Prognostic analysis of molecular subtypes of invasive bladder cancer and PD-L1 as a potential prognostic marker
-
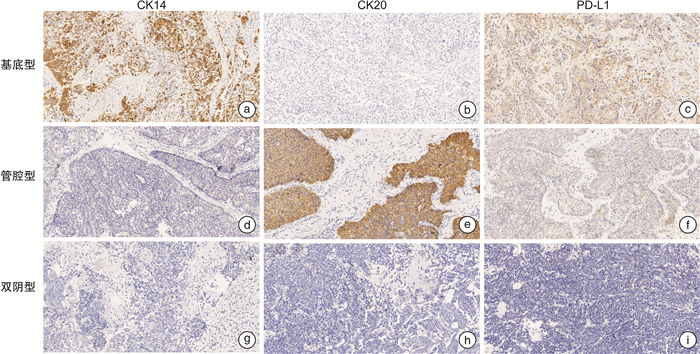
摘要: 目的 探讨浸润性膀胱癌(invasive bladder cancer,IBC)分子分型与预后的关系以及PD-L1在不同分子分型中的表达情况。方法 回顾性分析2016年1月—2018年12月内蒙古医科大学附属医院122例IBC患者的临床资料并进行了随访;采用免疫组织化学方法检测CK14、CK20在IBC中的表达,将IBC分为基底型(CK14+,CK20-)、管腔型(CK14-,CK20+)和双阴型(CK14-,CK20-)三种分子亚型;比较三组患者的临床病理特征;比较不同分子分型膀胱癌患者的生存率;分析PD-L1的表达与分子亚型的相关性。结果 122例患者中,基底型43例,管腔型56例,双阴型23例;与管腔型肿瘤比较,基底型和双阴型肿瘤的病理分期多在T2期以上;与管腔型、双阴型肿瘤患者比较,基底型肿瘤患者更易发生远处转移;管腔型膀胱癌患者的生存率显著高于基底型和双阴型膀胱癌患者(P< 0.05);与管腔型和双阴型比较,PD-L1在基底型IBC中高表达(P< 0.05)。结论 与管腔型肿瘤患者比较,基底型和双阴型肿瘤患者预后较差;与管腔型和双阴型肿瘤相比,PD-L1在基底型肿瘤中高表达;提示PD-L1可能成为该型患者潜在的免疫治疗靶点。Abstract: Objective To investigate the relationship between molecular classification of invasive bladder cancer (IBC) and prognosis, along with the expression level of PD-L1 in different molecular subtypes of IBC.Methods We collected and operated retrospective analysis of the medical record data and follow-up information of total 122 patients at Affiliated Hospital of Inner Mongolia Medical University from Jan. 2016 to Dec. 2018. Based on the expression level of biomarkers of CK14 and CK20 detected by immunohistochemistry staining, clinical cases were categorized as basal (CK14+, CK20-) IBC, luminal (CK14-, CK20+) IBC and double-negative (CK14-, CK20-) IBC. We compared the survival rates of patients, as well as the clinicopathological features of the three subtypes. We also elucidated the expression pattern of PD-L1 in different subgroups of IBC.Results Total 122 cases were classified as 43 cases of basal IBC, 56 cases of luminal IBC and 23 cases of double negative subtype IBC. As for pathological stages, compared with luminal IBC, the basal IBC and double negative IBC were more than stage T2. Patients with basal IBC were more likely to have distant metastasis. Meanwhile, patients with luminal IBC showed significantly higher survival rate than those patients with basal subtype (P< 0.05) or double negative subtype (P< 0.05). Additionally, we detected relative higher PD-L1 expression level in basal IBC compared with that in luminal IBC or in double-negative IBC (P< 0.05).Conclusion Among three subtypes of IBC, patients with basal IBC or double negative IBC had a worse prognosis. Compared with luminal and double negative IBC, PD-L1 expression level was higher in basal IBC, suggesting that PD-L1 may be a potential target for immunotherapy to benefit those patients.
-
Key words:
- invasive bladder cancer /
- prognosis /
- molecular subgroup /
- immunohistochemistry /
- molecular target
-

-
表 表 1 不同分子分型的IBC患者的临床病理特征比较
例(%) 变量 基底型
(n=43)管腔型
(n=56)双阴型
(n=23)χ2 P值 变量 基底型
(n=43)管腔型
(n=56)双阴型
(n=23)χ2 P值 年龄 4.653 0.098 肿瘤分期 16.973 0.009 ≤70岁 32(74.4) 36(64.3) 11(47.8) T1 20(48.8) 28(48.2) 10(43.5) >70岁 11(25.6) 20(35.7) 12(52.5) T2 13(27.9) 25(46.4) 4(17.4) 性别 0.633 0.729 T3 6(14.0) 3(5.5) 7(30.4) 男 34(79.1) 46(82.1) 20(87.0) T4 4(9.3) 0 2(8.7) 女 9(20.9) 10(17.9) 3(13.0) 脉管侵犯 2.413 0.299 肿瘤大小 3.424 0.18 有 9(20.9) 7(12.5) 6(21.6) ≤3 cm 23(53.5) 40(71.4) 14(60.9) 无 34(79.1) 49(87.5) 17(73.9) >3 cm 20(46.5) 16(28.6) 9(39.1) 淋巴结转移 4.218 0.121 肿瘤数目 1.896 0.388 有 6(14.0) 2(3.6) 1(4.3) 单发 36(83.7) 44(78.6) 21(91.3) 无 37(86.0) 54(96.4) 22(95.7) 多发 7(16.3) 12(21.4) 2(8.7) 远处转移 11.320 0.001 组织学变异 2.856 0.24 有 7(16.3) 0 0 有 15(34.9) 13(23.2) 4(17.4) 无 36(83.7) 56(100.0) 23(100.0) 无 28(65.1) 43(76.8) 19(82.6) 复发史 5.836 0.054 肿瘤分级 2.535 0.281 有 6(14.0) 11(19.6) 9(39.1) 低级别 36(83.7) 51(91.1) 18(78.3) 无 37(86.0) 45(80.4) 14(60.9) 高级别 7(16.3) 5(8.9) 5(21.7) 表 表 2 不同分子分型IBC患者的生存率比较
分子分型 例数 生存例数 生存率/% χ2 P值 基底型 43 27 62.8 管腔型 56 48 85.7 7.677 0.022 双阴型 23 15 65.2 表 表 3 PD-L1与CK14及CK20的相关性
PD-L1 CK14 CK20 阴性 阳性 阴性 阳性 阴性 54 29 33 50 阳性 13 26 26 13 P值 0.001 0.005 rs 0.297 -0.251 表 表 4 PD-L1与IBC分子分型的相关性
分子分型 例数 PD-L1 χ2 P值 阴性 阳性 基底型 43 17 26 25.214 0 管腔型 56 48 8 双阴型 23 18 5 -
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] [6] [7] [8] [9] [10] [11] [12] [13] [14] [15] [16] -




 下载:
下载: