-
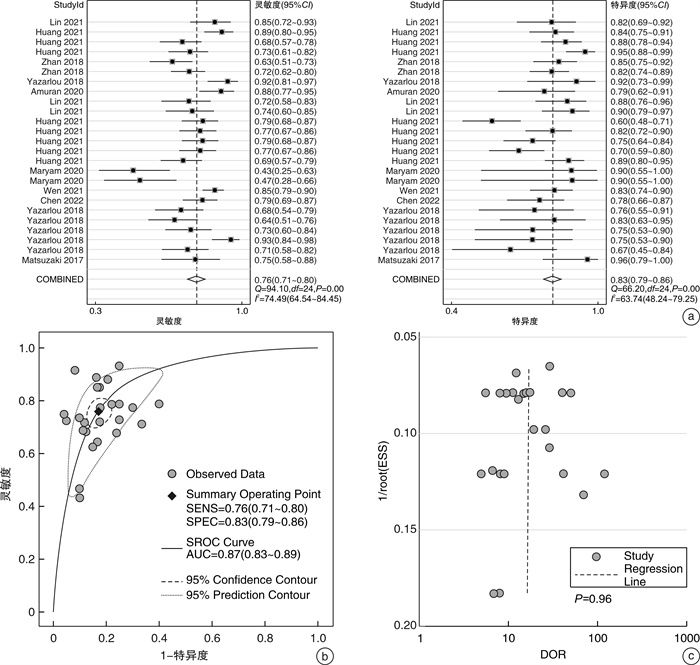
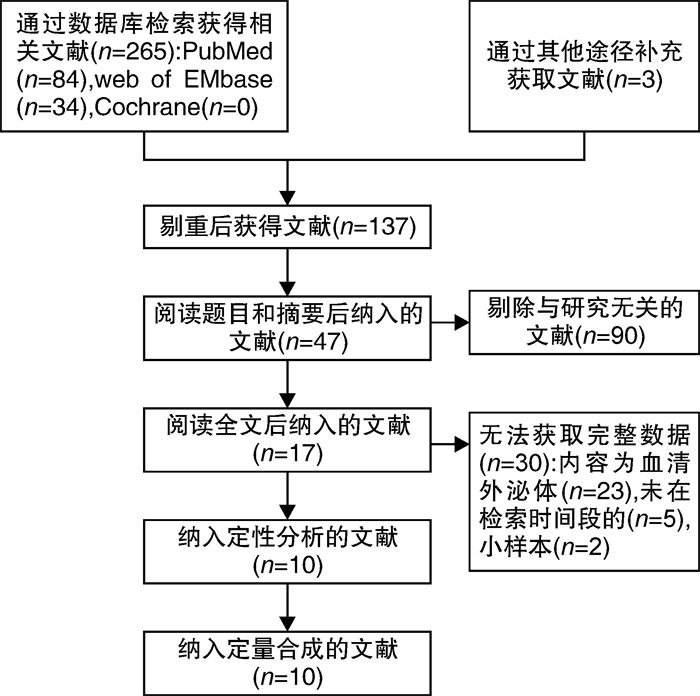
摘要: 目的 外泌体(Exosomes)可由泌尿系统肿瘤细胞直接释放到尿液中,因此检测尿Exosomes在泌尿系统肿瘤的非侵入性诊断和监测方面具有很大的潜力。本研究的目的是系统地评估尿外泌体在膀胱癌中的诊断价值。方法 计算机检索PubMed、Web of Science、Cochrane Library、Embase等数据库,截止到2022年4月1日。数据采用Stata 12.0和Meta-Disc 1.4软件进行统计分析。采用随机效应模型合并分析灵敏度、特异度、阳性似然比、阴性似然比和诊断优势比。通过受试者工作特征(ROC)曲线和曲线下面积(AUC)估计整体检验效能。结果 确定有10篇文章中的26项研究被纳入meta分析,共有1748例患者和1357例健康对照组。合并的灵敏度和特异度分别为0.76(95%CI:0.71~0.80)和0.83(95%CI:0.79~0.86);合并阳性似然比为4.45(95%CI:3.66~5.41),阴性似然比为0.29(95%CI:0.25~0.35),诊断优势比为15.23(95%CI:11.53~20.12)。合并的AUC为0.87(95%CI:0.83~0.89)。亚组分析表明,多分子联合检测对BCa诊断具有较高的准确性。结论 尿外泌体可作为膀胱癌诊断的早期临床筛选和辅助检查。临床仍需进行高质量前瞻性的病例对照研究验证,以推广尿外泌体在早期膀胱癌中的诊断作用。Abstract: Objective Urinary exosomes are outstanding as novel cancer biomarkers with great prospects. Hence, we aimed to summarize the overall diagnostic assessment of urinary exosomes for bladder cancer (Bca).Methods We searched PubMed, Cochrane Library, Web of Science and Scopus for studies published before April 1st, 2022. We applied the software of Meta-Disc 1.4 and Stata 12.0 to the meta-analysis. The pooled sensitivity, specificity, positive and negative likelihood ratios, diagnostic odds ratio, and area under the curve (AUC) were analyzed using random effect model. The overall test efficacy was estimated using the summary ROC curve and the AUC.Results A total of 10 studies from 26 articles were included in the meta-analysis, with a total of 1748 patients and 1357 controls. The pooled sensitivity and specificity were 0.76 (95%CI: 0.71-0.80) and 0.83 (95%CI: 0.79-0.86), respectively. The pooled positive likelihood ratio was 4.45 (95%CI: 3.66-5.41), negative likelihood ratio was 0.29 (95%CI: 0.25-0.35), and diagnostic odds ratio was 15.23 (95%CI: 11.53-20.12). The pooled AUC was 0.87 (95%CI: 0.83-0.89). Subgroup analyses indicated that the multiple urinary exosomes assays showed high accuracies in diagnosing BCa.Conclusion The urinary exosomes assays may serve as a potential noninvasive diagnostic tool for the detection of BCa. However, the clinical application of urinary exosomes assays for BCa diagnosis still needs further validation by large prospective studies.
-
Key words:
- urinary exosomes /
- bladder cancer /
- diagnostic accuracy /
- meta-analysis
-

-
表 1 纳入研究的基本特征
研究 年份 病例/对照 靶分子检测 SEN/% SPE/% Matsuzaki[10] 2017 36/24 miR-21-5p 75.0 95.8 Güllü[11] 2020 59/34 Panel of miRNAs① 80.0 88.2 Yazarlou[12] 2018 59/24 MAGE-B4 71.7 66.7 Yazarlou[13] 2018 59/24 UCA1-201
UCA1-203
MALAT1
LINC00355
lncRNA Panel ②93.0
72.4
63.8
68.0
92.075.4
75.0
83.3
79.2
91.7Zhan[14] 2018 104/104
80/80Panel of lncRNAs③ 70.2
62.585.6
85.0Chen[15] 2022 89/63 TERC 78.65 77.78 Wen[16] 2021 168/90 CA9 mRNA 85.18 83.15 Abbastabar[17] 2020 30/10 ANRIL
PCAT-146.67
43.387.5
87.5Huang[18] 2021 80/80 KLHDC7B
CASP14
PRSS1
MIR205HG
GAS5
mRNA panel④
lncRNA panel⑤
Five RNA panel68.5
77.5
78.1
77.3
78.7
71.9
67.1
88.588.3
70.6
75.0
83.1
60.3
95.2
87.1
83.3Lin[19] 2021 53/51 miR-93-5P
miR-516a-5P
panel of miRNAs⑥74.1
72.9
85.290.2
89.9
82.4注:①miR-19b1-5p+miR-136-3p+miR139-5p+urinary APE1/Ref1+BLCA-4,CRK;②UCA1-201+UCA1-203+MALAT1+LINC00355;③MALAT1+PCAT-1+SPRY4-IT1;④KLHDC7+CASP14+PRSS1;⑤MIR205HG+GAS5;⑥miR-93-5P+miR-516a-5P。 表 2 亚组分析结果
亚组 SEN(95%CI) SPE(95%CI) PLR(95%CI) NLR(95%CI) DOR(95%CI) AUC(95%CI) SUE 0.74 (0.68~0.79) 0.81 (0.76~0.86) 3.16 (3.10~5.05) 0.32 (0.27~0.39) 12.42 (9.10~16.95) 0.85 (0.81~0.88) MUE 0.80 (0.71~0.86) 0.86 (0.82~0.89) 5.59 (4.38~7.13) 0.24 (0.16~0.34) 23.03 (13.81~38.41) 0.89 (0.86~0.92) Overall 0.76 (0.71~0.80) 0.83 (0.79~0.86) 4.45 (3.66~5.41) 0.29 (0.25~0.35) 15.23 (11.53~20.12) 0.87 (0.83~0.89) -
[1] 殷金成, 陈建华, 沈伟, 等. miR-802负调控CYLD促进膀胱尿路上皮癌病理发生与发展[J]. 临床泌尿外科杂志, 2021, 34(5): 371-377. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.1001-1420.2019.05.009
[2] Lokeshwar VB, Soloway MS. Current bladder tumor tests: does their projected utility fulfill clinical necessity?[J]. J Urol, 2001, 165(4): 1067-1077. doi: 10.1016/S0022-5347(05)66428-2
[3] 林智谦, 王世博, 梁英, 等. 液体活检技术在前列腺癌中的应用及研究进展[J]. 临床泌尿外科杂志, 2021, 34(2): 154-156, 160. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.1001-1420.2019.02.017
[4] Yoshida K, Tsuda M, Matsumoto R, et al. Exosomes containing ErbB2/CRK induce vascular growth in premetastatic niches and promote metastasis of bladder cancer[J]. Cancer Sci, 2019, 110(7): 2119-2132. doi: 10.1111/cas.14080
[5] Chen C, Luo Y, He W, et al. Exosomal long noncoding RNA LNMAT2 promotes lymphatic metastasis in bladder cancer[J]. J Clin Invest, 2020, 130(1): 404-421.
[6] Chen C, Zheng H, Luo Y, et al. Sumoylation promotes extracellular vesicle-mediated transmission of lncRNA ELNAT1 and lymph node metastasis in bladder cancer[J]. J Clin Invest, 2021, 131(8): e146431. doi: 10.1172/JCI146431
[7] Wortzel I, Dror S, Kenific CM, et al. Exosome-mediated metastasis: communication from a distance[J]. Dev Cell, 2019, 49(3): 347-360. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2019.04.011
[8] 王倩倩, 刘天琦, 蒲小勇, 等. 尿液标记物在前列腺癌诊断中的价值探讨[J]. 临床泌尿外科杂志, 2021, 36(9): 749-753, 758. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.1001-1420.2021.09.017
[9] Whiting PF, Rutjes AW, Westwood ME, et al. QUADAS-2: a revised tool for the quality assessment of diagnostic accuracy studies[J]. Ann Intern Med, 2011, 155(8): 529-536. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-155-8-201110180-00009
[10] Matsuzaki K, Fujita K, Jingushi K, et al. MiR-21-5p in urinary extracellular vesicles is a novel biomarker of urothelial carcinoma[J]. Oncotarget, 2017, 8(15): 24668-24678. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.14969
[11] Güllü Amuran G, Tinay I, Filinte D, et al. Urinary micro-RNA expressions and protein concentrations may differentiate bladder cancer patients from healthy controls[J]. Int Urol Nephrol, 2020, 52(3): 461-468. doi: 10.1007/s11255-019-02328-6
[12] Yazarlou F, Mowla SJ, Oskooei VK, et al. Urine exosome gene expression of cancer-testis antigens for prediction of bladder carcinoma[J]. Cancer Manag Res, 2018, 10: 5373-5381. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S180389
[13] Yazarlou F, Modarressi MH, Mowla SJ, et al. Urinary exosomal expression of long non-coding RNAs as diagnostic marker in bladder cancer[J]. Cancer Manag Res, 2018, 10: 6357-6365. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S186108
[14] Zhan Y, Du L, Wang L, et al. Expression signatures of exosomal long non-coding RNAs in urine serve as novel non-invasive biomarkers for diagnosis and recurrence prediction of bladder cancer[J]. Mol Cancer, 2018, 17(1): 142. doi: 10.1186/s12943-018-0893-y
[15] Chen C, Shang A, Sun Z, et al. Urinary Exosomal long noncoding RNA TERC as a noninvasive diagnostic and prognostic biomarker for bladder urothelial carcinoma[J]. J Immunol Res, 2022, 2022: 9038808.
[16] Wen J, Yang T, Mallouk N, et al. Urinary exosomal CA9 mRNA as a novel liquid biopsy for molecular diagnosis of bladder cancer[J]. Int J Nanomedicine, 2021, 16: 4805-4811. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S312322
[17] Abbastabar M, Sarfi M, Golestani A, et al. Tumor-derived urinary exosomal long non-coding RNAs as diagnostic biomarkers for bladder cancer[J]. EXCLI J, 2020, 19: 301-310.
[18] Huang H, Du J, Jin B, et al. Combination of urine exosomal mRNAs and lncRNAs as novel diagnostic biomarkers for bladder cancer[J]. Front Oncol, 2021, 11: 667212. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.667212
[19] Lin H, Shi X, Li H, et al. Urinary exosomal miRNAs as biomarkers of bladder Cancer and experimental verification of mechanism of miR-93-5p in bladder Cancer[J]. BMC Cancer, 2021, 21(1): 1293. doi: 10.1186/s12885-021-08926-x
[20] Caraguel CG, Vanderstichel R. The two-step Fagan's nomogram: ad hoc interpretation of a diagnostic test result without calculation[J]. Evid Based Med, 2013, 18(4): 125-128. doi: 10.1136/eb-2013-101243
[21] Georgantzoglou N, Pergaris A, Masaoutis C, et al. Extracellular vesicles as biomarkers carriers in bladder cancer: diagnosis, surveillance, and treatment[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2021, 22(5): 2744. doi: 10.3390/ijms22052744
[22] Pegtel DM, Gould SJ. Exosomes[J]. Annu Rev Biochem, 2019, 88: 487-514. doi: 10.1146/annurev-biochem-013118-111902
[23] Melo SA, Luecke LB, Kahlert C, et al. Glypican-1 identifies cancer exosomes and detects early pancreatic cancer[J]. Nature, 2015, 523(7559): 177-182. doi: 10.1038/nature14581
[24] Zhou H, Yuen PS, Pisitkun T, et al. Collection, storage, preservation, and normalization of human urinary exosomes for biomarker discovery[J]. Kidney Int, 2006, 69(8): 1471-1476. doi: 10.1038/sj.ki.5000273
[25] Xu Y, Lou J, Yu M, et al. Urinary exosomes diagnosis of urological tumors: a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Front Oncol, 2021, 11: 734587. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.734587
-

| 引用本文: | 刘亮程, 曹贵华, 滕东海, 等. 尿外泌体检测对膀胱癌诊断性能的meta分析[J]. 临床泌尿外科杂志, 2023, 38(2): 114-119. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.1001-1420.2023.02.007 |
| Citation: | LIU Liangcheng, CAO Guihua, TENG Donghai, et al. Urinary exosomes as biomarkers for bladder cancer: a diagnostic meta-analysis[J]. J Clin Urol, 2023, 38(2): 114-119. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.1001-1420.2023.02.007 |
- Figure 1.
- Figure 2.
- Figure 3.



 下载:
下载: