Establishment and internal validation of nomogram for prediction of ISUP upgrading of prostate biopsy Gleason score 6 or 7
-
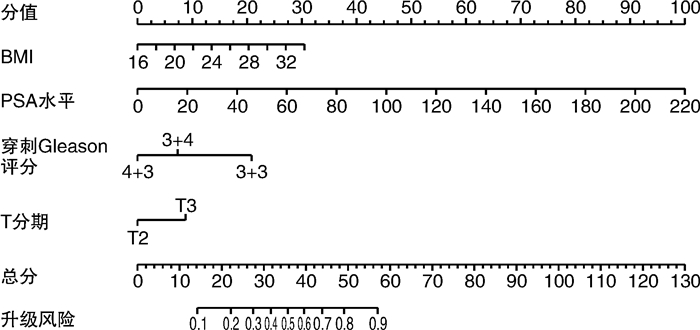
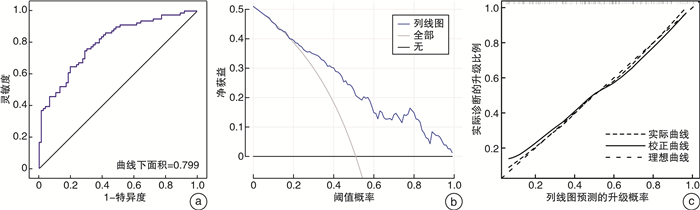
摘要: 目的 穿刺Gleason评分6~7分的前列腺癌患者术后易发生国际泌尿病理学会(International Society of Urological Pathology,ISUP)升级。因此,本研究通过临床指标构建一个预测ISUP分级升级的列线图模型并进行内部验证。方法 回顾性收集我院2019年1月—2021年12月因前列腺癌行手术治疗的患者临床病理资料。根据术后ISUP分级是否升级将纳入患者分为升级组和未升级组,Student t检验及χ2检验比较2组患者的临床指标,桑基图显示穿刺与术后ISUP的变化程度。通过logistic回归分析明确与ISUP升级相关的临床指标,构建术后ISUP升级的预测模型,受试者工作特征(ROC)曲线和曲线下面积用于评估模型的预测能力,校准曲线和决策曲线用于分析评估模型的准确性和临床有效性。结果 本研究共纳入155例患者。升级组和未升级组分别为79例和76例,升级比例为51.0%。在穿刺Gleason评分3+3、3+4、4+3分中,ISUP升级的比例分别为68.8%、47.1%和25.0%。预测列线图模型由体重指数(BMI)、穿刺前PSA水平、穿刺Gleason评分及临床T分期4个指标组成。ROC曲线结果显示预测模型的准确性高达0.799,校准曲线和决策曲线均提示预测模型具有一致性以及较好的临床获益。结论 由BMI、穿刺前PSA水平、穿刺Gleason评分及临床T分期4个指标构建的预测ISUP升级的列线图模型准确性相对较高,该模型有助于临床医师进行术前评估及为患者咨询提供个体化信息。
-
关键词:
- 前列腺癌 /
- 国际泌尿病理学会分级 /
- 根治性前列腺切除术 /
- 列线图
Abstract: Objective Gleason score 6 or 7 of biopsy pathology tend to upgrade after radical surgery. So this study aimed to develop and internally validate a nomogram to predict ISUP upgrading.Methods Clinicopathological information of prostate cancer patients, who underwent radical prostatectomy between January 2019 and December 2021 in our hospital were collected retrospectively. Patients were divided into two groups according to ISUP upgrading. Student t test and Chi-square test were applied to compare clinical parameters and Sankey diagram to describe ISUP group change. A predictive nomogram, which was constructed on the basis of four clinical indicators, was evaluated by receiver operation characteristic(ROC) curve and the area under the curve, furthermore, calibration curve and decision curve analysis were performed to evaluate the accuracy and efficiency of the nomogram.Results Totally 155 patients were enrolled and the groups with and without ISUP upgrading were 79 and 76 patients, respectively. The overall proportion of upgrading was 51.0%, and the corresponding proportion of biopsy Gleason score 3+3, 3+4 and 4+3 were 68.8%, 47.1% and 25.0%, respectively. The predictive nomogram was based on BMI, pre-biopsy PSA value, biopsy Gleason score and clinical T stage. The accuracy of nomogram was 0.799 and calibration curve and decision curve analysis proved the robustness and satisfactory clinical benefit of predictive model.Conclusion Our study proposed a predictive nomogram for ISUP upgrading with relatively high accuracy and the nomogram was helpful for preoperative evaluation and individualized consultation.-
Key words:
- prostate cancer /
- ISUP grading /
- radical prostatectomy /
- nomogram
-

-
表 1 穿刺和手术病理ISUP未升级组和升级组临床病理资料比较
例,X±S 项目 未升级组(76例) 升级组(79例) P值 年龄/岁 66.16±6.81 66.68±6.74 0.723 BMI/(kg/m2) 23.09±2.51 24.43±2.60 0.009 PSA/(ng/mL) 13.43±10.96 26.85±30.35 <0.001 穿刺病理 <0.001 3+3 20 44 3+4 27 24 4+3 29 11 T分期 0.011 T2 51 37 T3 25 42 手术切缘 0.804 阴性 59 60 阳性 17 19 淋巴结 0.086 阴性 76 76 阳性 0 3 前列腺体积/mL 48.60±30.36 46.03±29.68 0.261 PSAD/(ng/mL2) 0.36±0.35 0.56±0.64 <0.001 表 2 穿刺和手术病理变化情况
例 手术病理 穿刺Gleason评分 总计 3+3 3+4 4+3 3+3 20 8 4 32 3+4 28 19 14 61 4+3 11 15 11 37 3+5 1 1 1 3 4+4 0 3 6 9 5+3 0 1 0 1 4+5 4 3 2 9 5+4 0 1 2 3 总计 64 51 40 155 表 3 多因素logistic回归分析结果
因素 HR(95%CI) P值 BMI 1.185(1.010~1.390) 0.037 T分期 2.295(1.037~5.082) 0.041 穿刺Gleason评分 0.333(0.198~0.559) <0.001 PSA水平 1.048(1.016~1.080) 0.003 -
[1] 李晓东, 瞿根义, 许宁, 等. ISUP版Gleason评分在前列腺癌根治术后评分升级的影响因素分析[J]. 中华男科学杂志, 2016, 22(5): 415-419. doi: 10.13263/j.cnki.nja.2016.05.006
[2] Freedland SJ, Kane CJ, Amling CL, et al. Upgrading and downgrading of prostate needle biopsy specimens: risk factors and clinical implications[J]. Urology, 2007, 69(3): 495-499. doi: 10.1016/j.urology.2006.10.036
[3] Pinthus JH, Witkos M, Fleshner NE, et al. Prostate cancers scored as Gleason 6 on prostate biopsy are frequently Gleason 7 tumors at radical prostatectomy: implication on outcome[J]. J Urol, 2006, 176(3): 979-984. doi: 10.1016/j.juro.2006.04.102
[4] Takeshima Y, Yamada Y, Teshima T, et al. Clinical significance and risk factors of International Society of Urological Pathology(ISUP)grade upgrading in prostate cancer patients undergoing robot-assisted radical prostatectomy[J]. BMC Cancer, 2021, 21(1): 501. doi: 10.1186/s12885-021-08248-y
[5] Delahunt B, Egevad L, Srigley JR, et al. Validation of International Society of Urological Pathology(ISUP)grading for prostatic adenocarcinoma in thin core biopsies using TROG 03.04'RADAR'trial clinical data[J]. Pathology, 2015, 47(6): 520-525. doi: 10.1097/PAT.0000000000000318
[6] Novak V, Vesely S, Luksanová H, et al. Preoperative prostate health index predicts adverse pathology and Gleason score upgrading after radical prostatectomy for prostate cancer[J]. BMC Urol, 2020, 20(1): 144. doi: 10.1186/s12894-020-00711-5
[7] Altok M, Troncoso P, Achim MF, et al. Prostate cancer upgrading or downgrading of biopsy Gleason scores at radical prostatectomy: prediction of regression to the mean using routine clinical features with correlating biochemical relapse rates[J]. Asian J Androl, 2019, 21(6): 598-604. doi: 10.4103/aja.aja_29_19
[8] Yang DD, Mahal BA, Muralidhar V, et al. Risk of upgrading and upstaging among 10 000 patients with gleason 3+4 favorable intermediate-risk prostate cancer [J]. Eur Urol Focus, 2019, 5(1): 69-76. doi: 10.1016/j.euf.2017.05.011
[9] Grenville ZS, Noor U, His M, et al. Diet and BMI correlate with metabolite patterns associated with aggressive prostate cancer [J]. Nutrients, 2022, 14(16): 3306. doi: 10.3390/nu14163306
[10] Perez-Cornago A, Dunneram Y, Watts EL, et al. Adiposity and risk of prostate cancer death: a prospective analysis in UK Biobank and meta-analysis of published studies[J]. BMC Med, 2022, 20(1): 143. doi: 10.1186/s12916-022-02336-x
[11] Ohwaki K, Endo F, Hattori K. Abdominal obesity, hypertension, antihypertensive medication use and biochemical recurrence of prostate cancer after radical prostatectomy[J]. Eur J Cancer, 2015, 51(5): 604-609. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2015.01.003
[12] de Cobelli O, Terracciano D, Tagliabue E, et al. Body mass index was associated with upstaging and upgrading in patients with low-risk prostate cancer who met the inclusion criteria for active surveillance[J]. Urol Oncol, 2015, 33(5): 201.e1-201.e8. doi: 10.1016/j.urolonc.2015.02.004
[13] Beckmann K, O'Callaghan M, Vincent A, et al. Extent and predictors of grade upgrading and downgrading in an Australian cohort according to the new prostate cancer grade groupings[J]. Asian J Urol, 2019, 6(4): 321-329. doi: 10.1016/j.ajur.2019.03.001
-





 下载:
下载: