Meta-analysis of the effect of alpha blockers on ureteral access sheath placement during flexible ureteroscopic lithotripsy
-
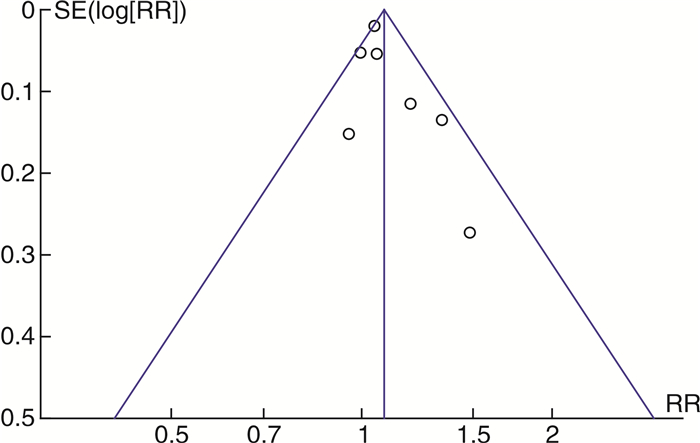
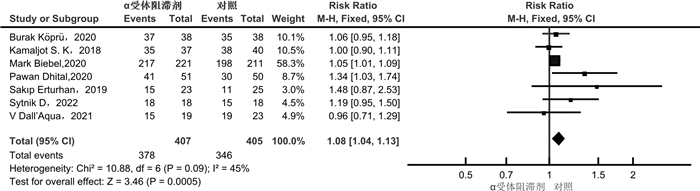
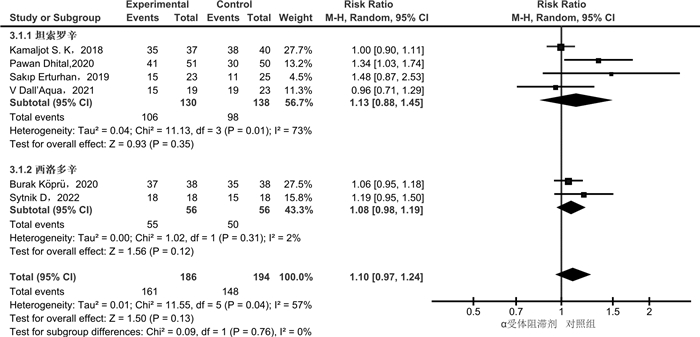
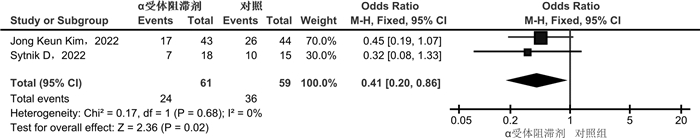
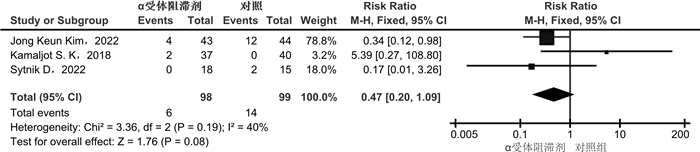
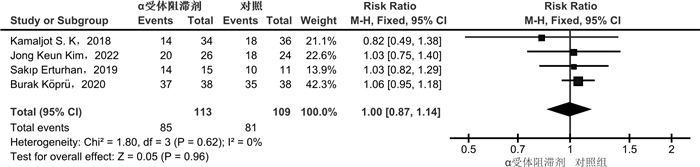
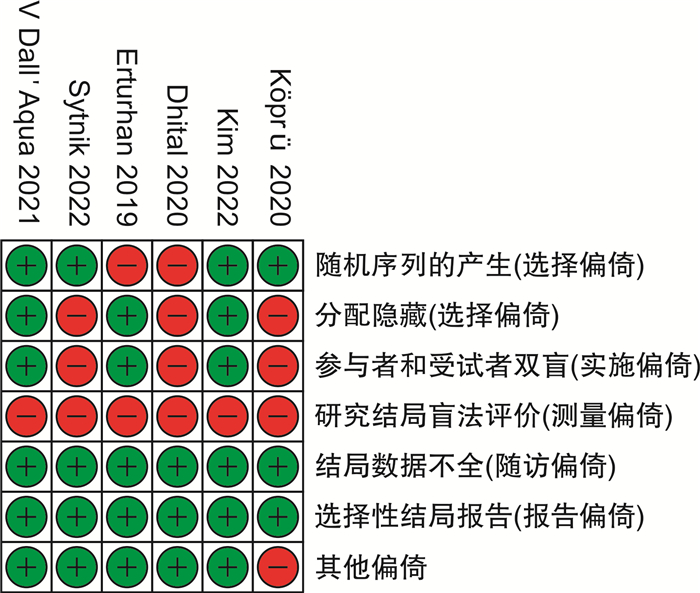
摘要: 目的 α受体阻滞剂可以减少输尿管收缩力和蠕动频率,降低放置输尿管通道鞘(ureteral access sheath,UAS)的阻力。较小的置鞘阻力与更低程度的置鞘损伤有关,并增加置鞘成功的可能性。目前相关研究的质量参差不齐,研究结果间存在差异。通过系统回顾和meta分析,评价术前应用α受体阻滞剂在置鞘过程中的作用。方法 系统检索PubMed、Web of Science和Cochrane library数据库,时间截至2023年3月1日,查找关于术前应用α受体阻滞剂对UAS置入影响的临床研究。按照术前是否应用α受体阻滞剂分为试验组和对照组,研究的主要结果为UAS置入成功率;次要结果为输尿管损伤、术后结石清除率。结果 经过筛选后共纳入8篇研究,899例患者。分析显示,试验组的置鞘成功率显著高于对照组(RR=1.08,95%CI:1.04~1.13,P < 0.05)。对药物种类的亚组分析显示,坦索罗辛和西洛多辛在置鞘过程中的效应相似(P>0.05)。依据输尿管损伤的PULS分级,对不同输尿管损伤等级进行亚组分析显示,≥0级输尿管损伤2组差异无统计学意义(RR=0.99,95%CI:0.86~1.13,P>0.05);≥1级输尿管损伤在试验组更低(RR=0.64,95%CI:0.44~0.93,P < 0.05);≥2级输尿管损伤2组差异无统计学意义(RR=0.47,95%CI:0.20~1.09,P>0.05)。2组具有相似的术后结石清除率(RR=1.04,95%CI:0.93~1.17,P>0.05)。结论 术前应用α受体阻滞剂可提高UAS置入成功率,可能与较低的输尿管损伤等级有关。坦索罗辛和西洛多辛在置鞘过程中的效应相似。Abstract: Objective To evaluate the role of α receptor blockers in the process of ureteral access sheath (UAS) placement before surgery through systematic review and meta-analysis.Methods A systematic search of PubMed, Web of Science and Cochrane library databases up to March 1st, 2023 was conducted to find clinical studies on the effect of preoperative alpha-blockers on sheath placement. The main results of the study were the success rate of UAS placement. Secondary outcomes were ureteral injury and postoperative stone free rate (SFR).Results After screening, a total of 8 studies with 899 patients were included. The results of analysis showed that the success rate of placement in the α-blocker group was significantly higher than that in the control group(RR=1.08, 95%CI: 1.04-1.13, P < 0.05). Subgroup analysis of drug types showed that tamsulosin and silodosin had similar effects during sheath placement(P>0.05). According to PULS grade of ureteral injury, subgroup analysis of ureteral injury grade ≥0 was similar between the two groups(RR=0.99, 95%CI: 0.86-1.13, P>0.05). Grade ≥1 ureteral injury was lower in the α-blocker group(RR=0.64, 95%CI: 0.44-0.93, P < 0.05). Grade ≥2 ureteral injury was similar between the two groups(RR=0.47, 95%CI: 0.20-1.09, P>0.05). The postoperative SFR was similar between the two groups(RR=1.04, 95%CI: 0.93-1.17, P>0.05).Conclusion Preoperative application of alpha-blockers increased the success rate of UAS placement, which may be associated with a lower grade of ureteral injury. The effects of tamsulosin and silodosin in the process of sheath placement are similar.
-
Key words:
- alpha receptor blockers /
- ureteral access sheath /
- ureteral injury /
- meta-analysis
-

-
表 1 纳入研究的基础特征表
纳入研究 研究类型 分组 用药方案 例数 置鞘成功率 输尿管损伤 SFR SFR 质量评价 UAS型号 置鞘辅助方式 0级 1级 ≥2级 时间/残石标准/方式 Kaler等[8]
2018
美国回顾 坦索罗辛 未提及,7 d 37 32/35 — — 2 14/34 3 d/4 mm/CT 8/9 16F,以及更小的型号 单根导丝 空白对照 — 40 17/38 0 18/36 Kim等[9]
2022
韩国随机对照 西洛多辛 8 mg q/d, 3 d 43 — 26 13 4 20/26 3个月/2 mm/CT 6/7 11/13F 透视 空白对照 — 44 18 14 12 18/24 Erturhan等[10]
2019
土耳其随机对照 坦索罗辛 0.4 mgq/d, 2周 23 15/23 - 14/15 2周/未提及/超声 5/7 9.5/11.5F 透视 空白对照 23 — 11/25 10/11 Biebel等[11]
2020
美国回顾 α受体阻滞剂 未提及 221 217/221 - - - 7/9 12/14 F 未提及 空白对照 211 198/211 Köprü等[12]
2020
土耳其随机对照 西洛多辛 8 mg q/d, 10 d 38 37/38 - 37/37 3个月/4 mm/CT 3/7 9.5 F 未提及 空白对照 — 38 35/35 35/35 Dall'Aqua等[13]
2021
巴西随机对照 坦索罗辛 0.4 mgq/d, 7 d 19 15/19 83 - - 6/7 未提及 未提及 空白对照 — 23 19/23 Dhital等[14]
2020
尼泊尔随机对照 坦索罗辛 0.4 mgq/d, ≥7 d 51 41/51 1618 - - 3/7 未提及 未提及 空白对照 — 50 30/50 Sytnik等[15]
2022
俄罗斯随机对照 西洛多辛 8 mg q/d, 4 d 18 18/18 11 7 0 - - 4/7 11/13F 未提及 — — 18 15/18 5 8 2 注:q/d:每天1次;CT:电子计算机断层扫描。 -
[1] de Coninck V, Keller EX, Rodríguez-Monsalve M, et al. Systematic review of ureteral access sheaths: facts and myths[J]. BJU Int, 2018, 122(6): 959-969. doi: 10.1111/bju.14389
[2] Zeng GH, Zhao ZJ, Mazzon G, et al. European association of urology section of urolithiasis and international alliance of urolithiasis joint consensus on retrograde intrarenal surgery for the management of renal stones[J]. Eur Urol Focus, 2022, 8(5): 1461-1468. doi: 10.1016/j.euf.2021.10.011
[3] Ecer G, Sönmez MG, Aydın A, et al. Comparison of retrograde intrarenal stone surgery with and without a ureteral access sheath using kidney injury molecule-1(KIM-1) levels: a prospective randomized study[J]. Urolithiasis, 2022, 50(5): 625-633. doi: 10.1007/s00240-022-01345-y
[4] Agrawal S, Patil A, Sabnis RB, et al. Initial experience with slimmest single-use flexible ureteroscope Uscope PU3033A(PUSENTM)in retrograde intrarenal surgery and its comparison with Uscope PU3022a: a single-center prospective study[J]. World J Urol, 2021, 39(10): 3957-3962. doi: 10.1007/s00345-021-03707-4
[5] Lildal SK, Nørregaard R, Andreassen KH, et al. Ureteral access sheath influence on the ureteral wall evaluated by cyclooxygenase-2 and tumor necrosis factor-α in a porcine model[J]. J Endourol, 2017, 31(3): 307-313. doi: 10.1089/end.2016.0773
[6] Staubli SE, Mordasini L, Engeler DS, et al. Economic aspects of morbidity caused by ureteral stents[J]. Urol Int, 2016, 97(1): 91-97. doi: 10.1159/000443379
[7] Joshi HB, Stainthorpe A, MacDonagh RP, et al. Indwelling ureteral stents: evaluation of symptoms, quality of life and utility[J]. J Urol, 2003, 169(3): 1065-1069;discussion 1069. doi: 10.1097/01.ju.0000048980.33855.90
[8] Kaler KS, Safiullah S, Lama DJ, et al. Medical impulsive therapy(MIT): the impact of 1 week of preoperative tamsulosin on deployment of 16-French ureteral access sheaths without preoperative ureteral stent placement[J]. World J Urol, 2018, 36(12): 2065-2071. doi: 10.1007/s00345-018-2336-1
[9] Kim JK, Choi CI, Lee SH, et al. Silodosin for prevention of ureteral injuries resulting from insertion of a ureteral access sheath: a randomized controlled trial[J]. Eur Urol Focus, 2022, 8(2): 572-579. doi: 10.1016/j.euf.2021.03.009
[10] Erturhan S, Bayrak Ö, Şen H, et al. Can alpha blockers facilitate the placement of ureteral access sheaths in retrograde intrarenal surgery?[J]. Turk J Urol, 2019, 45(2): 108-112. doi: 10.5152/tud.2019.63373
[11] Biebel M, Merheb S, Boyko A, et al. Do pre-operative alpha-blockers increase the success of ureteral access sheath placement?[J]. J Urol, 2020, 203(Supplement 4): e208.
[12] Köprü B, Ebilo lu T, Kaya E, et al. Does preoperative use of silodosin affect the stages of F-URS procedure?[J]. Arch Esp Urol, 2020, 73(1): 47-53.
[13] Dall'Aqua V, Lopes AC Neto, Rodrigues A, et al. Medical impulsive therapy: early results from a randomized controlled trial to evaluate tamsulosin use before ureteral access sheath deployment[J]. Journal of endourology / Endourological Society, 2021(SUPPL 1).
[14] Dhital P, Gnyawali D, Sharma U, et al. pd34-09 preoperative tamsulosin in increasing the probability of ureteral access sheath insertion during retrograde intrarenal surgery: a prospective randomized study[J]. J Urol, 2020, 203(Suppl 4): E714.
[15] Sytnik D, Popov S, Orlov I, et al. The using of silodosin to reduce ureteral injury during RIRS with the use of the ureteral access sheath[J]. Eur Urol Open Sci, 2022, 39: S83. doi: 10.1016/S2666-1683(22)00153-7
[16] Schoenthaler M, Buchholz N, Farin E, et al. The Post-Ureteroscopic Lesion Scale(PULS): a multicenter video-based evaluation of inter-rater reliability[J]. World J Urol, 2014, 32(4): 1033-1040. doi: 10.1007/s00345-013-1185-1
[17] Koo KC, Yoon JH, Park NC, et al. The impact of preoperative α-adrenergic antagonists on ureteral access sheath insertion force and the upper limit of force required to avoid ureteral mucosal injury: a randomized controlled study[J]. J Urol, 2018, 199(6): 1622-1630. doi: 10.1016/j.juro.2017.09.173
[18] Giuliano F. Impact of medical treatments for benign prostatic hyperplasia on sexual function[J]. BJU Int, 2006, 97(Suppl 2): 34-38;discussion 44-45.
[19] Abrams P, Speakman M, Stott M, et al. A dose-ranging study of the efficacy and safety of tamsulosin, the first prostate-selective alpha 1A-adrenoceptor antagonist, in patients with benign prostatic obstruction(symptomatic benign prostatic hyperplasia)[J]. Br J Urol, 1997, 80(4): 587-596. doi: 10.1046/j.1464-410X.1997.00380.x
[20] Rossi M, Roumeguère T. Silodosin in the treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia[J]. Drug Des Devel Ther, 2010, 4: 291-297.
[21] Sharma G, Pareek T, Kaundal P, et al. Comparison of efficacy of three commonly used alpha-blockers as medical expulsive therapy for distal ureter stones: a systematic review and network meta-analysis[J]. Int Braz J Urol, 2022, 48(5): 742-759. doi: 10.1590/s1677-5538.ibju.2020.0548
[22] Chapple CR, Montorsi F, Tammela TL, et al. Silodosin therapy for lower urinary tract symptoms in men with suspected benign prostatic hyperplasia: results of an international, randomized, double-blind, placebo-and active-controlled clinical trial performed in Europe[J]. Eur Urol, 2011, 59(3): 342-352. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2010.10.046
[23] Zelenko N, Coll D, Rosenfeld AT, et al. Normal ureter size on unenhanced helical CT[J]. AJR Am J Roentgenol, 2004, 182(4): 1039-1041. doi: 10.2214/ajr.182.4.1821039
[24] Pedro RN, Weiland D, Reardon S, et al. Ureteral access sheath insertion forces: implications for design and training[J]. Urol Res, 2007, 35(2): 107-109. doi: 10.1007/s00240-007-0086-4
[25] Ulvik Ø, Wentzel-Larsen T. A novel method to measure the mechanical pushing and pulling forces during ureteroscopy in a normal clinical setting[J]. J Endourol, 2013, 27(5): 625-630. doi: 10.1089/end.2012.0563
[26] Tapiero S, Kaler KS, Jiang PB, et al. Determining the safety threshold for the passage of a ureteral access sheath in clinical practice using a purpose-built force sensor[J]. J Urol, 2021, 206(2): 364-372. doi: 10.1097/JU.0000000000001719
[27] Gangkak G, Teli RD, Yadav SS, et al. A single oral dose of Silodosin and Diclofenac sodium is effective in reducing pain after ureteric stent removal: a prospective, randomized, double blind placebo-controlled study[J]. Springerplus, 2016, 5: 23. doi: 10.1186/s40064-015-1662-7
-




 下载:
下载: