Expression of lncRNA PCGEM1 in prostate cancer and its effects on proliferation, apoptosis, invasion, migration and epithelial mesenchymal transition of prostate cancer PC3 cells
-
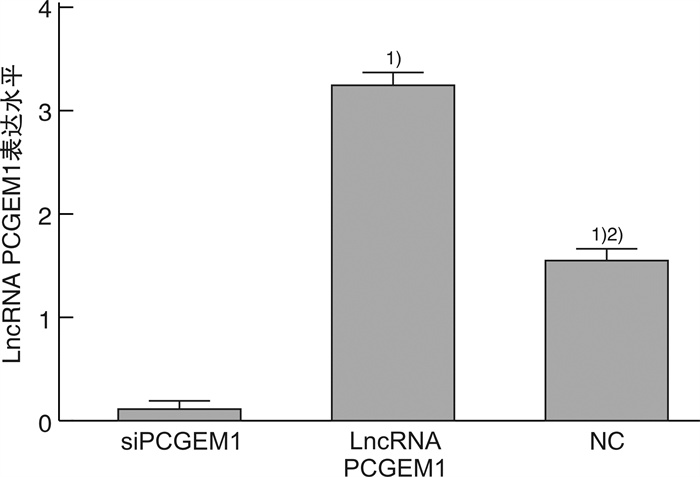
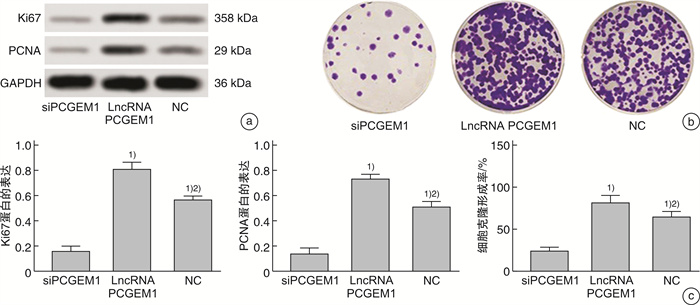
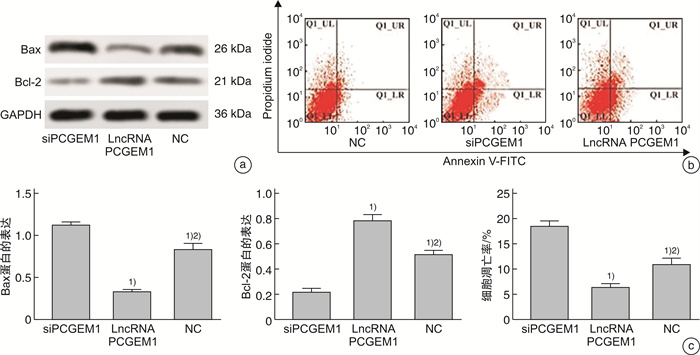
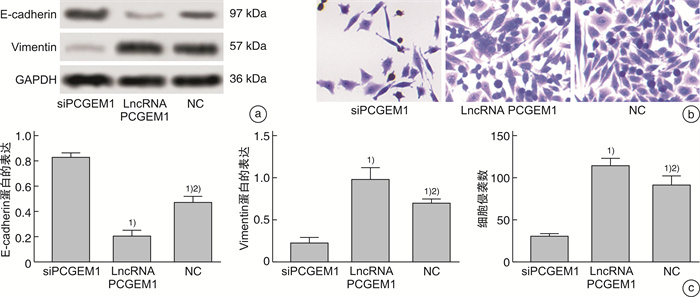
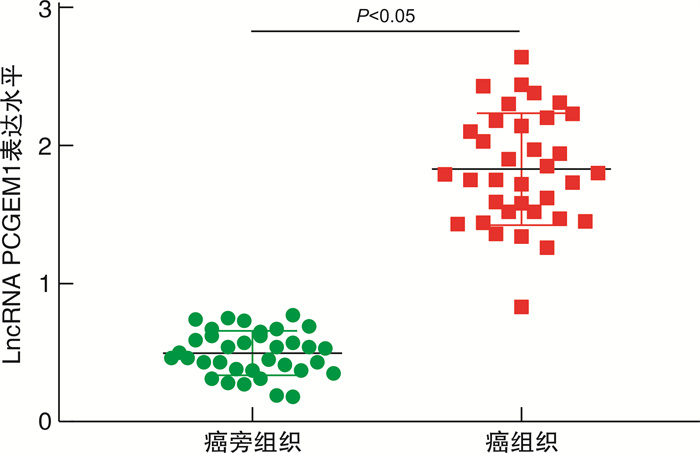
摘要: 目的 探究lncRNA PCGEM1在前列腺癌组织中的表达情况及lncRNA PCGEM1对前列腺癌PC3细胞增殖、凋亡、迁移、侵袭和上皮间质转化(epithelial mesenchymal transition,EMT)的影响。方法 选取2018年1月—2020年12月在武汉市第三医院确诊的前列腺癌患者35例,分别取其癌组织和癌旁组织,检测其lncRNA PCGEM1表达情况; 体外培养前列腺癌PC3细胞并构建lncRNA PCGEM1沉默细胞系(siPCGEM1)、过表达lncRNA PCGEM1细胞系(lncRNA PCGEM1)和阴性对照(NC); 采用克隆形成实验检测各组细胞增殖并用蛋白质印迹法检测增殖蛋白Ki67和PCNA表达情况; 采用流式细胞术检测细胞凋亡率,采用蛋白免疫印迹(Western blot,WB)检测检测凋亡蛋白Bcl-2和Bax表达情况; 采用Transwell小室实验检测各组细胞侵袭情况并用WB检测E钙粘蛋白(E-cadherin)及波形蛋白(Vimentin)的表达情况。结果 35例患者的癌组织中lncRNA PCGEM1表达水平显著高于癌旁组织(P<0.05);与siPCGEM1组比校,lncRNA PCGEM1和NC组细胞中lncRNA PCGEM1水平、Ki67蛋白相对表达水平、PCNA蛋白相对表达水平、克隆形成率、Bcl-2蛋白相对表达水平、Vimentin蛋白相对表达水平、单位面积侵袭细胞数目显著升高(P<0.05),E-cadherin蛋白相对表达水平和Bax蛋白相对表达水平显著降低(P<0.05);与lncRNA PCGEM1组比较,NC组细胞lncRNA PCGEM1水平、Ki67蛋白相对表达水平、PCNA蛋白相对表达水平、克隆形成率、Bcl-2蛋白相对表达水平、Vimentin蛋白相对表达水平、单位面积侵袭细胞数目显著降低(P<0.05),E-cadherin蛋白相对表达水平和Bax蛋白相对表达水平显著升高(P<0.05)。结论 前列腺癌组织中lncRNA PCGEM1表达水平会异常升高,降低其表达水平可以有效抑制前列腺癌PC3细胞增殖、侵袭并促进其凋亡,同时通过调控EMT过程降低PC3细胞的侵袭能力。
-
关键词:
- lncRNA PCGEM1 /
- PC3细胞 /
- 细胞增殖 /
- 细胞凋亡 /
- 上皮间质转化
Abstract: Objective To investigate the expression of lncRNA PCGEM1 in prostate cancer tissues and the effects of lncRNA PCGEM1 on the proliferation, apoptosis, migration, invasion and epithelial mesenchymal transition (EMT) of prostate cancer PC3 cells.Methods Thirty-five prostate cancer patients diagnosed in Wuhan Third Hospital from January 2018 to December 2020 were selected to collect their cancerous tissues and adjacent tissues. lncRNA PCGEM1 expression was detected. lncRNA PCGEM1 silenced cell line(siPCGEM1), lncRNA PCGEM1 overexpressed cell line(lncRNA PCGEM1) and negative control(NC) were constructed in vitro with prostate cancer PC3 cells. Cell proliferation was detected by clonal formation assay. The expressions of proliferating protein Ki67 and PCNA were detected by western blotting. The apoptosis rate was detected by flow cytometry. The expressions of apoptotic proteins Bcl-2 and Bax were detected by western blotting. Transwell assay was used to detect cell invasion in each group. The expression of E-cadherin and Vimentin was detected by western blot.Results lncRNA PCGEM1 expression level in cancer tissues of 35 patients was significantly higher than that in paracancer tissues (P<0.05). Compared with siPCGEM1 group, the level of lncRNA PCGEM1, the relative expression level of Ki67 protein, the relative expression level of PCNA protein, the cloning rate, the relative expression level of Bcl-2 protein, the relative expression level of Vimentin protein and the number of invading cells per unit area in lncRNA PCGEM1 group and NC group were significantly increased (P<0.05). Compared with siPCGEM1 group, the relative expression level of E-cadherin protein and Bax protein in lncRNA PCGEM1 group and NC group were significantly decreased (P<0.05). Compared with lncRNA PCGEM1 group, the lncRNA PCGEM1 level, the relative expression level of Ki67 protein, the relative expression level of PCNA protein, the clone formation rate, the relative expression level of Bcl-2 protein, the relative expression level of Vimentin protein and the number of invading cells per unit area were significantly decreased in NC group (P<0.05). Compared with lncRNA PCGEM1 group, the relative expression level of E-cadherin protein and Bax protein in NC group were significantly increased (P<0.05).Conclusion lncRNA PCGEM1 expression levels in prostate cancer tissues are abnormally elevated. Reducing the expression level can effectively inhibit the proliferation, invasion and promote apoptosis of adenocarcinoma PC3 cells. The invasion ability of PC3 cells can be suppressed through the regulation of EMT process.-
Key words:
- lncRNA PCGEM1 /
- PC3 cells /
- cell proliferation /
- cell apoptosis /
- epithelial mesenchymal transition
-

-
[1] Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2016. CA Cancer J Clin[J], 2016, 66(1): 7-30. doi: 10.3322/caac.21332
[2] de Bono JS, Oudard S, Ozguroglu M, et al. Prednisone plus cabazitaxel or mitoxantrone for metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer progressing after docetaxel treatment: a randomised open-label trial[J]. Lancet, 2010, 376(9747): 1147-1154. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(10)61389-X
[3] Tannock IF, de Wit R, Berry WR, et al. Docetaxel plus prednisone or mitoxantrone plus prednisone for advanced prostate cancer[J]. N Engl J Med, 2004, 351(15): 1502-1512. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa040720
[4] Kaplan SA. Re: Impact of 5α-Reductase Inhibitor and α-Blocker Therapy for Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia on Prostate Cancer Incidence and Mortality[J]. J Urol, 2020, 203(5): 856-857. doi: 10.1097/JU.0000000000000763.02
[5] Srikantan V, Zou Z, Petrovics G, et al. PCGEM1, a prostate-specific gene, is overexpressed in prostate cancer[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2000, 97(22): 12216-12221. doi: 10.1073/pnas.97.22.12216
[6] Chen J, Yuan D, Hao Q, et al. lncRNA PCGEM1 mediates oxaliplatin resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma via miR-129-5p/ETV1 axis in vitro[J]. Adv Clin Exp Med, 2021, 30(8): 831-838. doi: 10.17219/acem/135533
[7] Xue Y, Wang M, Kang M, et al. Association between lncRNA PCGEM1 polymorphisms and prostate cancer risk[J]. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis, 2013, 16(2): 139-144, S1. doi: 10.1038/pcan.2013.6
[8] Loriot Y, Bianchini D, Ileana E, et al. Antitumour activity of abiraterone acetate against metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer progressing after docetaxel and enzalutamide(MDV3100)[J]. Ann Oncol, 2013, 24(7): 1807-1812. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdt136
[9] Mo M, Ma X, Luo Y, et al. Liver-specific lncRNA FAM99A may be a tumor suppressor and promising prognostic biomarker in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. BMC Cancer, 2022, 22(1): 11-15. doi: 10.1186/s12885-021-09051-5
[10] Liu SL, Chen MH, Wang XB, et al. lncRNA PCGEM1 contributes to malignant behaviors of glioma by regulating miR-539-5p/CDK6 axis[J]. Aging(Albany NY), 2021, 13(4): 5475-5484.
[11] Walsh AL, Tuzova AV, Bolton EM, et al. Long noncodingRNAs and prostatecarcinogenesis: 'linc'?[J]. Trends Mol Med, 2014, 20(8): 428-436. doi: 10.1016/j.molmed.2014.03.005
[12] Piao H, Zhang J. 2013P Gastric cancer-derived exosomallncRNA PCGEM1 promotes invasion and metastasis by inducing vascular angiogenesis-Science Direct[J]. Ann Oncol, 2020, 31(5): 48-51.
[13] Wen H, Feng H, Ma Q, et al. lncRNA PCGEM1 induces proliferation and migration in non-small cell lung cancer cells through modulating the miR-590-3p/SOX11 axis[J]. BMC Pulm Med, 2021, 21(1): 234. doi: 10.1186/s12890-021-01600-9
[14] Chen W, Cen S, Zhou X, et al. Circular RNA CircNOLC1, Upregulated by NF-KappaB, Promotes the Progression of Prostate Cancer via miR-647/PAQR4 Axis[J]. Front Cell Dev Biol, 2020, 8: 624764.
[15] Wei DM, Chen WJ, Meng RM, et al. Augmented expression of Ki-67 is correlated with clinicopathological characteristics and prognosis for lung cancer patients: an up-dated systematic review and meta-analysis with 108 studies and 14, 732 patients[J]. Respir Res, 2018, 19(1): 150. doi: 10.1186/s12931-018-0843-7
[16] Mrouj K, Andrés-Sánchez N, Dubra G, et al. Ki-67 regulates global gene expression and promotes sequential stages of carcinogenesis[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2021, 118(10): e2026507118. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2026507118
[17] Stamatiou K, Vagnarelli P. Chromosome clustering in mitosis by the nuclear protein Ki-67[J]. Biochem Soc Trans, 2021, 49(6): 2767-2776. doi: 10.1042/BST20210717
[18] Cardano M, Tribioli C, Prosperi E. Targeting Proliferating Cell Nuclear Antigen(PCNA)as an Effective Strategy to Inhibit Tumor Cell Proliferation[J]. Curr Cancer Drug Targets, 2020, 20(4): 240-252. doi: 10.2174/1568009620666200115162814
[19] Cai J, Yi M, Tan Y, et al. Natural product triptolide induces GSDME-mediated pyroptosis in head and neck cancer through suppressing mitochondrial hexokinase-Ⅱ[J]. J ExpClin Cancer Res, 2021, 40(1): 190-194.
[20] Hu Y, Li H, Li R, et al. Protective effects of Schisandrin B against D-GalN-induced cell apoptosis in human hepatocyte(L02) cells via modulating Bcl-2 and Bax[J]. Bioengineered, 2021, 12(1): 7205-7214.
[21] Flores-Romero H, Ros U, Garcia-Saez AJ. Pore formation in regulated cell death[J]. EMBO J, 2020, 39(23): e105753. doi: 10.15252/embj.2020105753
[22] Dongre A, Weinberg RA. New insights into the mechanisms of epithelial-mesenchymal transition and implications for cancer[J]. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol, 2019, 20(2): 69-84.
[23] Igarashi K, Nishizawa H, Saiki Y, et al. The transcription factor BACH1 at the crossroads of cancer biology: From epithelial-mesenchymal transition to ferroptosis[J]. J Biol Chem, 2021, 297(3): 101032. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2021.101032
[24] Usman S, Waseem NH, Nguyen T, et al. Vimentin Is at the Heart of Epithelial Mesenchymal Transition(EMT)Mediated Metastasis[J]. Cancers(Basel), 2021, 13(19): 4985.
-




 下载:
下载: