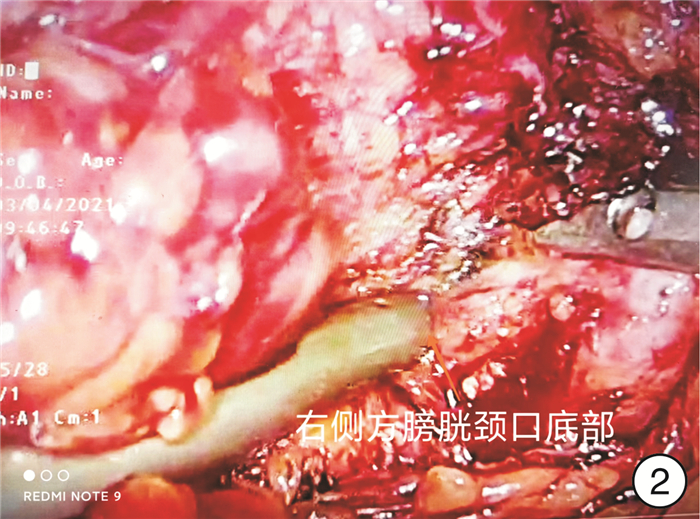
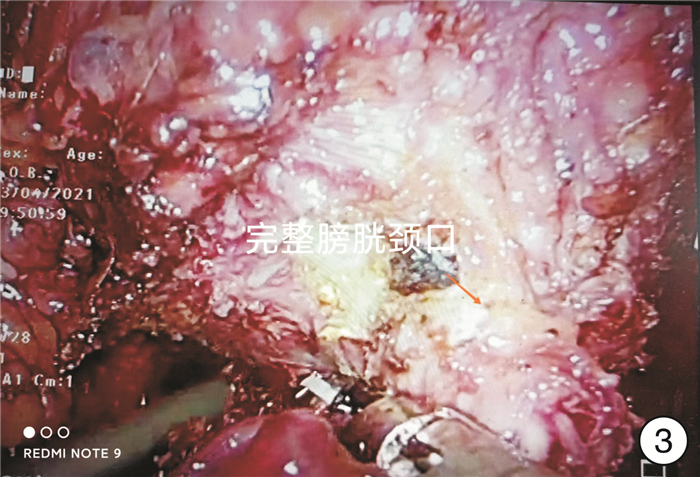
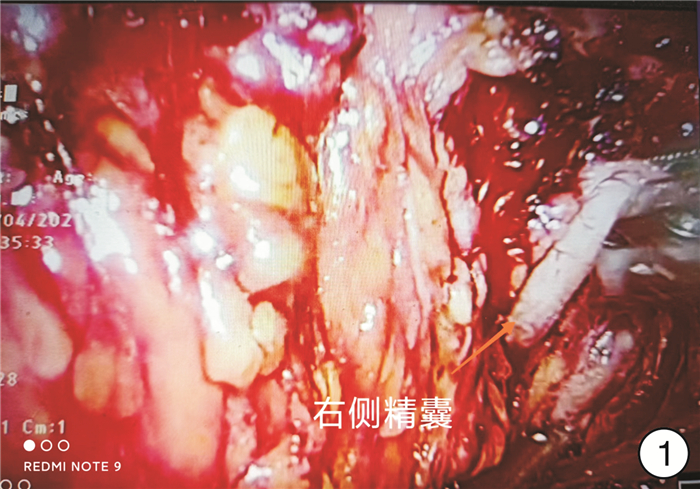
Clinical effect of immediate urinary control in patients undergoing radical prostatectomy with bladder neck preservation via lateral seminal vesicle approach
-
摘要: 目的 探讨改良腹腔镜下侧方精囊入路保留完整膀胱颈口技术在根治性前列腺切除术中的早期尿控恢复的临床效果。方法 前瞻性纳入2021年6月—2022年12月温岭市中医院收治的T1~T3b期100例前列腺癌患者,分为传统组(A组)及保留膀胱颈口组(B组)。记录保留膀胱颈完整性及成功率、膀胱尿道吻合时间、拔除导尿管时间、住院时间;观察拔除导尿管后1周、1个月、3个月时尿控评分和尿垫情况,并观察不良事件情况等。采用t检验、χ2检验和Fisher确切概率法比较2组患者的术前临床资料、围手术期相关结果及术后尿控情况。结果 2组患者的年龄、前列腺重量、术前前列腺特异性抗原(PSA)及Gleason评分均差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。2组患者的手术时间、术中出血量、病理学分期、切缘阳性率均差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。A组拔除导尿管后1周、1个月、3个月尿失禁问卷国际咨询-尿失禁(ICIQ-UI)评分为15(14,16)、13(13,15)、6(5,11)分,B组为5(1,12)、1.5(0,9)、0(0,0)分,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.001)。以使用0片尿垫为判断标准,A组拔尿管1周及1个月、3个月达到尿控的患者分别为1例(2%)、9例(18%)、32例(64%),B组分别为36例(72%)、42例(84%)、48例(96%),B组拔尿管1周及1个月、3个月达到尿控的比例高于A组(P < 0.001)。结论 改良腹腔镜下侧方精囊入路技术在前列腺癌根治术中保留了完整的膀胱颈口,可以更好地减少尿失禁发生,术后即刻尿控能力大大提高,患者术后生活质量明显提升,是一项值得推广的新技术。
-
关键词:
- 前列腺癌 /
- 腹腔镜前列腺癌根治术 /
- 即刻尿控 /
- 精囊入路
Abstract: Objective To investigate the effect of a modified laparoscopic lateral seminal vesicle approach with bladder neck preservation(BNP) on early urinary control recovery in radical prostatectomy(RP).Methods One hundred patients with prostate cancer in T1-T3b stage admitted to Wenling Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine between June 2021 to December 2022 were prospectively assessed and categorized into the routine group(A) and lateral seminal vesicle approach group(B). The integrity and success rate of retaining bladder neck, the time of vesicourethral anastomosis, the time of catheter removal, hospital stay, urinary control score at the first week, first month, and third-month post-catheter removal, and the condition of urine pad and adverse events were recorded. T-test, χ2 test, and Fisher's exact test were used to compare the preoperative clinical data, perioperative results, and postoperative urinary control of the two groups.Results There was no difference in age, prostate volume, preoperative PSA(prostate-specific antigen), or Gleason score between the two studied groups(P>0.05). There was no statistically significant difference between the two groups in the variables such as operation time, intraoperative blood loss, pathological stage, or positive rate of incision margin. In the first week, first month, and third month, the ICIQ-UI score for group A was 15(14, 16), 13(13, 15), and 6(5, 11), which was higher than those of group B (5[1, 12], 1.5[0, 9] and 0[0, 0])(P < 0.001). Based on the use of 0 piece of urine pad, 1(2%), 9(18%), and 32(64%) patients in group A reached urinary control in the first week, first month and third-month postcatheter removal, and 36(72%), 42(84%) and 48(96%) patients in group B, respectively. The proportion of group B patients reaching urinary control in the first week, first month, and third month after catheter removal was higher compared to group A(P < 0.001).Conclusion The modified laparoscopic lateral seminal vesicle approach completely preserves the bladder neck in RP, which can better reduce the occurrence of urinary incontinence, greatly improve the ability of urinary control immediately after surgery, and significantly improve the post-surgery quality of patient life. It is a new technique worthy of promotion. -

-
表 1 2组患者基线资料比较
例(%),X±S,M(Q1,Q3) 基线资料 A组(50例) B组(50例) P值 BMI/(kg/m2) 23.76±7.35 22.97±6.22 0.512 3 年龄/岁 72.56±7.34 72.36±6.36 0.920 6 前列腺重量/g 34.75 (25.91,47.58) 32.67 (25.31,47.39) 0.383 8 PSA/(ng/mL) 9.69 (0.50,167.77) 9.93 (0.24,101.50) 0.887 6 临床危险分层 低 28(56) 27(54) 0.462 1 中 14(28) 16(32) 高 8(16) 7(14) Gleason分级(术后) 0.436 1 Ⅰ 20(40) 21(42) Ⅱ 15(30) 14(28) Ⅲ 9(18) 10(20) Ⅳ 4(8) 3(6) Ⅴ 2(4) 2(4) 保留NVB 0.178 5 无 4(8) 6(12) 单侧 30(60) 32(64) 双侧 16(32) 12(24) 表 2 2组在1周、1个月和3个月时ICIQ-UI评分和尿垫使用情况的比较
例(%),M(Q1,Q3) 指标 A组(50例) B组(50例) U/χ2 P值 1周 ICIQ-UI评分 15(14, 16) 5(1, 12) 6.532 <0.001 尿垫量/片 <0.001 0(尿控好) 1(2) 36(72) 1~2(轻微尿失禁) 30(60) 11(22) 3~5(中度尿失禁) 19(38) 3(6) >5(重度尿失禁) 0(0) 0(0) 每日尿垫使用量/片 2(2, 3) 0(0, 2) 5.255 <0.001 1个月 ICIQ-UI评分 13(13, 15) 1.5(0, 9) 6.533 <0.001 尿垫量/片 0(尿控好) 9(18) 32(64) 1~2(轻微尿失禁) 26(52) 18(36) 3~5(中度尿失禁) 15(30) 0(0) >5(重度尿失禁) 0(0) 0(0) 每日尿垫使用量/片 2(2, 3) 0(0, 1) 5.776 <0.001 3个月 ICIQ-UI评分 6(5, 11) 0(0, 0) 7.239 <0.001 尿垫量/片 0(尿控好) 32(64) 48(96) 1~2(轻微尿失禁) 12(24) 2(4) 3~5(中度尿失禁) 6(12) 0(0) >5(重度尿失禁) 0(0) 0(0) 每日尿垫使用量/片 0(0, 1.5) 0(0, 0) 3.696 <0.001 表 3 围手术期患者资料比较
例(%),X±S,M(Q1,Q3) 指标 A组(50例) B组(50例) t/U/χ2 P值 手术时间/min 138.30±15.47 117.08±13.79 6.65 <0.001 出血量/mL 243.00±72.79 235.75±82.43 0.66 0.508 住院时间/d 11(9, 13) 9(8, 11) 7.44 <0.001 留置导尿管时间/d 10(8, 15) 8(7, 9) 7.46 <0.001 TNM分期 1.000 T1 20(40) 21(42) T2 21(42) 21(42) T3 7(14) 7(14) T4 2(4) 1(2) 并发症 14(28) 11(22) >0.05 直肠损伤 0(0) 1(2) >0.05 术后发热 4(8) 4(8) >0.05 尿路感染 4(8) 3(6) >0.05 漏尿 3(6) 1(2) >0.05 输血 2(4) 0(0) <0.001 淋巴漏 1(2) 1(2) >0.05 盆腔积液 0(0) 1(2) >0.05 术后3个月PSA/(ng/mL) 0.003(0, 0.20) 0.003(0, 0.17) >0.05 -
[1] Covas Moschovas M, Bhat S, Onol FF, et al. Modified apical dissection and lateral prostatic fascia preservation improves early postoperative functional recovery in robotic-assisted laparoscopic radical prostatectomy: results from a propensity score-matched analysis[J]. Eur Urol, 2020, 78(6): 875-884. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2020.05.041
[2] Malhotra NR, Wallis MC, Allen CM, et al. Continence outcomes following a modification of the Mitchell bladder neck reconstruction in myelomeningocele: a single institution experience[J]. J Pediatr Urol, 2020, 16(5): 653.e1-653.e8. doi: 10.1016/j.jpurol.2020.06.032
[3] Martínez-Holguín E, Herranz-Amo F, Lledó-García E, et al. Comparison between laparoscopic and open prostatectomy: Postoperative urinary continence analysis[J]. Actas Urol Esp, 2020, 44(8): 535-541. doi: 10.1016/j.acuro.2019.10.002
[4] Sessa F, Nicoletti R, Pecoraro A, et al. Urinary continence recovery after robotic radical prostatectomy without anterior or posterior reconstruction: experience from a tertiary referral center[J]. J Clin Med, 2023, 12(4): 1358. doi: 10.3390/jcm12041358
[5] Tutolo M, Rosiello G, Stabile G, et al. The key role of levator ani thickness for early urinary continence recovery in patients undergoing robot-assisted radical prostatectomy: a multi-institutional study[J]. Neurourol Urodyn, 2022, 41(7): 1563-1572. doi: 10.1002/nau.25001
[6] Nyarangi-Dix JN, Tichy D, Hatiboglu G, et al. Complete bladder neck preservation promotes long-term post-prostatectomy continence without compromising midterm oncological outcome: analysis of a randomised controlled cohort[J]. World J Urol, 2018, 36(3): 349-355. doi: 10.1007/s00345-017-2134-1
[7] Belousov II, Tokhtamishyan SK, Ismailov RS. Correction of incontinence during radical prostates-tomy[J]. Urologiia, 2019, (6): 137-141.
[8] Martini A, Falagario UG, Villers A, et al. Contemporary techniques of prostate dissection for robot-assisted prostatectomy[J]. Eur Urol, 2020, 78(4): 583-591. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2020.07.017
[9] Gu X, Araki M, Wong C. Continence outcomes after bladder neck preservation during robot-assisted laparoscopic prostatectomy(RALP)[J]. Minim Invasive Ther Allied Technol, 2015, 24(6): 364-371. doi: 10.3109/13645706.2015.1027711
[10] Stolzenburg JU, Kallidonis P, Hicks J, et al. Effect of bladder neck preservation during endoscopic extraperitoneal radical prostatectomy on urinary continence[J]. Urol Int, 2010, 85(2): 135-138. doi: 10.1159/000314842
[11] Sood A, Grauer R, Jeong W, et al. Evaluating post radical prostatectomy mechanisms of early continence[J]. Prostate, 2022, 82(12): 1186-1195. doi: 10.1002/pros.24371
[12] Trinh L, Mingo S, Vanstrum EB, et al. Survival analysis using surgeon skill metrics and patient factors to predict urinary continence recovery after robot-assisted radical prostatectomy[J]. Eur Urol Focus, 2022, 8(2): 623-630. doi: 10.1016/j.euf.2021.04.001
[13] Hung AJ, Ma RZ, Cen S, et al. Surgeon automated performance metrics as predictors of early urinary continence recovery after robotic radical prostatectomy-a prospective Bi-institutional study[J]. Eur Urol Open Sci, 2021, 27: 65-72. doi: 10.1016/j.euros.2021.03.005
[14] Freire MP, Weinberg AC, Lei Y, et al. Anatomic bladder neck preservation during robotic-assisted laparoscopic radical prostatectomy: description of technique and outcomes[J]. Eur Urol, 2009, 56(6): 972-980. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2009.09.017
[15] Wiatr T, Choragwicki D, Gronostaj K, et al. Long-term functional outcomes of vesicourethral anastomosis with bladder neck preservation and distal urethral length preservation after videolaparoscopic radical prostatectomy[J]. Wideochir Inne Tech Maloinwazyjne, 2022, 17(3): 540-547.
[16] Lee Z, Sehgal SS, Graves RV, et al. Functional and oncologic outcomes of graded bladder neck preservation during robot-assisted radical prostatectomy[J]. J Endourol, 2014, 28(1): 48-55. doi: 10.1089/end.2013.0290
[17] Ratanapornsompong W, Pacharatakul S, Sangkum P, et al. Effect of puboprostatic ligament preservation during robotic-assisted laparoscopic radical prostatectomy on early continence: Randomized controlled trial[J]. Asian J Urol, 2021, 8(3): 260-268. doi: 10.1016/j.ajur.2020.11.002
[18] Heo JE, Lee JS, Goh HJ, et al. Urethral realignment with maximal urethral length and bladder neck preservation in robot-assisted radical prostatectomy: urinary continence recovery[J]. PLoS One, 2020, 15(1): e0227744. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0227744
[19] Kalampokis N, Grivas N, Karavitakis M, et al. Re: Aina Salazar, Lucas Regis, Jacques Planas, et al. A Randomised Controlled Trial to Assess the Benefit of Posterior Rhabdosphincter Reconstruction in Early Urinary Continence Recovery after Robot-assisted Radical Prostatectomy. Eur Urol Oncol 2022;5: 460-3[J]. Eur Urol Oncol, 2022, 5(4): 472-473. doi: 10.1016/j.euo.2021.08.004
-




 下载:
下载: