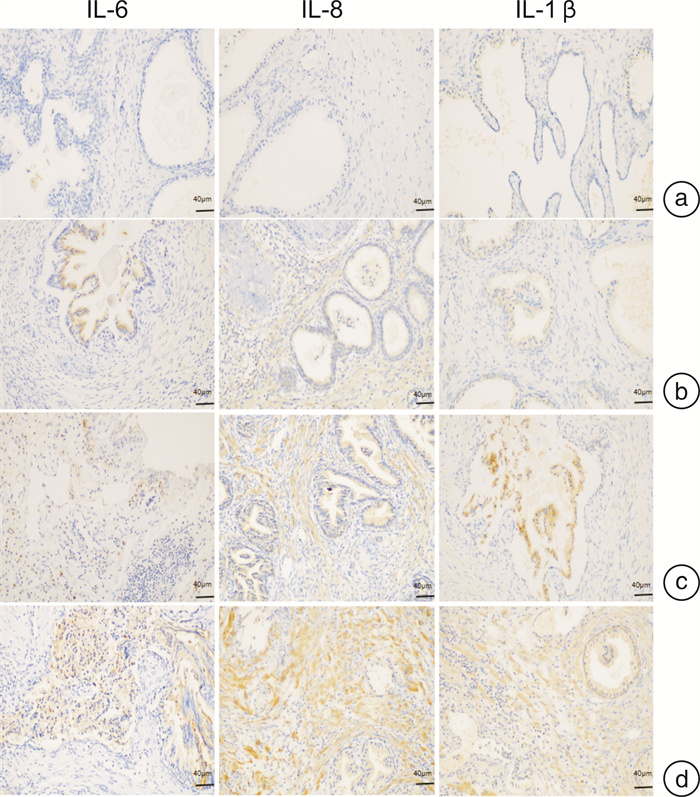
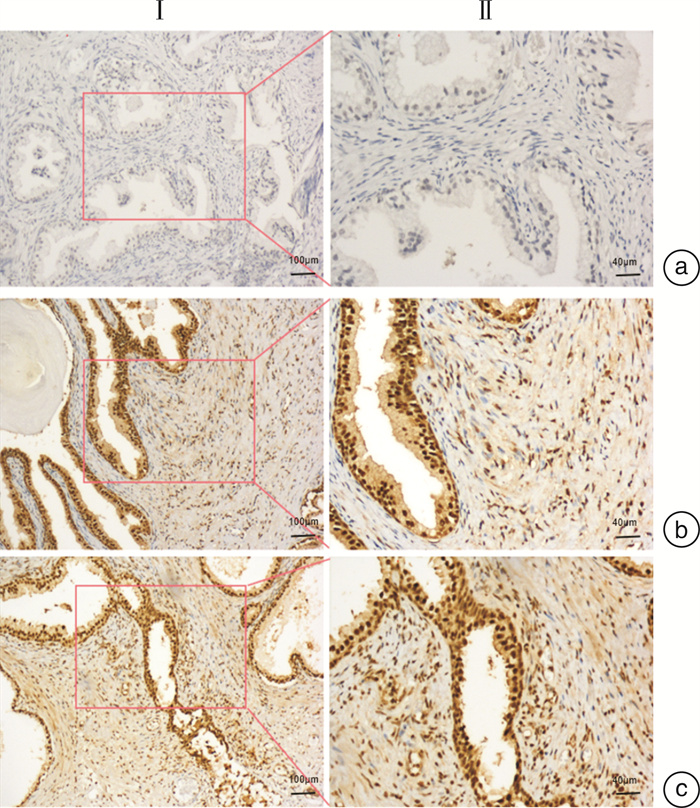
Expression of circadian clock protein Rev-erbα in prostate tissues of different degrees of inflammation
-
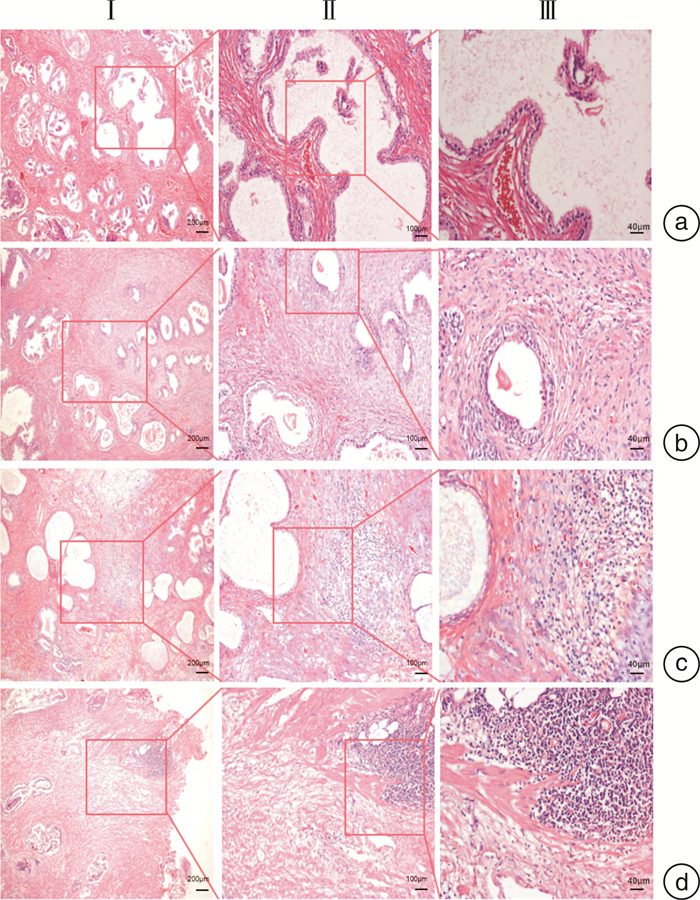
摘要: 目的 探讨良性前列腺增生(BPH)人群中前列腺组织炎症与生物钟蛋白Rev-erbα表达的相关性。方法 收集诊断为BPH并行经尿道前列腺手术的前列腺组织标本。对前列腺组织进行炎症程度分级。免疫组化(IHC)评估前列腺组织中CD4、CD8、白细胞介素(IL)-6、IL-8、IL-1β和Rev-erbα的表达情况;qRT-PCR检测前列腺组织中IL-1β、IL-6和IL-8和Rev-erbα的表达水平。分析前列腺组织炎症程度与前列腺组织Rev-erbα表达强度的相关性。结果 收集84例BPH组织标本,73例(86.9%)伴有不同程度的组织炎症。IHC提示前列腺组织中不同炎症程度与炎症因子(IL-6、IL-8和IL-1β)表达强度一致;组织炎症细胞中,CD4+细胞数量远多于CD8+细胞数量;前列腺组织中Rev-erbα的表达强度与前列腺组织炎症程度呈负相关,其相关系数为-0.691(P < 0.001)。qRT-PCR提示不同的前列腺组织炎症程度与组织中IL-1β、IL-6、IL-8的mRNA表达差异趋势一致,与组织中Rev-erbα的mRNA表达差异趋势相反。结论 生物钟蛋白Rev-erbα可能在前列腺组织中有降低组织局部炎症的作用,可能成为防治前列腺组织炎症的潜在靶点。
-
关键词:
- 良性前列腺增生 /
- 组织炎症 /
- 生物钟蛋白Rev-erbα
Abstract: Objective To investigate the relationship between inflammation of prostate tissue and the expression of clock protein Rev-erbα in prostatic tissues.Methods Prostate tissue specimens diagnosed as BPH and undergoing transurethral prostate surgery were collected. The inflammation degree of prostate tissue was graded. Immunohistochemistry(IHC) was used to evaluate the expression of CD4, CD8, IL-6, IL-8, IL-1β and Rev-erbα in prostate tissue, and the expression level of IL-1β, IL-6, IL-8 and Rev-erbα were detected by qRT-PCR in prostate tissues. The correlation between the degree of inflammation in prostate tissue and the expression intensity of Rev-erbα in prostate tissue was analyzed.Results A total of 84 cases of prostate tissue specimens were collected, of which 73 cases(86.9%) were accompanied by tissue inflammation. IHC showed that different levels of inflammation in prostate tissue were consistent with the expression intensity of inflammatory factors(IL-6, IL-8 and IL-1β), and the number of CD4+ cells was far greater than the number of CD8+ cells. The expression intensity of Rev-erbα in prostate tissue was negatively correlated with the degree inflammation in prostate tissues, and the correlation coefficient was-0.691(P < 0.001). QRT-PCR indicated the trend of differences in the expression of IL-1β, IL-6 and IL-8 was consistent with the trend of the degree of inflammation in prostate tissues, but the trend of differences in the expression of Rev-erbα was opposite to the trend of the degree of inflammation in prostate tissues.Conclusion The circadian clock protein Rev-erbα may have the effect of reducing local inflammation in the prostate tissue, and it may become a potential target for the prevention and treatment of inflammation in the prostate tissue. -

-
表 1 前列腺组织Rev-erbα的表达强度与组织炎症程度相关性分析
生物钟蛋白 表达强度 前列腺组织炎症程度/例 相关性 无(11例) 轻度(30例) 中度(31例) 重度(12例) r P Rev-erbα 轻度表达 0 3 12 11 -0.691 < 0.001 中度表达 0 14 17 1 高度表达 11 13 2 0 -
[1] 黄健. 中国泌尿外科和男科疾病诊断治疗指南: 第1版[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2020: 207-208.
[2] 周硕明, 朱自强, 康健. 炎症小体与前列腺炎及代谢综合征所致良性前列腺增生关系的研究进展[J]. 临床泌尿外科杂志, 2020, 35(9): 744-747. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.1001-1420.2020.09.015
[3] Nickel JC, Roehrborn CG, O'Leary MP, et al. The relationship between prostate in flammation and lower urinary tract symptoms: Examination of baseline data from the REDUCE Trial[J]. Eur Urol, 2008, 54(6): 1379-1384. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2007.11.026
[4] McLaren ID, Jerde TJ, Bushman W. Role of interleukins, IGF and stem cells in BPH[J]. Differentiation, 2011, 82(4-5): 237-243. doi: 10.1016/j.diff.2011.06.001
[5] Song L, Zhu Y, Han P, et al. A retrospective study: correlation of histologic inflammation in biopsy specimens of Chinese men undergoing surgery for benign prostatic hyperplasia with serum prostate-specific antigen[J]. Urology, 2011, 77(3): 688-692. doi: 10.1016/j.urology.2010.07.493
[6] Lo HC, Yu DS, Gao HW, et al. IL-27/IL-27RA signaling may modulate inflammation and progression of benign prostatic hyperplasia via suppressing the LPS/TLR4 pathway[J]. Transl Cancer Res, 2020, 9(8): 4618-4634. doi: 10.21037/tcr-20-1509
[7] 彭彩霞, 史晓凤, 李昱卓, 等. 代谢综合征诱导炎症反应与下尿路症状相关性研究进展[J]. 临床泌尿外科杂志, 2019, 34(11): 920-925. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.1001-1420.2019.11.018
[8] Abele SH, Meadows KE, Medeiros D, et al. Time is on the Immune System's Side, Yes it is[J]. Yale J Biol Med, 2019, 92(2): 225-231.
[9] Zhang G, Li J, Purkayastha S, et al. Hypothalamic programming of systemic ageing involving IKK-beta, NF-kappaB and GnRH[J]. Nature, 2013, 497(7448): 211-216. doi: 10.1038/nature12143
[10] Osborn O, Olefsky JM. The cellular and signaling networks linking the immune system and metabolism in disease[J]. Nat Med, 2012, 18(3): 363-374. doi: 10.1038/nm.2627
[11] Cho H, Zhao X, Hatori M, et al. Regulation of circadian behaviour and metabolism by REV-ERB-alpha and REV-ERB-beta[J]. Nature, 2012, 485(7396): 123-127. doi: 10.1038/nature11048
[12] Gibbs JE, Blaikley J, Beesley S, et al. The nuclear receptor REV-ERBalpha mediates circadian regulation of innate immunity through selective regulation of inflammatory cytokines[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2012, 109(2): 582-587. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1106750109
[13] Baxter M, Ray DW. Circadian rhythms in innate immunity and stress responses[J]. Immunology, 2020, 161(4): 261-267. doi: 10.1111/imm.13166
[14] Axiotis CA, Monteagudo C, Merino MJ, et al. Immunohistochemical detection of P-glycoprotein in endometrial adenocarcinoma[J]. Am J Pathol, 1991, 138(4): 799-806.
[15] GBD 2017 Disease and Injury Incidence and Prevalence Collaborators. Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 354 diseases and injuries for 195 countries and territories, 1990-2017: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017[J]. Lancet. 2018, 392(10159): 1823-1824.
[16] 刘玉明, 陆凯, 葛建章, 等. 外周血雄雌激素水平及雄雌激素比与前列腺增生的相关性研究[J]. 临床泌尿外科杂志, 2021, 36(6): 464-467. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.1001-1420.2021.06.008
[17] 何跃, 杨璐, 魏强. 良性前列腺增生的可逆转危险因素[J]. 四川医学, 2022, 43(1): 99-102. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SCYX202201021.htm
[18] 冯子嫣, 任正举, 柳良仁, 等. 抗炎症介质治疗良性前列腺增生的研究进展[J]. 国际泌尿系统杂志, 2020, 40(6): 1147-1140.
[19] Yang M, Xu Z, Zhuang Z. Macrophages affect immune inflammation and proliferation in benign prostatic hyperplasia via androgen receptor and CD40/CD40 L signaling pathway[J]. Tissue Cell, 2020, 64: 101343. doi: 10.1016/j.tice.2020.101343
[20] De Nunzio C, Salonia A, Gacci M, et al. Inflammation is a target of medical treatment for lower urinary tract symptoms associated with benign prostatic hyperplasia[J]. World J Urol, 2020, 38(11): 2771-2779. doi: 10.1007/s00345-020-03106-1
[21] Rastrelli G, Vignozzi L, Corona G, et al. Testosterone and benign prostatic hyperplasia[J]. Sex Med Rev, 2019, 7(2): 259-271. doi: 10.1016/j.sxmr.2018.10.006
[22] Torkko KC, Wilson RS, Smith EE, et al. Prostate biopsy markers of inflammation are associated with risk of clinical progression of benign prostatic hyperplasia: findings from the MTOPS study[J]. J Urol, 2015, 194(2): 454-461. doi: 10.1016/j.juro.2015.03.103
[23] Steiner GE, Newman ME, Paikl D, et al. Expression and function of pro-inflammatory interleukin IL-17 and IL-17 receptor in normal, benign hyperplastic, and malignant prostate[J]. Prostate, 2003, 56(3): 171-182. doi: 10.1002/pros.10238
[24] Bostanci Y, Kazzazi A, Momtahen S, et al. Correlation between benign prostatic hyperplasia and inflammation[J]. Curr Opin Urol, 2013, 23(1): 5-10. doi: 10.1097/MOU.0b013e32835abd4a
[25] Musiek ES, Holtzman DM. Mechanisms linking circadian clocks, sleep, and neurodegeneration[J]. Science, 2016, 354(6315): 1004-1008. doi: 10.1126/science.aah4968
[26] Amir M, Chaudhari S, Wang R, et al. REV-ERBα Regulates TH17 Cell Development and Autoimmunity[J]. Cell Rep, 2018, 25(13): 3733-3749. e8.
[27] Chang C, Loo CS, Zhao X, et al. The nuclear receptor REV-ERBα modulates Th17 cell-mediated autoimmune disease[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2019, 116(37): 18528-18536.
[28] 何跃, 徐航, 冯德超, 等. 生物钟蛋Rev-erbα激动剂抑制高脂饮食诱导小鼠前列腺组织炎症的实验研究[J]. 中国实验动物学报, 2022, 30(4): 469-475. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGSD202204003.htm
-




 下载:
下载: