Clinical characteristics analysis and treatment strategies of neuroendocrine prostate cancer under MDT mode
-
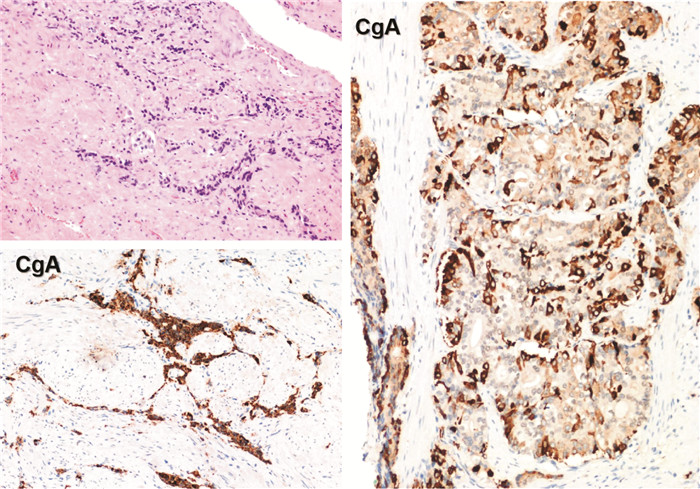
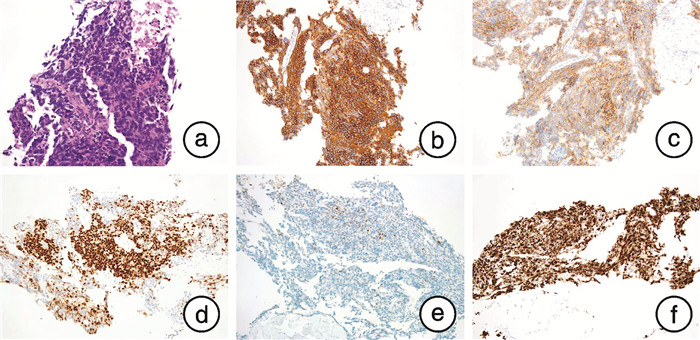
摘要: 神经内分泌前列腺癌是前列腺癌的特殊类型,具有独特的临床及病理特征,本文报道3例典型病例。例1,63岁,初始前列腺特异性抗原(prostate specific antigen,PSA)34.39 ng/mL,病理确诊前列腺腺癌,Gleason评分9分(4+5),伴少数区域神经内分泌分化,68Ga-PSMA PET/CT分期T3bN0M1b,3年内分泌治疗后出现双下肢水肿,右肺动脉干及肾下极平面下腔静脉栓子,遂行转移淋巴结二次穿刺,获取病理为前列腺小细胞癌。MDT讨论后更换恩杂鲁胺,同时行EP方案化疗。例2,53岁,初始PSA 34.13 ng/mL,穿刺病理前列腺腺癌,Gleason评分8分(3+5),临床分期T4N1M1b。免疫组织化学证实神经内分泌阳性,在内分泌治疗基础上行腹主动脉旁及盆腔挽救性放疗。例3,40岁,初始PSA 47.99 ng/mL,穿刺活检为前列腺腺癌,Gleason评分8分(4+4),临床分期T4N1M1a。行去势+抗雄+新辅助化疗6个周期,机器人辅助腹腔镜下前列腺减瘤性切除术+扩大盆腔淋巴结清扫,病理提示前列腺腺癌伴高级别神经内分泌癌,MDT讨论后行盆腔延伸野及前列腺瘤床区、盆腹腔可见肿大淋巴结挽救性放疗。神经内分泌前列腺癌发病相对年轻,PSA水平与肿瘤分期不相称,原发病灶重复穿刺或转移灶获取病理具有重要诊断价值,MDT模式可以有力保证规范化治疗。Abstract: Neuroendocrine prostate cancer is a special type of prostate cancer with unique clinical and pathological features, and three typical cases were reported here. Case 1, 63 years old, initial PSA 34.39 ng/mL, pathologically confirmed prostate adenocarcinoma, Gleason score 9(4+5), with a few regional neuroendocrine differentiation, 68Ga-PSMA PET/CT stage T3bN0M1b, 3 years of endocrine therapy, double lower limbs edema, right pulmonary artery trunk and inferior vena cava embolus of lower renal pole, secondary puncture of metastatic lymph nodes, obtain pathology as prostate small cell carcinoma. Enzalutamide and chemotherapy with EP protocol were replaced after MDT. Case 2, 53 years old, initial PSA 34.13 ng/mL, puncture pathological adenocarcinoma of prostate, Gleason score 8(3+5), and clinical stage T4N1M1b. Immunohistochemistry confirmed positive neuroendocrine staining, and para-aortic and pelvic salvage radiotherapy were performed based on endocrine therapy. Case 3, 40 years old, initial PSA 47.99 ng/mL, needle biopsy was prostate adenocarcinoma with Gleason score 8(4+4) and clinical stage T4N1M1a. Six cycles of castration+antiandrogen+neoadjuvant chemotherapy, robot-assisted laparoscopic prostate tumor resection+expand pelvic lymph nodes dissection were performed. Pathological results showed prostate adenocarcinoma with high-grade neuroendocrine cancer. The pelvic extension field and the forefront adenoma bed area, pelvic cavity visible enlarged lymph nodes salvage radiotherapy were performed after MDT. The onset of neuroendocrine prostate cancer is relatively young, and PSA level is not commensurate with the tumor stage. Repeated puncture of the primary lesion or obtaining pathology of the metastatic lesion has important diagnostic value, and MDT mode can effectively guarantee standardized treatment.
-

-
[1] Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2019[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2019, 69(1): 7-34. doi: 10.3322/caac.21551
[2] Zaffuto E, Pompe R, Zanaty M, et al. Contemporary incidence and cancer control outcomes of primary neuroendocrine prostate cancer: a SEER database analysis[J]. Clin Genitourin Cancer, 2017, 15(5): e793-e800. doi: 10.1016/j.clgc.2017.04.006
[3] Aggarwal R, Huang JT, Alumkal JJ, et al. Clinical and genomic characterization of treatment-emergent small-cell neuroendocrine prostate cancer: a multi-institutional prospective study[J]. J Clin Oncol, 2018, 36(24): 2492-2503. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2017.77.6880
[4] Abida W, Cyrta J, Heller G, et al. Genomic correlates of clinical outcome in advanced prostate cancer[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2019, 116(23): 11428-11436. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1902651116
[5] Cornford P, Bellmunt J, Bolla M, et al. EAU-ESTRO-SIOG guidelines on prostate cancer. part Ⅱ: treatment of relapsing, metastatic, and castration-resistant prostate cancer[J]. Eur Urol, 2017, 71(4): 630-642. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2016.08.002
[6] Weissenrieder JS, Reilly JE, Neighbors JD, et al. Inhibiting geranylgeranyl diphosphate synthesis reduces nuclear androgen receptor signaling and neuroendocrine differentiation in prostate cancer cell models[J]. Prostate, 2019, 79(1): 21-30. doi: 10.1002/pros.23707
[7] Chen RQ, Dong XS, Gleave M. Molecular model for neuroendocrine prostate cancer progression[J]. BJU Int, 2018, 122(4): 560-570. doi: 10.1111/bju.14207
[8] Mu P, Zhang ZD, Benelli M, et al. SOX2 promotes lineage plasticity and antiandrogen resistance in TP53-and RB1-deficient prostate cancer[J]. Science, 2017, 355(6320): 84-88. doi: 10.1126/science.aah4307
[9] Deorah S, Rao MB, Raman R, et al. Survival of patients with small cell carcinoma of the prostate during 1973-2003: a population-based study[J]. BJU Int, 2012, 109(6): 824-830. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-410X.2011.10523.x
[10] Netto GJ, Amin MB, Berney DM, et al. The 2022 World Health Organization Classification of Tumors of the Urinary System and Male Genital Organs-Part B: Prostate and Urinary Tract Tumors[J]. Eur Urol, 2022, 82(5): 469-482. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2022.07.002
[11] Mottet N, Bellmunt J, Bolla M, et al. EAU-ESTRO-SIOG guidelines on prostate cancer. part 1: screening, diagnosis, and local treatment with curative intent[J]. Eur Urol, 2017, 71(4): 618-629. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2016.08.003
[12] Prendeville S, Al-Bozom I, Compérat E, et al. Prostate carcinoma with amphicrine features: further refining the spectrum of neuroendocrine differentiation in tumours of primary prostatic origin?[J]. Histopathology, 2017, 71(6): 926-933. doi: 10.1111/his.13330
[13] 古亚楠, 惠珂, 吴开杰. 药物诱导性神经内分泌前列腺癌研究的最新进展[J]. 现代泌尿外科杂志, 2020, 25(2): 190-193. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-8291.2020.02.023
[14] Davies AH, Beltran H, Zoubeidi A. Cellular plasticity and the neuroendocrine phenotype in prostate cancer[J]. Nat Rev Urol, 2018, 15(5): 271-286. doi: 10.1038/nrurol.2018.22
[15] Reisch N, Reincke M. Endocrine paraneoplastic syndromes[J]. Internist, 2018, 59(2): 125-133. doi: 10.1007/s00108-017-0377-y
[16] Corn PG, Heath EI, Zurita A, et al. Cabazitaxel plus carboplatin for the treatment of men with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancers: a randomised, open-label, phase 1-2 trial[J]. Lancet Oncol, 2019, 20(10): 1432-1443. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(19)30408-5
[17] Iwamoto H, Nakagawa R, Makino T, et al. Treatment outcomes in neuroendocrine prostate cancer[J]. Anticancer Res, 2022, 42(4): 2167-2176. doi: 10.21873/anticanres.15699
[18] Zhu SM, Zhang Z, Zhang H, et al. DNA-repair status should be assessed in treatment-emergent neuroendocrine prostate cancer before platinum-based therapy[J]. Prostate, 2022, 82(4): 464-474. doi: 10.1002/pros.24292
[19] van den Broeck T, van den Bergh RCN, Arfi N, et al. Prognostic value of biochemical recurrence following treatment with curative intent for prostate cancer: a systematic review[J]. Eur Urol, 2019, 75(6): 967-987. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2018.10.011
-




 下载:
下载: