Clinical application of bilateral anterior urethral suspension combined with intrafascial excision in robot-assisted radical prostatectomy
-
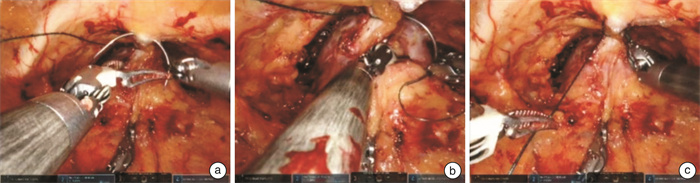
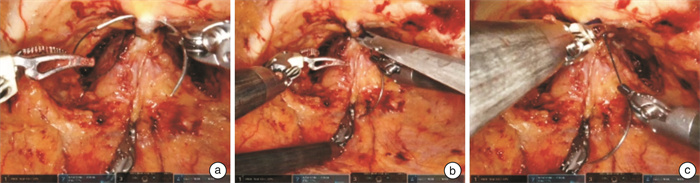
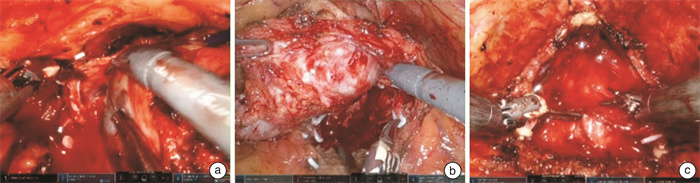
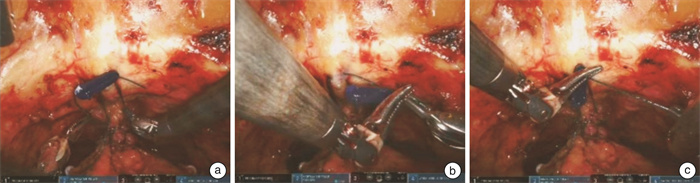
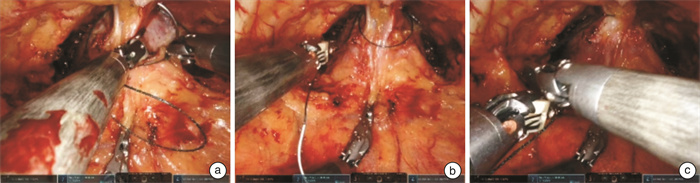
摘要: 目的 探讨双边尿道前悬吊联合筋膜内切除技术在机器人辅助根治性前列腺切除术(robot assisted radical prostatectomy,RARP)后早期尿控恢复中的作用。方法 收集2022年6月—2023年6月上海交通大学医学院附属新华医院收治的50例前列腺癌患者,采用上述技术进行RARP,所有患者均为低危或中危病例。相比于传统的RARP,该技术的核心主要为双边尿道前悬吊和筋膜内切除技术。尿道前悬吊是将耻骨前列腺韧带-背血管复合体缝扎后悬吊于耻骨骨膜,从而提高术后尿道的稳固性。术中执行的是双边悬吊技术,相比于单边悬吊,可以更好地维持尿道稳定性。筋膜内切除技术根据患者情况,分为保留单侧神经血管束和保留双侧神经血管束。结果 所有患者均顺利完成手术。术后6周复查总前列腺特异性抗原(total prostate-specific antigen,tPSA)提示,所有患者瘤控良好。术后52%的患者实现即刻控尿,其中保留单侧神经血管束组和保留双侧神经血管束组分别为40%和70%。术后6周,96%的患者实现良好控尿,保留单侧神经血管束组和保留双侧神经血管束组分别为95.0%和96.6%。术后3个月,全部患者实现良好控尿。结论 在RARP中,双边尿道前悬吊联合筋膜内切除技术可以帮助患者实现早期尿控恢复,对于中低危前列腺癌患者而言,值得运用和推广。Abstract: Objective To investigate the effect of bilateral anterior urethral suspension combined with intrafascial excision on early recovery of urinary continence after robot-assisted radical prostatectomy(RARP).Methods Fifty patients with prostate cancer were treated with the RARP from June 2022 to June 2023 in Xinhua Hospital Affiliated to Medical College of Shanghai Jiao Tong University. All patients were low-risk or medium-risk cases. Compared with the traditional RARP, the core techniques in our operation are mainly bilateral anterior urethral suspension and intrafascial excision. The anterior urethral suspension is to suspend the puboprostatic ligamental-dorsal vascular complex from the pubic periosteum after suture to improve the stability of the urethra after surgery. The bilateral suspension technique is performed during the operation, which can better maintain urethral stability than unilateral suspension. According to the patient's condition, the technique of intrafascial resection can be divided into unilateral and bilateral neurovascular bundle preservation techniques.Results All patients were successfully completed the operation. The tPSA reexamination 6 weeks after surgery indicated that all patients had good tumor control. In terms of immediate postoperative urinary continence, 52% of patients achieved immediate urinary continence, and 40% and 70% of patients in the unilateral and bilateral neurovascular bundle preservation groups, respectively. In terms of urine continence recovery at 6 weeks after surgery, 96% of patients achieved good urine continence, including 95.0% and 96.6% in the group with unilateral and bilateral neurovascular bundle preservation, respectively. At 3 months after surgery, all patients achieved good urinary continence.Conclusion In RARP, bilateral anterior urethral suspension combined with intrafascial excision can help patients achieve early recovery of urinary continence, and it is worthy of application and promotion for middle and low risk prostate cancer patients.
-

-
[1] 王劲松, 魏家燕, 彭敏. 2023年美国癌症统计报告和全球最新癌症统计数据解读及启示[J]. 实用肿瘤杂志, 2023, 38(6): 523-527. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYZZ202306006.htm
[2] Urkmez A, Ranasinghe W, Davis JW. Surgical techniques to improve continence recovery after robot-assisted radical prostatectomy[J]. Transl Androl Urol, 2020, 9(6): 3036-3048. doi: 10.21037/tau.2020.03.36
[3] Ju GQ, Wang ZJ, Shi JZ, et al. A comparison of perioperative outcomes between extraperitoneal robotic single-port and multiport radical prostatectomy with the da Vinci Si Surgical System[J]. Asian J Androl, 2021, 23(6): 640-647. doi: 10.4103/aja.aja_50_21
[4] Culp MB, Soerjomataram I, Efstathiou JA, et al. Recent global patterns in prostate cancer incidence and mortality rates[J]. Eur Urol, 2020, 77(1): 38-52. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2019.08.005
[5] 刘子豪, 刘洋, 牛远杰, 等. 不同入路途径机器人辅助腹腔镜根治性前列腺切除术的研究进展[J]. 临床泌尿外科杂志, 2024, 39(1): 65-68, 71. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.1001-1420.2024.01.012
[6] Zattoni F, Artibani W, Patel V, et al. Technical innovations to optimize continence recovery after robotic assisted radical prostatectomy[J]. Ital J Urol Nephrol, 2019, 71(4): 324-338.
[7] 兰芳, 范祎, 孙吉. 根治性前列腺切除术后早期尿控影响因素研究进展[J]. 浙江医学, 2023, 45(21): 2349-2352. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZJYE202321025.htm
[8] 王鑫哲, 范成娟, 赵战魁. 前列腺根治性切除术中尿控及性功能保护的研究进展[J]. 国际泌尿系统杂志, 2022, 42(4): 750-753. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn431460-20201211-00204
[9] Walz J, Epstein JI, Ganzer R, et al. A critical analysis of the current knowledge of surgical anatomy of the prostate related to optimisation of cancer control and preservation of continence and erection in candidates for radical prostatectomy: an update[J]. Eur Urol, 2016, 70(2): 301-311. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2016.01.026
[10] Gacci M, de Nunzio C, Sakalis V, et al. Latest evidence on post-prostatectomy urinary incontinence[J]. J Clin Med, 2023, 12(3): 1190. doi: 10.3390/jcm12031190
[11] 成宇翔, 何屹. 前列腺根治性切除术后尿失禁的治疗现状与进展[J]. 国际泌尿系统杂志, 2023, 43(4): 719-723.
[12] Ferreira A, Duarte Cruz C. The urethra in continence and sensation: Neural aspects of urethral function[J]. Neurourol Urodyn, 2021, 40(3): 744-752. doi: 10.1002/nau.24632
[13] Patel VR, Coelho RF, Palmer KJ, et al. Periurethral suspension stitch during robot-assisted laparoscopic radical prostatectomy: description of the technique and continence outcomes[J]. Eur Urol, 2009, 56(3): 472-478. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2009.06.007
[14] Moschovas MC, Patel V. Nerve-sparing robotic-assisted radical prostatectomy: how I do it after 15.000 cases[J]. Int Braz J Urol, 2022, 48(2): 369-370.
[15] 曲发军, 徐丁, 虞永江, 等. 经腹膜外途径行单孔机器人辅助腹腔镜前列腺癌根治术的临床应用(附36例报告)[J]. 腹腔镜外科杂志, 2022, 27(8): 607-611, 617. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FQJW202208010.htm
-




 下载:
下载: