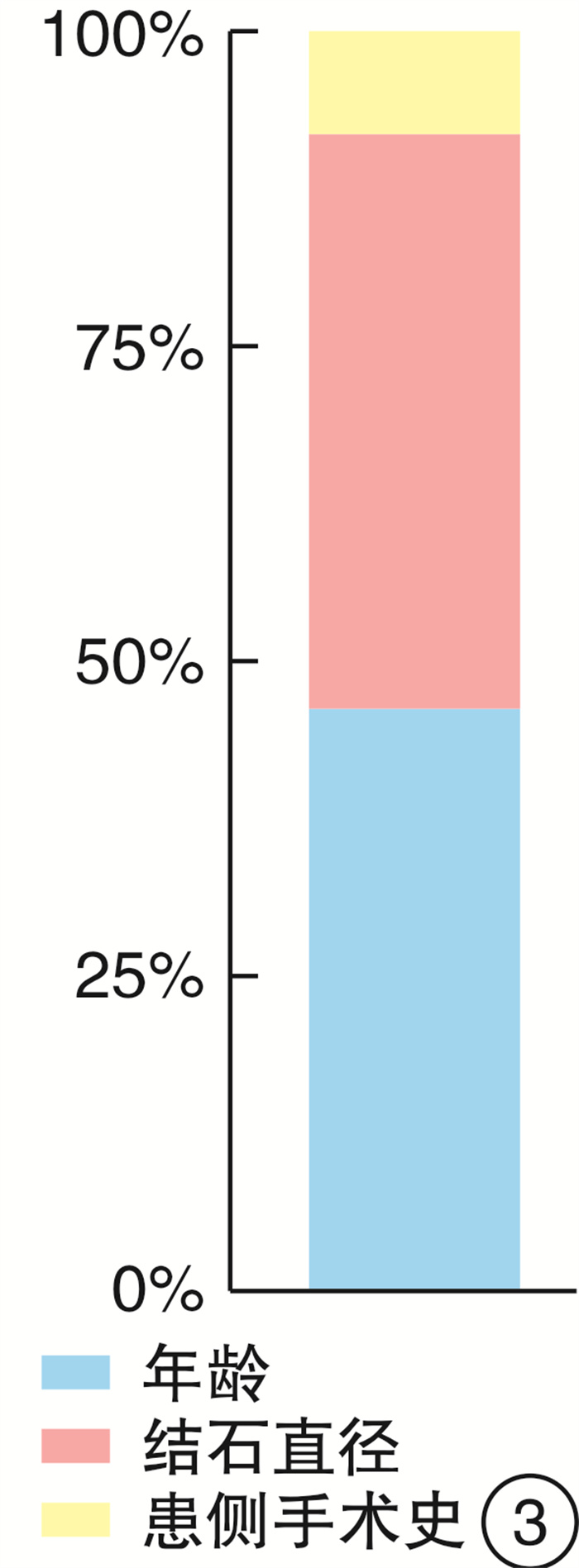Risk factors analysis and prediction model construction of ureteroscopic failure: a single-center, prospective clinical study
-
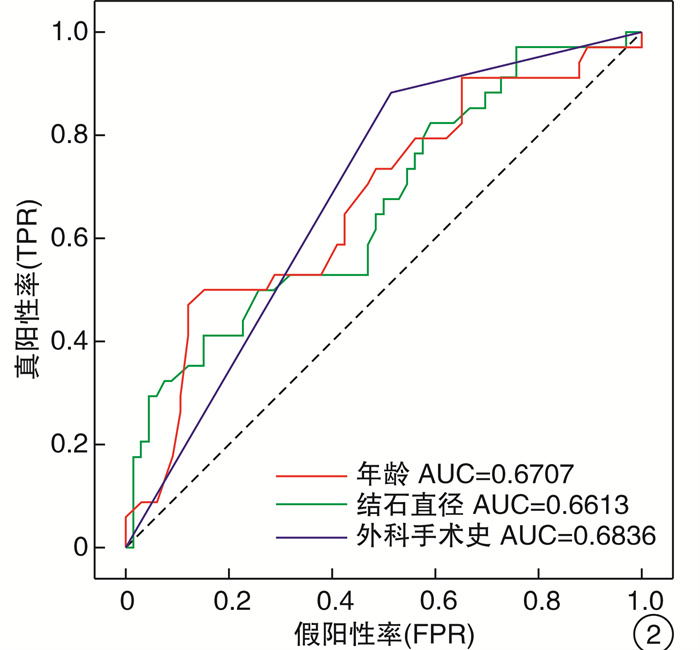
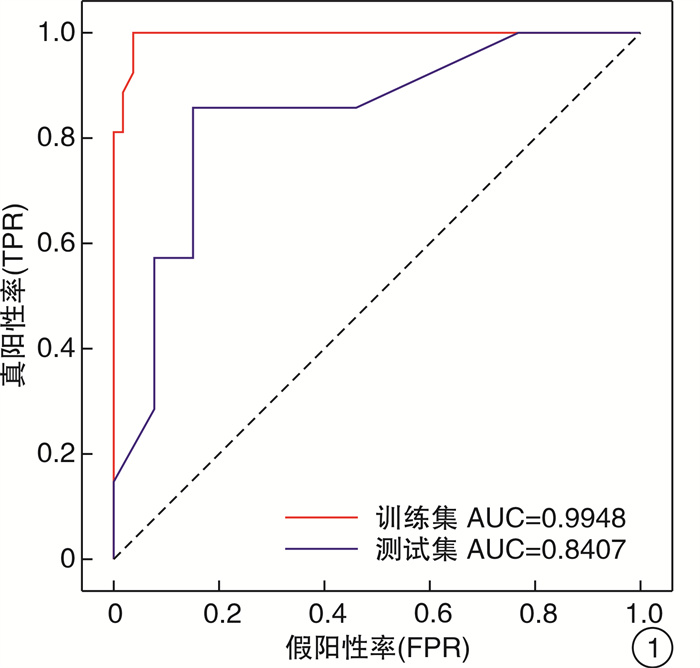
摘要: 目的 在输尿管镜碎石取石术(ureteroscopic lithotripsy,URL)中,探讨输尿管镜入镜失败的危险因素,并建立输尿管镜能否成功入镜的预测模型。方法 前瞻性、单中心纳入拟行URL的患者。首先采用成人输尿管镜(8/9.8F)进行手术,若因输尿管腔细小难以入镜时,则进一步使用小儿输尿管镜(6/7.5F)进行手术。根据输尿管镜是否到达结石位置,设定结局变量为:成人输尿管镜入镜成功组和失败组,小儿输尿管镜入镜成功与失败组。采用单因素、多因素分析对特征进行筛选,并使用筛选后的特征构建随机森林预测模型。结果 共纳入102例患者进行数据分析,其中男83例,女19例,平均年龄为(41.2±13.1)岁,平均结石直径为(7.81±3.73) mm。输尿管上、中、下段结石分别占41.2%、14.7%、44.1%。采用成人输尿管镜(8/9.8F)入镜成功率66.7%;进一步联合小儿输尿管镜(6/7.5F)入镜成功率为91.2%。单因素分析显示,年龄、结石直径是影响成人输尿管镜入镜的因素,患侧有腔镜手术史、患有慢性病可以提高成人输尿管镜入镜的成功率。考虑慢性病与年龄具有相关性,将患者年龄、结石直径、患侧有腔镜手术史纳入多因素分析,并计算上述因素cutoff值。结果显示,年龄小于29.5岁(P=0.022)、结石直径小于5.3 mm(P=0.038)是成人输尿管镜入镜失败的独立危险因素,患侧腔镜手术史(P=0.056)可能有助于成人输尿管镜入镜。联合应用年龄、结石直径、腔镜手术史的随机森林预测模型的AUC值在验证集中达到了0.84,其中年龄、结石直径所占权重超过90%。结论 年龄小于29.5岁和结石直径小于5.3 mm是成人输尿管镜入镜失败的独立危险因素,泌尿系腔镜手术史可能有助于输尿管镜入镜。随机森林预测模型能够较好地预测入镜成功率。Abstract: Objective To investigate the risk factors for failure of ureteroscopic lithotripsy(URL) and to establish a prediction model for the success of URL.Methods Patients who underwent URL were prospectively enrolled in a single center. The adult ureteroscope(8/9.8F) was used for the operation at first, and the pediatric ureteroscope(6/7.5F) was used for the operation if the small ureter was difficult to enter. According to whether the ureteroscope reached the stone position, the patients were divided into the(adult ureteroscope or pediatric ureteroscope) success group and the failure group. Univariate analysis and multivariate analysis were used to screen the features, and the selected features were used to construct the random forest prediction model.Results A total of 102 patients were prospectively enrolled, including 83 males and 19 females. The mean age was(41.2±13.1) years, and the stone diameter was(7.81±3.73) mm. Upper, middle and lower ureteral calculi accounted for 41.2%, 14.7% and 44.1%, respectively. The success rate of adult ureteroscopy(8/9.8F) was 66.7%, and the success rate of pediatric ureteroscopy(6/7.5F) was 91.2%. Univariate analysis showed that age and stone diameter were factors for affecting adult ureteroscopy success. The success rate of adult ureteroscopy could be improved by history of endoscopic surgery and chronic diseases. Considering the obvious correlation between chronic diseases and age, the patient's age, stone diameter, and history of endoscopic surgery were included in the multivariate analysis. The results showed that age less than 29.5 years(P=0.022) and stone diameter less than 5.3 mm(P=0.038) were independent risk factors for failure of adult ureteroscopy. History of endoscopic surgery on the affected side(P=0.056) may be helpful for adult ureteroscopy. The AUC value of the random forest prediction model combined with age, stone diameter and history of endoscopic surgery reached 0.84 in the validation set, in which age and stone diameter accounted for more than 90% of the weight.Conclusion Age less than 29.5 years and stone diameter less than 5.3 mm are independent risk factors for failure of adult ureteroscopy. History of urologic endoscopic surgery may be helpful for ureteroscopy. The random forest prediction model can better predict the success rate of ureteroscopic access.
-
Key words:
- ureteral calculi /
- ureteroscopic lithotripsy /
- endoscopy failure /
- risk factors /
- random forest
-

-
表 1 输尿管镜上镜成功组与失败组资料比较
例(%),X±S 项目 成功组(68例) 失败组(34例) P值 年龄/岁 43.59±12.80 36.44±12.45 0.009 性别 0.719 男 56(82.4) 27(79.4) 女 12(17.6) 7(20.6) BMI/(kg/m2) 24.31±3.55 25.65±5.00 0.124 腹围/cm 84.96±8.76 89.21±12.01 0.073 保守治疗病程/d 41.00±104.40 19.10±31.70 0.235 结石直径/mm 8.45±4.00 6.53±2.77 0.014 手术史 15(22.1) 1(2.9) 0.012 慢性病史 16(23.5) 2(5.9) 0.028 钙通道阻滞剂 8(11.8) 0(0) 0.091 结石侧别 0.888 左侧 37(54.4) 18(52.9) 右侧 31(45.6) 16(47.1) 结石位置 0.439 上段 26(38.2) 16(47.1) 中段 9(13.2) 6(17.6) 下段 33(48.5) 12(35.3) 结石透光性 0.150 阳性 44(64.7) 18(52.9) 弱阳性 10(14.7) 3(8.8) 阴性 14(20.6) 13(38.2) 肾积水程度/mm 25.76±4.92 22.19±11.20 0.222 表 2 输尿管镜上镜失败logistic回归分析结果
项目 β S.E. Wald P值 Exp(B) 95%CI 年龄 -0.043 0.019 5.219 0.022 0.958 0.923~0.994 结石直径 -0.183 0.088 4.294 0.038 0.833 0.701~0.990 手术史 2.068 1.081 3.659 0.056 7.910 0.950~65.841 -
[1] Romero V, Akpinar H, Assimos DG. Kidney stones: a global picture of prevalence, incidence, and associated risk factors[J]. Rev Urol, 2010, 12(2-3): e86-e96.
[2] Scales CD, Smith AC, Hanley JM, et al. Prevalence of kidney stones in the United States[J]. Eur Urol, 2012, 62(1): 160-165. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2012.03.052
[3] Thongprayoon C, Krambeck AE, Rule AD. Determining the true burden of kidney stone disease[J]. Nat Rev Nephrol, 2020, 16(12): 736-746. doi: 10.1038/s41581-020-0320-7
[4] Washino S, Hosohata K, Miyagawa T. Roles played by biomarkers of kidney injury in patients with upper urinary tract obstruction[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2020, 21(15): 5490. doi: 10.3390/ijms21155490
[5] Khoder WY, Bader M, Sroka R, et al. Efficacy and safety of Ho: YAG laser lithotripsy for ureteroscopic removal of proximal and distal ureteral calculi[J]. BMC Urol, 2014, 14: 62. doi: 10.1186/1471-2490-14-62
[6] Ather MH, Nazim SM, Sulaiman MN. Efficacy of semirigid ureteroscopy with pneumatic lithotripsy for ureteral stone surface area of greater than 30 mm2[J]. J Endourol, 2009, 23(4): 619-622. doi: 10.1089/end.2008.0182
[7] Ueno A, Kawamura T, Ogawa A, et al. Relation of spontaneous passage of ureteral calculi to size[J]. Urology, 1977, 10(6): 544-546. doi: 10.1016/0090-4295(77)90097-8
[8] 熊海云, 盛义雨, 冯宇鹏, 等. 预示输尿管镜碎石手术上镜失败的临床因素分析[J/OL]. 中华腔镜泌尿外科杂志(电子版), 2020, 14(4): 279-282.
[9] Waseda Y, Takazawa R, Kobayashi M, et al. Risk factors and predictive model for incidence of difficult ureter during retrograde ureteroscopiclithotripsy[J]. Int J Urol, 2022, 29(6): 542-546. doi: 10.1111/iju.14835
[10] 陈大可, 黄卫文, 鲍文朔. 输尿管镜钬激光治疗输尿管结石并发输尿管狭窄36例临床分析[J]. 中国医师进修杂志, 2011, 34(12): 49-50. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1673-4904.2011.12.024
[11] 魏汉平, 焦志敏, 袁晓亮, 等. 腔内微创手术治疗输尿管结石合并输尿管远端狭窄的安全性及有效性分析[J]. 中国临床新医, 2020, 13(11): 1138-1141. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-3806.2020.11.15
[12] 张斌斌, 强亚勇, 郭巍, 等. 四种腔镜治疗输尿管上段直径>1 cm结石的疗效对比研究[J]. 中华泌尿外科杂志, 2018, 39(4): 300-304.
[13] 何文强, 屈颖伟, 郑聪, 等. 顺行输尿管软镜治疗输尿管中下段结石合并远端输尿管复杂病变[J]. 临床泌尿外科杂志, 2019, 34(7): 542-544. https://lcmw.whuhzzs.com/article/doi/10.13201/j.issn.1001-1420.2019.07.010
-




 下载:
下载: