-
摘要: 目的 探索新型软性肾镜在经皮肾镜取石术(percutaneous nephrolithotomy,PCNL)中的应用效果。方法 回顾性分析2022年1月—2023年2月海军军医大学第一附属医院通过标准通道PCNL治疗的肾结石患者临床资料,依据术中是否使用新型软性肾镜将患者分为联合软性肾镜组和单用硬镜组;比较2组患者手术相关临床数据。结果 联合软性肾镜组52例,单用硬镜组42例,2组患者年龄[(55.9±11.3)岁vs (53.7±13.7)岁,P=0.407]、体重指数(BMI)[(24.7±3.3) kg/m2 vs (24.6±3.3) kg/m2,P=0.915]及结石最大径[(33.5±13.6) mm vs (39.0±17.0) mm,P=0.085]比较差异无统计学意义。联合软性肾镜组11例患者术中通过软性肾镜成功寻找到硬镜无法处理的残余结石并成功碎石取石。联合软性肾镜组结石清除率显著高于单用硬镜组的患者(84.6% vs 57.1%,P=0.003)且术后住院时间更短[(3.4±1.4) d vs (4.81±2.2) d,P < 0.001]。结论 超细、超短的新型电子软性肾镜可以有效检出单通道PCNL硬镜碎石后残留结石,提高结石清除率,缩短术后住院时间。Abstract: Objective To explore the effectiveness of a novel flexible nephroscope in percutaneous nephrolithotomy (PCNL).Methods From January 2022 to February 2023, a retrospective study was conducted on the clinical data of the patients with renal calculi who underwent PCNL with standard channel. Patients were divided into two groups according to whether the novel flexible electronic nephroscope was used during the operation: the combined flexible nephroscope group and the rigid nephroscope group. The clinical data of two groups were compared.Results There were 52 cases in the combined flexible nephroscope group and 42 cases in the rigid nephroscope group. Age ([55.9±11.3] years vs [53.7±13.7] years, P=0.407), BMI ([24.7±3.3] kg/m2vs [24.6±3.3] kg/m2, P=0.915) and maximum diameter of stone ([33.5±13.6] mm vs [39.0±17.0] mm, P=0.085) were not statistically significant between two groups. In 11 patients of the combined flexible nephroscope group, residual stones that could not be handled by the rigid nephroscope were successfully located and treated during surgery using the new flexible nephroscope, resulting in successful fragmentation and removal of the stones. The combined flexible nephroscope group had a significantly higher stone clearance rate than the rigid nephroscope group alone (84.6% vs 57.1%, P=0.003) and a shorter postoperative hospital stay ([3.4±1.4] d vs [4.81±2.2] d, P < 0.001).Conclusion The new ultra-fine and ultra-short electronic flexible nephroscope can effectively detect residual stones after single-channel rigid nephroscopy, improve the stone clearance rate and reduce postoperative hospital stay.
-
Key words:
- renal calculi /
- percutaneous nephroscope /
- flexible nephroscope
-

-
表 1 联合软性肾镜组与单用硬镜组基本资料比较
例,X±S 项目 联合软性肾镜组(52例) 单用硬镜组(42例) t χ2 P值 男/女 40/12 24/18 4.184 0.048 年龄/岁 55.9±11.3(31~81) 53.7±13.7(22~81) 0.833 0.407 BMI/(kg/m2) 24.7±3.3(16.5~36.7) 24.6±3.3(19.1~33.7) 0.107 0.915 结石最大径/mm 33.5±13.6(11.0~73.5) 39.0±17.0(13.3~79.1) -1.702 0.085 表 2 联合软性肾镜组与单用硬镜组手术资料比较
例(%),X±S 项目 联合软性肾镜组(52例) 单用硬镜组(42例) t χ2 P值 手术时间/min 99.1±44.6(35~245) 111.2±41.4(35~210) -1.355 0.179 结石清除率 44(84.6) 24(57.1) 8.764 0.003 残留结石总直径/mm 13.6±6.5(5.1~24.6) 19.2±9.6(6.0~45.0) -1.864 0.074 术后1 d血红蛋白下降量/(g/L) 8.7±9.5(-6.0~38.0) 11.3±12.9(-8.0~59.0) -1.111 0.269 住院天数/d 3.4±1.4(1~8) 4.8±2.2(2~14) -3.771 < 0.001 术后并发症率 5(9.6) 9(21.4) 2.558 0.096 -
[1] Cracco CM, Knoll T, Liatsikos EN, et al. Rigid-only versus combined rigid and flexible percutaneous nephrolithotomy: a systematic review[J]. Minerva Urol Nefrol, 2017, 69(4): 330-341. http://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28124870/
[2] Thomas K, Smith NC, Hegarty N, et al. The Guy's stone score——grading the complexity of percutaneous nephrolithotomy procedures[J]. Urology, 2011, 78(2): 277-281. doi: 10.1016/j.urology.2010.12.026
[3] Nottingham CU, Large T, Lingeman JE, et al. A Comparison of Perioperative Stone-Free Rates and Complications Following Unilateral, Single-Access Percutaneous Nephrolithotomy by Access Location in 767 Patients[J]. Urology, 2020, 142: 70-75. doi: 10.1016/j.urology.2020.02.031
[4] Song Y, Jin W, Hua S, et al. Middle calyx access is better for single renal pelvic stone in ultrasound-guided percutaneous nephrolithotomy[J]. Urolithiasis, 2016, 44(5): 459-463. doi: 10.1007/s00240-016-0866-9
[5] Aminsharifi A, Eslahi A, Safarpour AR, et al. Stone scattering during percutaneous nephrolithotomy: role of renal anatomical characteristics[J]. Urolithiasis, 2014, 42(5): 435-439. doi: 10.1007/s00240-014-0678-8
[6] Perrella R, Vicentini FC, Paro ED, et al. Supine versus Prone Percutaneous Nephrolithotomy for Complex Stones: A Multicenter Randomized Controlled Trial[J]. J Urol, 2022, 207(3): 647-656. doi: 10.1097/JU.0000000000002291
[7] Zhou Z, Li Y, Chen Y, et al. One-Stage Flexible Ureteroscopy during Single-Tract Percutaneous Nephrolithotomy in the Treatment of Parallel Calyceal Stones[J]. Urol Int, 2022, 106(12): 1233-1240. doi: 10.1159/000525591
[8] Liu YH, Jhou HJ, Chou MH, et al. Endoscopic Combined Intrarenal Surgery Versus Percutaneous Nephrolithotomy for Complex Renal Stones: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis[J]. J Pers Med, 2022, 12(4): 532. doi: 10.3390/jpm12040532
[9] Raman JD, Bagrodia A, Bensalah K, et al. Residual fragments after percutaneous nephrolithotomy: cost comparison of immediate second look flexible nephroscopy versus expectant management[J]. J Urol, 2010, 183(1): 188-193. doi: 10.1016/j.juro.2009.08.135
[10] 马魏魏, 傅鑫华, 高贇, 等. 经皮肾通道顺行输尿管软镜在特殊类型输尿管结石的临床应用[J]. 临床泌尿外科杂志, 2023, 38(3): 223-225. https://lcmw.whuhzzs.com/article/doi/10.13201/j.issn.1001-1420.2023.03.015
[11] Pan SY, Huang CP, Chen WC, et al. Percutaneous Nephrolithotomy Combined Antegrade Flexible Ureteroscope for Complete Staghorn Stones: A Case Report of a New Concept of Stone Surgery[J]. Medicina(Kaunas), 2022, 59(1): 35. http://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35773639/
[12] Yang H, Li J, Long G, et al. The application of a novel integrated rigid and flexible Nephroscope in percutaneous nephrolithotomy for renal staghorn stones[J]. BMC Urol, 2017, 17(1): 67. doi: 10.1186/s12894-017-0257-8
-

| 引用本文: | 彭泳涵, 李超, 张书玮, 等. 新型软性肾镜在经皮肾镜取石术中的应用[J]. 临床泌尿外科杂志, 2023, 38(6): 414-417. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.1001-1420.2023.06.004 |
| Citation: | PENG Yonghan, LI Chao, ZHANG Shuwei, et al. Application of a novel flexible nephroscope in percutaneous nephrolithotomy[J]. J Clin Urol, 2023, 38(6): 414-417. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.1001-1420.2023.06.004 |
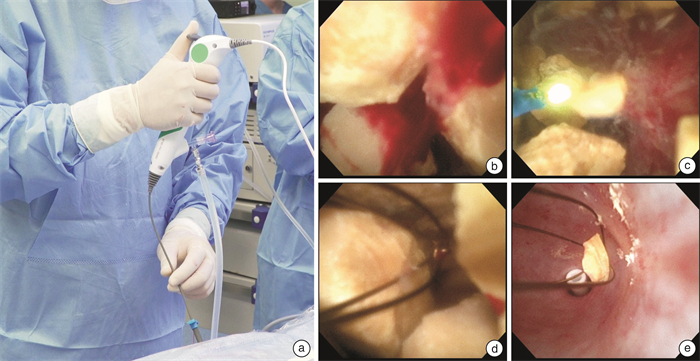
- Figure 1.



 下载:
下载: