Clinical effect of 4.5Fr/8Fr ureteroscope assisted "Sheath-free Tract" percutaneous nephrolithotomy for the treatment of residual renal calculi
-
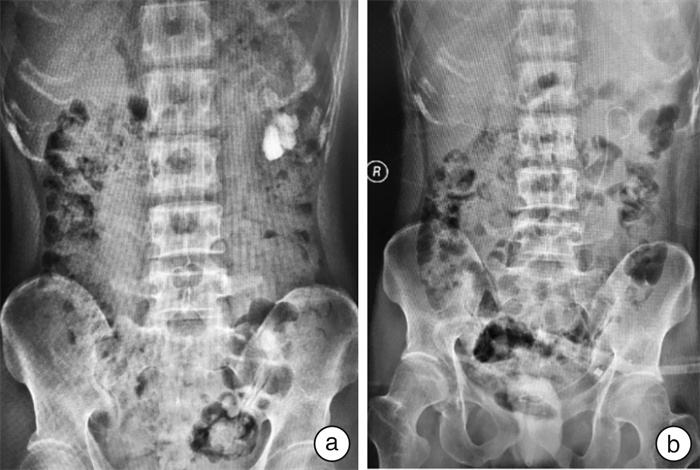
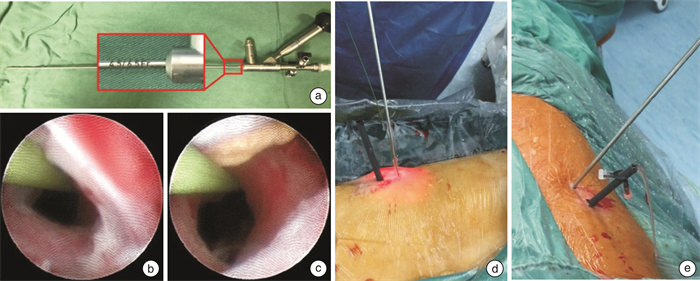
摘要: 探讨采用4.5Fr/8Fr输尿管硬镜建立无扩张鞘极微通道处理经皮肾镜取石术(PCNL)中残石的可行性及安全性。回顾性分析自2018年11月—2021年10月收治的19例复杂性上尿路结石患者的临床资料。其中,平行盏结石15例,鹿角形结石4例;男11例,女8例。本组19例患者均行PCNL,首先在超声引导下建立F18微通道(第1通道)进行碎石,然后利用4.5Fr/8Fr输尿管硬镜建立无扩张鞘极微通道(第2、3通道)处理肾盏内残石。本组19例患者均成功建立2~3个经皮肾镜通道,其中双通道16例,三通道3例。第1通道留置peel-away鞘,第2、第3通道未使用扩张鞘。一期清石率达89.5%(17/19);2例有残留结石,术后行ESWL后自行排出。平均手术时间为(64.7±22.1) min,平均住院天数为(7.4±2.3) d,术后2 h血红蛋白平均下降(7.8±2.9) g/L。术中及术后无严重出血及感染病例,无输血及动脉栓塞治疗病例,也无胸膜、结肠等腹腔脏器损伤等并发症发生。采用4.5Fr/8Fr输尿管硬镜建立无扩张鞘极微通道处理PCNL术中肾盏残石可行、安全、有效、且更微创,可成为处理PCNL术中残留结石的一种选择。Abstract: To explore the efficiency and safety of 4.5Fr/8Fr ureteroscope assisted "sheath-free tract" percutaneous nephrolithotomy (PCNL) in the treatment of residual renal calculi. There were 19 patients (11 males and 8 females; parallel calyx calculi in 15 cases and staghorn calculi in 4 cases) undergoing 4.5Fr/8Fr ureteroscope assisted "sheath-free tract" PCNL from November 2018 to October 2021. "Sheath-free tract" was applied during PCNL in all cases. After establishing a standard F18 minimal tract (primary tract) and performing lithotripsy with holmium laser, we used 4.5Fr/8Fr ureteroscope assisted "sheath-free tract" procedure to treat residual renal calculi. The "sheath-free tract" procedure were established successfully in all 19 cases, including two channels in 16 cases, and three channels in 3 cases. The peel-away sheath was placed in the primary tract, while no sheath was used in the second or third tract. The operations of 17 cases were successful, but later extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy was needed in another 2 cases because of residual stones. The mean operation duration was (64.7±22.1) minutes, hospital stay was (7.4±2.3) days, and hemoglobin decrease was (7.8±2.9) g/L, respectively. No patient received blood transfusion in the postoperative setting. There were no major complications. The 4.5Fr/8Fr ureteroscope assisted "sheath-free tract" PCNL is safe, minimally invasive, and effective with a low complication rate in the treatment of residual renal calculi.
-
Key words:
- residual renal stone /
- inflexible ureteroscope /
- sheath-free Tract /
- PCNL /
- parallel calyx
-

-
[1] Taguchi K, Cho SY, Ng AC, et al. The Urological Association of Asia clinical guideline for urinary stone disease[J]. Int J Urol, 2019, 26(7): 688-709. doi: 10.1111/iju.13957
[2] 李建兴, 肖博. 经皮肾镜手术通道的发展与创新[J]. 中华泌尿外科杂志, 2020, 35(9): 679-683. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCMW202009001.htm
[3] Bansal SS, Pawar PW, Sawant AS, et al. Predictive factors for fever and sepsis following percutaneous nephrolithotomy: A review of 580 patients[J]. Urol Ann, 2017, 9(3): 230-233. doi: 10.4103/UA.UA_166_16
[4] Yuan D, Zhang W, Zhan X, et al. Super-Mini Percutaneous Nephrolithotomy Reduces the Incidence of Postoperative Adverse Events in Pediatric Patients: A Retrospective Cohort Study[J]. Urol Int, 2019, 103(1): 81-88. doi: 10.1159/000495514
[5] Curry D, Srinivasan R, Kucheria R, et al. Supine Percutaneous Nephrolithotomy in the Galdako-Modified Valdivia Position: A High-Volume Single Center Experience[J]. J Endourol, 2017, 31(10): 1001-1006. doi: 10.1089/end.2017.0064
[6] Liang T, Zhao C, Wu G, et al. Multi-tract percutaneous nephrolithotomy combined with EMS lithotripsy for bilateral complex renal stones: our experience[J]. BMC Urol, 2017, 17(1): 15. doi: 10.1186/s12894-017-0205-7
[7] 袁晓龙, 乔丽娜, 朱岩, 等. 标准通道经皮肾镜取石一期多通道和单通道PCNL治疗复杂性肾结石疗效对比[J]. 潍坊医学院学报, 2021, 43(5): 355-357. doi: 10.16846/j.issn.1004-3101.2021.05.010
[8] Wang Z, Feng D, Cao D, et al. Comparison of safety and efficacy between single-tract and multiple-tract percutaneous nephrolithotomy treatment of complex renal calculi: a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Minerva Urol Nephrol, 2021, 73(6): 731-738.
[9] Hennessey DB, Kinnear NK, Troy A, et al. Mini PCNL for renal calculi: does size matter?[J]. BJU Int, 2017, 119 Suppl 5: 39-46.
[10] Choong S, DE LA Rosette J, Denstedt J, et al. Classification and standardized reporting of percutaneous nephrolithotomy(PCNL): International Alliance of Urolithiasis(IAU)Consensus Statements[J]. Minerva Urol Nephrol, 2022, 74(1): 110-118.
[11] Poudyal S. Current insights on haemorrhagic complications in percutaneous nephrolithotomy[J]. Asian J Urol, 2022, 9(1): 81-93. doi: 10.1016/j.ajur.2021.05.007
[12] Jung HD, Kim JC, Ahn HK, et al. Real-time simultaneous endoscopic combined intrarenal surgery with intermediate-supine position: Washout mechanism and transport technique[J]. Investig Clin Urol, 2018, 59(5): 348-354. doi: 10.4111/icu.2018.59.5.348
[13] Datta SN, Solanki R, Desai J. Prospective Outcomes of Ultra Mini Percutaneous Nephrolithotomy: A Consecutive Cohort Study[J]. J Urol, 2016, 195(3): 741-746. doi: 10.1016/j.juro.2015.07.123
[14] Simayi A, Liu Y, Yiming M, et al. Clinical application of super-mini PCNL(SMP)in the treatment of upper urinary tract stones under ultrasound guidance[J]. World J Urol, 2019, 37(5): 943-950. doi: 10.1007/s00345-018-2465-6
[15] Desai MR, Sharma R, Mishra S, et al. Single-step percutaneous nephrolithotomy(microperc): the initial clinical report[J]. J Urol, 2011, 186(1): 140-145. doi: 10.1016/j.juro.2011.03.029
[16] 夏金生, 李林, 洪波, 等. 基于倾向性评分匹配分析的经皮肾镜取石术后尿路感染的危险因素探讨[J]. 临床泌尿外科杂志, 2021, 36(12): 949-953. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCMW202112007.htm
[17] 张际青, 张军晖, 康宁, 等. 自制F4.85可视穿刺针联合输尿管通道鞘在超微经皮肾镜碎石术中的应用[J]. 中华泌尿外科杂志, 2017, 38(11): 852-856. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1000-6702.2017.11.012
[18] 梁兆军, 刘文武, 王军, 等. 经皮肾镜取石术中监测及控制肾盂内压力的研究进展[J]. 临床泌尿外科杂志, 2021, 36(7): 583-586. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCMW202107016.htm
-




 下载:
下载: