Super-veil extraperitoneal single-port robotic radical prostatectomy: surgical technique and clinical application
-
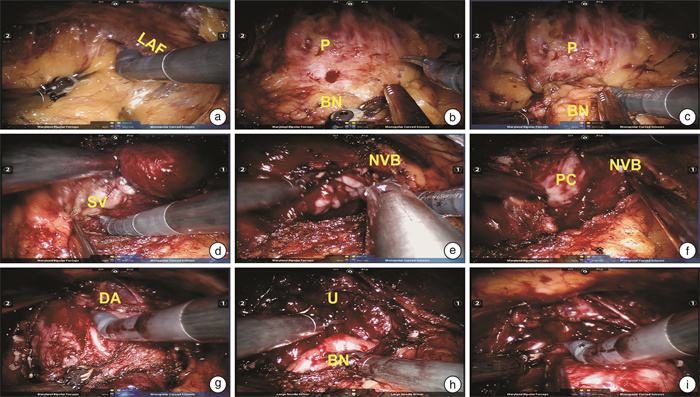
摘要: 目的 描述“超级面纱法”腹膜外单孔机器人前列腺癌根治术(super-veil extraperitoneal single-port robotic assisted radical prostatectomy,sesRARP)的手术步骤,总结短期随访结果,探讨其最佳应用场景。方法 回顾性分析2018年12月—2021年6月行sesRARP的41例器官局限性前列腺癌患者的临床资料。年龄52~79岁,平均(63.9±4.3)岁; 前列腺特异性抗原(PSA)中位数8.70(6.35,11.84) ng/mL,中位前列腺体积32.90(28.98,33.85) mL,术前排尿功能正常,规律行性生活。术中取耻骨上5 cm横切口。性神经保留采用“超级面纱法”,将双侧血管神经束及腹侧的背深静脉丛、逼尿肌裙与耻骨膀胱韧带紧贴前列腺包膜完整分离。记录围术期并发症、出院前疼痛评分、住院天数、PSA随访指标、尿控恢复时间、性功能恢复时间等。结果 平均手术时间(93.3±28.29) min。术中出血量72.7(50~150) mL,未输血。切缘阳性率为14.6%(6/41)。术后住院天数为3(1.0,3.0) d。出院前疼痛评分为0(0,1.75)分,术后第7天拔除导尿管。围术期无Clavien Ⅲ级或以上并发症。中位随访时间为13(3~31)个月。术后12个月无生化复发生存率为97.2%(35/36)。即刻尿控恢复率为24.4%(10/41),术后1、3、6、12个月尿控恢复率分别为56.1%(23/41)、70.7%(29/41)、84.6%(33/39)、94.4%(34/36)。术后6、12个月性功能恢复率为41.0%(16/39)、63.9%(23/36)。结论 sesRARP具有创伤更小、术后恢复更快、并发症风险更低等优点,术后短期尿控与性功能恢复率高,对于较年轻、对术后生活质量要求较高的局灶期前列腺癌患者可能是更优的术式,但应充分把握适应证与适用人群,同时做好术前临床与影像学评估。Abstract: Objective To demonstrate the surgical steps of super-veil extraperitoneal single-port robotic assisted radical prostatectomy (sesRARP), review its short-term functional outcomes, and discuss the optimal application scenario.Methods Forty-one organ-confined prostate cancer patients who had undergone sesRARP were retrospectively included from December 2018 to June 2021. The patients aged 52 to 79 years (mean±SD, 63.9±4.3) with a baseline median prostate specific antigen (PSA) of 8.70 (6.35, 11.84) ng/mL and a median prostate volume of 32.90 (28.98, 33.85) mL. All patients had normal micturition and were sexually active. A 5 cm transverse incision was adopted above the pubis symphysis. Super-veil nerve-sparing technique was adopted, in which bilateral neurovascular bundles and ventral anatomical structures surrounding the prostate, namely the deep venous complex, detrusor apron and pubovesical ligaments were preserved as an entity. Perioperative complications, pain score on discharge, length of stay, postoperative PSA, and continence and potency recovery were documented.Results Mean operative time was (93.3±28.29) min. Estimated blood loss was 72.7 mL (range, 50-150 mL). No patient required blood transfusion. Positive surgical margin was 14.6% (6/41). Postoperative length of stay was 3 days (1.0, 3.0). Pain score on discharge was 0 (0, 1.75). Foley catheter was removed on postoperative day 7. No complications graded Clavien Ⅲ or above were documented. Median follow-up time was 13 months (range, 3-31 months). Twelve-month biochemical recurrence-free survival was 97.2% (35/36). Instant continence recovery was 24.4% (10/41), and 1-, 3-, 6-, and 12-month recovery were 56.1% (23/41), 70.7% (29/41), 84.6% (33/39) and 94.4% (34/36), respectively.Conclusion Super-veil extraperitoneal single-port robotic-assisted radical prostatectomy has potential merits of less trauma, more rapid recovery, lower comorbidities, with faster short-term continence and potency recovery. It is best indicated for younger patients with localized disease and higher demand of postoperative quality of life, therefore caution must be paid on patient selection and preoperative clinical and radiological evaluations.
-
Key words:
- extraperitoneal /
- da Vinci robot /
- single-port surgery /
- nerve-sparing /
- radical prostatectomy
-

-
[1] Mottet N, van den Bergh R, Briers E, et al. EAU-EANM-ESTRO-ESUR-SIOG Guidelines on Prostate Cancer-2020 Update. Part 1: Screening, Diagnosis, and Local Treatment with Curative Intent[J]. Eur Urol, 2021, 79(2): 243-262. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2020.09.042
[2] Menon M, Shrivastava A, Bhandari M, et al. Vattikuti Institute prostatectomy: technical modifications in 2009[J]. Eur Urol, 2009, 56(1): 89-96. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2009.04.032
[3] Ghani KR, Trinh QD, Menon M. Vattikuti Institute Prostatectomy-Technique in 2012[J]. J Endourol, 2012, 26(12): 1558-1565. doi: 10.1089/end.2012.0455
[4] Clarebrough EE, Challacombe BJ, Briggs C, et al. Cadaveric analysis of periprostatic nerve distribution: an anatomical basis for high anterior release during radical prostatectomy?[J]. J Urol, 2011, 185(4): 1519-1525. doi: 10.1016/j.juro.2010.11.046
[5] Kaouk JH, Goel RK, Haber GP, et al. Robotic single-port transumbilical surgery in humans: initial report[J]. BJU Int, 2009, 103(3): 366-369. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-410X.2008.07949.x
[6] Abaza R, Martinez O, Murphy C, et al. Adoption of Single-Port Robotic Prostatectomy: Two Alternative Strategies[J]. J Endourol, 2020, 34(12): 1230-1234. doi: 10.1089/end.2020.0425
[7] Bertolo R, Garisto J, Bove P, et al. Perioperative Outcomes Between Single-Port and "Multi-Port" Robotic Assisted Radical Prostatectomy: Where do we stand?[J]. Urology, 2021, 155: 138-143. doi: 10.1016/j.urology.2021.06.005
[8] Desai MM, Aron M, Berger A, et al. Transvesical robotic radical prostatectomy[J]. BJU Int, 2008, 102(11): 1666-1669. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-410X.2008.08004.x
[9] Kaouk J, Valero R, Sawczyn G, et al. Extraperitoneal single-port robot-assisted radical prostatectomy: initial experience and description of technique[J]. BJU Int, 2020, 125(1): 182-189. doi: 10.1111/bju.14885
[10] Ramirez D, Maurice MJ, Kaouk JH. Robotic perineal radical prostatectomy and pelvic lymph node dissection using a purpose-built single-port robotic platform[J]. BJU Int, 2016, 118(5): 829-833. doi: 10.1111/bju.13581
[11] Wilson CA, Aminsharifi A, Sawczyn G, et al. Outpatient Extraperitoneal Single-Port Robotic Radical Prostatectomy[J]. Urology, 2020, 144: 142-146. doi: 10.1016/j.urology.2020.06.029
[12] 高旭, 王海峰, 王燕, 等. 基于浏览器/服务器架构的前列腺癌数据库的构建和临床应用[J]. 中华泌尿外科杂志, 2015, 36(9): 694-698. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1000-6702.2015.09.017
[13] White MA, Haber GP, Autorino R, et al. Robotic laparoendoscopic single-site radical prostatectomy: technique and early outcomes[J]. Eur Urol, 2010, 58(4): 544-550. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2010.06.040
[14] Aron M, Canes D, Desai MM, et al. Transumbilical single-port laparoscopic partial nephrectomy[J]. BJU international, 2009, 103: 516-521. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-410X.2008.08007.x
[15] 吴震杰, 王坚超, 王杰, 等. 机器人单孔腹腔镜肾上腺肿瘤切除术初步临床应用报告[J]. 临床泌尿外科杂志, 2017, 32(6): 437-439, 443. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCMW201706008.htm
[16] Joseph RA, Goh AC, Cuevas SP, et al. "Chopstick" surgery: a novel technique improves surgeon performance and eliminates arm collision in robotic single-incision laparoscopic surgery[J]. Surg Endosc, 2010, 24(6): 1331-1335. doi: 10.1007/s00464-009-0769-8
[17] Chang Y, Lu X, Zhu Q, et al. Single-port transperitoneal robotic-assisted laparoscopic radical prostatectomy(spRALP): Initial experience[J]. Asian J Urol, 2019, 6(3): 294-297. doi: 10.1016/j.ajur.2018.08.002
[18] Chang YF, Gu D, Mei N, et al. Initial experience on extraperitoneal single-port robotic-assisted radical prostatectomy[J]. Chin Med J(Engl), 2020, 134(2): 231-233.
[19] Chang Y, Xu W, Lu X, et al. Robotic Perineal Radical Prostatectomy: Initial Experience with the da Vinci Si Robotic System[J]. Urol Int, 2020, 104(9-10): 710-715. doi: 10.1159/000505557
[20] 杜巍, 徐伟东, 杨悦, 等. 多种路径机器人辅助单孔腹腔镜根治性前列腺切除术的初步疗效[J]. 中华泌尿外科杂志, 2020, 41(11): 815-819. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112330-20200909-00657
[21] Saidian A, Fang AM, Hakim O, et al. Perioperative Outcomes of Single vs Multi-Port Robotic Assisted Radical Prostatectomy: A Single Institutional Experience[J]. J Urol, 2020, 204(3): 490-495. doi: 10.1097/JU.0000000000000811
[22] Walsh AL, Dasgupta P. A comparative analysis of single port versus multi-port robotic assisted radical prostatectomy for prostate cancer[J]. Investig Clin Urol, 2020, 61(4): 335-337. doi: 10.4111/icu.2020.61.4.335
[23] Uy M, Cassim R, Kim J, et al. Extraperitoneal versus transperitoneal approach for robot-assisted radical prostatectomy: a contemporary systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. J Robot Surg, 2021.
[24] Tavukçu HH, Aytac O, Atug F. Nerve-sparing techniques and results in robot-assisted radical prostatectomy[J]. Investig Clin Urol, 2016, 57(Suppl 2): S172-S184. doi: 10.4111/icu.2016.57.S2.S172
[25] Kumar A, Patel VR, Panaiyadiyan S, et al. Nerve-sparing robot-assisted radical prostatectomy: Current perspectives[J]. Asian J Urol, 2021, 8(1): 2-13. doi: 10.1016/j.ajur.2020.05.012
[26] 钟培锋, 李浩民, 赖彩永. 勃起功能保护——基于解剖认识的膀胱癌根治术[J]. 临床泌尿外科杂志, 2021, 36(1): 61-67. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCMW202101015.htm
[27] Martini A, Falagario UG, Villers A, et al. Contemporary Techniques of Prostate Dissection for Robot-assisted Prostatectomy[J]. Eur Urol, 2020, 78(4): 583-591. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2020.07.017
[28] Cochetti G, Boni A, Barillaro F, Pohja S, Cirocchi R, Mearini E. Full Neurovascular Sparing Extraperitoneal Robotic Radical Prostatectomy: Our Experience with PERUSIA Technique[J]. J endourol, 2017, 31: 32-37. doi: 10.1089/end.2016.0477
-




 下载:
下载: