Clinical value of dual-energy computed tomography in identifying urinary calculi composition
-
摘要: 目的 探讨Revolution单源双能CT对泌尿系结石成分定性诊断的影像价值。方法 选取2018年4月-2020年6月在我院接受治疗的泌尿系统结石患者, 收集不同部位结石共105枚, 患者均进行单源双能CT扫描, 并通过工作站进行结石成分分析, 测得70 Kev CT值、有效原子序数, 将影像分析结果与临床通过红外光谱法分析的结果进行比较, 分析单源双能CT对体内结石成分分析的准确性。各组比较采用单因素方差分析, 组间多重比较采用LSD法。结果 以临床红外光谱分析结果为标准, 单源双能CT应用碘水基物质图分析尿酸结石的准确率达99%, 应用有效原子序数这一指标分析非尿酸结石中草酸钙结石、混合结石的准确率分别为79%、87%。碘水基物质图像区分尿酸与非尿酸结石的灵敏度、特异度分别为100%、100%。结论 单源双能CT能有效诊断泌尿系结石成分, 为临床治疗方案提供有力依据。Abstract: Objective To explore the imaging value of Revolution dual-energy computed tomography (DECT) in the qualitative diagnosis of urinary calculi composition.Methods From April 2018 to June 2020, 105 patients with urinary calculi who were treated in our hospital were selected for DECT scanning and composition analysis using workstation. CT value and effective atomic number (Zeff) were measured at 70Kev, and the imaging results were compared with those obtained by clinical infrared spectroscopy to analyze the accuracy of DECT in the diagnosis of calculi composition. One-way analysis of variance was used for comparison between groups, and LSD method was used for multiple comparisons among groups.Results Based on the results of clinical infrared spectroscopy analysis, the accuracy of DECT in the analysis of uric acid stones using iodine water based substance image was 99%, and the accuracy of using the effective atomic number to analyze calcium oxalate stones and mixed stones in non-uric acid stones were 79% and 87%, respectively. The sensitivity and specificity for distinguishing uric acid and non-uric acid stones using iodine based substance image were 100% and 100%, respectively.Conclusion DECT can effectively diagnose the composition of urinary calculi and provide a favorable basis for clinical treatment plan.
-
Key words:
- dual-energy CT /
- urinary calculi /
- effective atomic number /
- CT value
-

-
表 1 CT影像与红外光谱的结石成分分析结果
枚(%) CT影像分析结果 红外光谱结果 阳性 阴性 尿酸 阳性 8(7.62) 0 阴性 1(0.95) 96(91.43) 草酸钙 阳性 45(42.86) 8(7.62) 阴性 14(13.33) 38(36.19) 磷酸氢钙 阳性 2(1.90) 5(4.76) 阴性 0 98(93.33) 磷酸镁铵 阳性 0 1(0.95) 阴性 2(1.90) 102(97.14) 胱氨酸 阳性 0 5(4.76) 阴性 0 100(95.24) 混合型 阳性 18(17.14) 13(12.38) 阴性 0 74(70.48) 表 2 CT诊断的灵敏度、特异度及准确率
% 诊断指标 影像结石分析结果 尿酸类 草酸钙 磷酸氢钙 混合 灵敏度 89 76 100 100 特异度 100 83 95 85 准确率 99 79 97 87 表 3 尿酸与非尿酸结石分型标准
% 诊断指标 灵敏度 特异度 水碘图 100 100 70 Kev下CT值 75 98 表 4 CT值与Zeff值的诊断效能
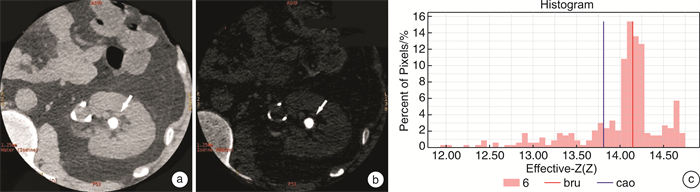
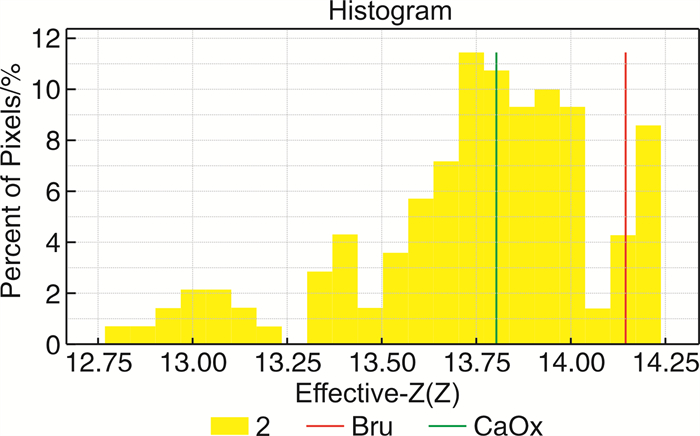
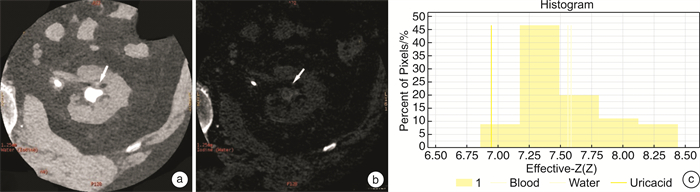
X±S 结石成分 Zeff值 70 Kev下CT值/HU 单纯型结石 尿酸(8枚) 7.86±0.39 522.65±91.38 草酸钙(53枚) 12.91±1.591) 1215.66±282.90 磷酸氢钙(7枚) 13.34±0.941)2) 1213.82±381.16 胱氨酸(5枚) 11.71±0.611)2)3) 860.55±283.26 混合型结石 草酸钙/磷酸氢钙(21枚) 13.65±0.83 1363.16±287.34 胱氨酸/磷酸镁铵(6枚) 11.28±0.47 771.33±244.61 草酸钙/磷酸氢钙/胱氨酸(4枚) 13.36±0.58 1395.21±145.96 F 24.15 13.14 P值 < 0.001 < 0.001 与尿酸比较,1)P < 0.05;与草酸钙比较,2)P < 0.05;与磷酸氢钙比较,3)P < 0.05。 -
[1] 叶章群, 刘浩然. 泌尿系结石的诊断治疗进展[J]. 临床外科杂志, 2017, 25(2): 85-88. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCWK201702001.htm
[2] Stępień M, Chrzan R, Gawlas W. In vitro analysis of urinary stone composition in dual-energy computed tomography[J]. Pol J Radiol, 2018, 83: 421-425. doi: 10.5114/pjr.2018.79588
[3] 陈泉桦, 黎军强. 双源CT双能量成像识别尿路结石成分的临床应用研究[J]. 中国CT和MRI杂志, 2018, 16(7): 133-135. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CTMR201807040.htm
[4] 朱润宇, 陈卫国. 输尿管镜碎石术中结石逃逸的治疗及疗效分析[J]. 临床泌尿外科杂志, 2022, 37(9): 693-697. https://lcmw.chinajournal.net.cn/WKC/WebPublication/paperDigest.aspx?paperID=71ddc206-43f3-4d30-ada7-1e3b1961b1c4
[5] 孙伟, 张炜, 付桥, 等. 经皮肾镜取石术与逆行输尿管软镜术在1.5~2.5 cm上尿路结石患者中的对比研究[J]. 临床泌尿外科杂志, 2022, 37(11): 853-856. https://lcmw.chinajournal.net.cn/WKC/WebPublication/paperDigest.aspx?paperID=3e46df45-c072-4872-95ac-466d2b5b1173
[6] 邢滇霞, 黄培, 赵冬青, 等. 能谱CT分析泌尿系结石成分与碎石难易程度的关系[J]. 医学信息, 2017, 30(9): 23-26. https://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10759-1017729281.htm
[7] Morsbach F, Wurnig MC. Feasibility of single-source dual-energy computed tomography for urinary stone characterization and value of iterative reconstructions[J]. Invest Radiol, 2014, 49(3): 125-130. doi: 10.1097/RLI.0000000000000002
[8] Kordbacheh H, Baliyan V, Uppot RN, et al. Dual-Source Dual-Energy CT in Detection and Characterization of Urinary Stones in Patients With Large Body Habitus: Observations in a Large Cohort[J]. AJR Am J Roentgenol, 2019, 212(4): 796-801. doi: 10.2214/AJR.18.20293
[9] 蔡磊, 叶冬晖, 陈剑锋, 等. 双能CT在人体泌尿系结石成分分析中的价值[J]. 现代泌尿外科杂志, 2021, 26(7): 578-581. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MNWK202107008.htm
[10] Kapanadze LB, Rudenko VI, Serova NS, et al. Dual-energy computed tomography in the diagnostics of urolithiasis[J]. Urologiia, 2019, (5): 31-36.
[11] 甘毅, 徐志锋, 潘爱珍, 等. 能谱CT有效原子序数对泌尿系结石成分的诊断价值[J]. 现代医用影像学, 2021, 30(11): 3. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDYY202111026.htm
[12] 苏鸿林, 吴小辉, 熊晓玲, 等. 双能量能谱CT扫描诊断尿路结石成分的临床价值[J]. 实用医技杂志, 2021, 28(8): 990-992. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYJ202108018.htm
[13] 吴小红, 高雅, 戴志军, 等. DSCT在泌尿系结石成分分析中的应用[J]. 宁夏医学杂志, 2020, 42(5): 419-421. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NXYX202005014.htm
[14] 姜明瀚, 盛伟华, 黄松, 等. 双能量能谱CT衰减值鉴别尿酸与非尿酸泌尿系结石的价值[J]. 医学影像学杂志, 2019, 29(10): 1781-1784. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XYXZ201910046.htm
[15] Chaytor, Richard J, Mcknight, et al. Determining the composition of urinary tract calculi using stone-targeted dual-energy CT: evaluation of a low-dose scanning protocol in a clinical environment[J]. Br J Radiol, 2016, 89(1067): 20160408.
-




 下载:
下载: