urol, 2021, 79(6): e176. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2021.02.042
[2] Nyberg M, Hugosson J, Wiklund P, et al. Functional and Oncologic Outcomes Between Open and Robotic Radical Prostatectomy at 24-month Follow-up in the Swedish LAPPRO Trial[J]. Eur Urol Oncol, 2018, 1(5): 353-360. doi: 10.1016/j.euo.2018.04.012
[3] Coughlin GD, Yaxley JW, Chambers SK, et al. Robot-assisted laparoscopic prostatectomy versus open radical retropubic prostatectomy: 24-month outcomes from a randomised controlled study[J]. Lancet Oncol, 2018, 19(8): 1051-1060. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(18)30357-7
[4] Lowrance WT, Eastham JA, Savage C, et al. Contemporary open and robotic radical prostatectomy practice patterns among urologists in the United States[J]. J Urol, 2012, 187(6): 2087-2092. doi: 10.1016/j.juro.2012.01.061
[5] Fanfani F, Restaino S, Gueli Alletti S, et al. TELELAP ALF-X Robotic-assisted Laparoscopic Hysterectomy: Feasibility and Perioperative Outcomes[J]. J Minim Invasive Gynecol, 2015, 22(6): 1011-1017. doi: 10.1016/j.jmig.2015.05.004
[6] Fanfani F, Monterossi G, Fagotti A, et al. The new robotic TELELAP ALF-X in gynecological surgery: single-center experience[J]. Surg Endosc, 2016, 30(1): 215-221. doi: 10.1007/s00464-015-4187-9
[7] Kim DK, Park DW, Rha KH. Robot-assisted Partial Nephrectomy with the REVO-I Robot Platform in Porcine Models[J]. Eur Urol, 2016, 69(3): 541-542. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2015.11.024
[8] Samalavicius NE, Janusonis V, Siaulys R, et al. Robotic surgery using Senhance((R))robotic platform: single center experience with first 100 cases[J]. J Robot Surg, 2020, 14(2): 371-376. doi: 10.1007/s11701-019-01000-6
[9] Thomas BC, Slack M, Hussain M, et al. Preclinical Evaluation of the Versius Surgical System, a New Robot-assisted Surgical Device for Use in Minimal Access Renal and Prostate Surgery[J]. Eur Urol Focus, 2021, 7(2): 444-452. doi: 10.1016/j.euf.2020.01.011
[10] Dai X, Fan S, Hao H, et al. Comparison of KD-SR-01 robotic partial nephrectomy and 3D-laparoscopic partial nephrectomy from an operative and ergonomic perspective: A prospective randomized controlled study in porcine models[J]. Int J Med Robot, 2021, 17(2): e2187.
[11] 熊盛炜, 贯华, 代晓飞, 等. 康多内镜手术机器人系统改良离断式"V"型肾盂瓣技术治疗成人马蹄肾合并肾积水1例[J/OL]. 泌尿外科杂志(电子版), 2021, 13(1): 29-31.
[12] 李学松, 樊书菠, 熊盛炜, 等. 国产内窥镜手术机器人系统在肾部分切除术中的初步临床应用[J]. 中华泌尿外科杂志, 2021, 42(5): 375-380. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112330-20210323-00144
[13] Fan S, Dai X, Yang K, et al. Robot-assisted pyeloplasty using a new robotic system, the KangDuo-Surgical Robot-01: a prospective, single-centre, single-arm clinical study[J]. BJU Int, 2021, 128(2): 162-165. doi: 10.1111/bju.15396
[14] Leow JJ, Chang SL, Meyer CP, et al. Robot-assisted Versus Open Radical Prostatectomy: A Contemporary Analysis of an All-payer Discharge Database[J]. Eur Urol, 2016, 70(5): 837-845. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2016.01.044
[15] 瞿旻, 林恒之, 王海峰, 等. 机器人辅助腹腔镜下根治性前列腺切除术治疗高危前列腺癌400例报告[J]. 中华泌尿外科杂志, 2017, 38(6): 424-427. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1000-6702.2017.06.007
[16] 陈晶, 梁朝朝, 周骏, 等. 达芬奇机器人辅助腹腔镜泌尿外科手术500例回顾性分析[J]. 微创泌尿外科杂志, 2018, 7(2): 77-82.
[17] 陈正军, 吕倩, 范世达, 等. 四孔法腹膜外机器人辅助腹腔镜前列腺根治性切除术22例报道[J]. 机器人外科学杂志(中英文), 2020, 1(4): 266-270.
[18] 袁仁斌, 曹敏, 潘玉龙, 等. 经腹膜外及经腹腔机器人辅助前列腺癌根治术疗效的Meta分析[J]. 四川医学, 2021, 42(5): 453-456. doi: 10.16252/j.cnki.issn1004-0501-2021.05.005
[19] Menon M, Shrivastava A, Kaul S, et al. Vattikuti Institute prostatectomy: contemporary technique and analysis of results[J]. Eur Urol, 2007, 51(3): 648-657;discussion 657-658. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2006.10.055
[20] Novara G, Ficarra V, Rosen RC, et al. Systematic review and meta-analysis of perioperative outcomes and complications after robot-assisted radical prostatectomy[J]. Eur Urol, 2012, 62(3): 431-452. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2012.05.044
[21] Yang CW, Wang HH, Hassouna MF, et al. Prediction of a positive surgical margin and biochemical recurrence after robot-assisted radical prostatectomy[J]. Sci Rep, 2021, 11(1): 14329. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-93860-y
[22] 郝瀚, 刘越, 陈宇珂, 等. 机器人辅助前列腺癌根治术后患者的控尿恢复时间[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(4): 697-703.
[23] Salazar A, Regis L, Planas J, et al. Early continence after radical prostatectomy: A systematic review[J]. Actas Urol Esp(Engl Ed), 2019, 43(10): 526-535. doi: 10.1016/j.acuro.2019.06.003
[24] Student VJ, Vidlar A, Grepl M, et al. Advanced Reconstruction of Vesicourethral Support(ARVUS)during Robot-assisted Radical Prostatectomy: One-year Functional Outcomes in a Two-group Randomised Controlled Trial[J]. Eur Urol, 2017, 71(5): 822-830. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2016.05.032
[25] Porpiglia F, Bertolo R, Manfredi M, et al. Total Anatomical Reconstruction During Robot-assisted Radical Prostatectomy: Implications on Early Recovery of Urinary Continence[J]. Eur Urol, 2016, 69(3): 485-495.
[26] Manfredi M, Checcucci E, Fiori C, et al. Total anatomical reconstruction during robot-assisted radical prostatectomy: focus on urinary continence recovery and related complications after 1000 procedures[J]. BJU Int, 2019, 124(3): 477-486.
[27] Song W, Kim CK, Park BK, et al. Impact of preoperative and postoperative membranous urethral length measured by 3 Tesla magnetic resonance imaging on urinary continence recovery after robotic-assisted radical prostatectomy[J]. Can Urol Assoc J, 2017, 11(3-4): E93-E99.
[28] Mungovan SF, Sandhu JS, Akin O, et al. Preoperative Membranous Urethral Length Measurement and Continence Recovery Following Radical Prostatectomy: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis[J]. Eur Urol, 2017, 71(3): 368-378.
[29] Michl U, Tennstedt P, Feldmeier L, et al. Nerve-sparing Surgery Technique, Not the Preservation of the Neurovascular Bundles, Leads to Improved Long-term Continence Rates After Radical Prostatectomy[J]. Eur Urol, 2016, 69(4): 584-589.
[30] Park YH, Kwon OS, Hong SH, et al. Effect of Nerve-Sparing Radical Prostatectomy on Urinary Continence in Patients With Preoperative Erectile Dysfunction[J]. Int Neurourol J, 2016, 20(1): 69-74.
[31] Wang W, Li J, Wang S, et al. System design and animal experiment study of a novel minimally invasive surgical robot[J]. Int J Med Robot, 2016, 12(1): 73-84.
[32] 刘荣, 赵国栋, 孙玉宁, 等. 5G远程机器人手术动物实验研究[J/OL]. 中华腔镜外科杂志(电子版), 2019, 12(1): 45-48.
-




 下载:
下载: