Construction and analysis of prognostic risk model for immune-related genes for clear cell renal cell carcinoma
-
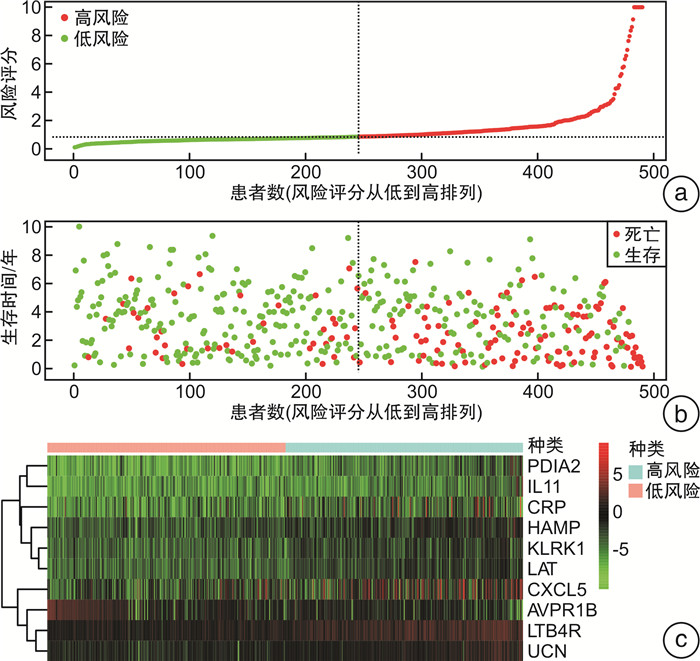
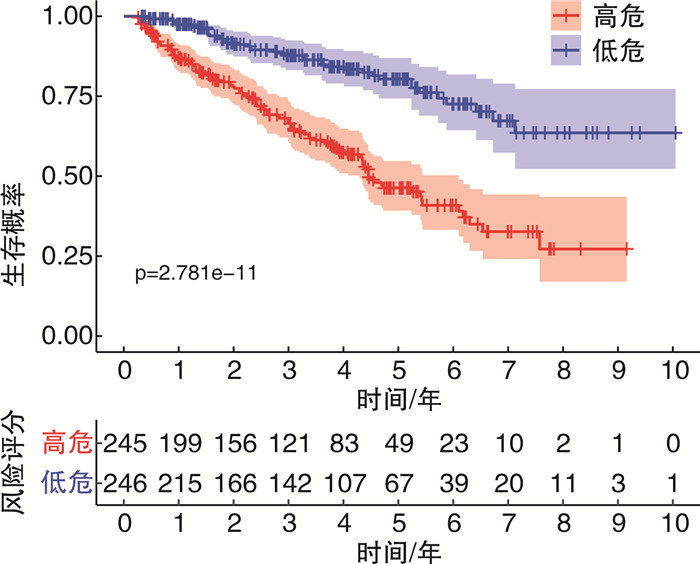
摘要: 目的 筛选肾透明细胞癌(clear cell renal cell carcinoma,ccRCC)预后免疫相关基因(immune-related genes,IRGs),并建立与免疫基因预后风险相关的评分模型。方法 通过TCGA数据库下载与ccRCC有关的转录测序信息,应用生物信息学方法 筛选出在ccRCC组织中的差异表达基因,并通过共表达分析方法获取IRGs,进一步在IRGs中筛选出与患者总生存期相关的基因,通过Cox回归构建预后风险评分模型,评估该模型在临床上的综合预测能力。结果 在ccRCC及其附近组织中共发现1 791个差异表达基因,在这些基因中,筛选出IRGs 220个,利用单因素Cox分析方法,我们发现了30个和患者预后密切相关的免疫基因,接着10个IRGs(PDIA2、HAMP、CXCL5、KLRK1、LTB4R、CRP、IL11、UCN、AVPR1B、LAT)通过多因素Cox分析被筛选出来,基于这10个IRGs构建预后模型,预后评分模型ROC曲线下面积(AUC)为0.758。根据风险评分中位数将患者分为高危组合低危组,生存曲线显示2组患者预后差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05),多因素分析显示该模型的风险评分为ccRCC预后的独立预测因子。结论 ccRCC中IRGs和患者的预后密切相关,基于其构建的风险评分模型不仅可有效预测ccRCC的预后,而且可用来作为ccRCC患者的预后生物标志物。Abstract: Objective In order to find reliable prognostic indicators and biomarkers for clear cell renal cell carcinoma(ccRCC) patients, ccRCC immune-related genes (IRGs) were screened by bioinformatics, aims to establish a scoring model related to the prognostic risk of immune genes.Methods Firstly, the transcription and sequencing information related to ccRCC was downloaded through TCGA database, and the differentially expressed genes in ccRCC tissues were screened by bioinformatics method. Then, IRGs were obtained by co-expression analysis, and the genes related to the overall survival (OS) of patients were further screened out among these IRGs. Lastly, a prognostic risk scoring model was constructed by Cox regression to evaluate the comprehensive predictive ability of the model in clinical practice.Results A total of 1 791 differentially expressed genes were found in ccRCC and its nearby tissues, among which 220 IRGs were screened. Thirty immune genes closely related to patient prognosis were found using univariate Cox analysis, then 10 IRGs(PDIA2, HAMP, CXCL5, KLRK1, LTB4R, CRP, IL11, UCN, AVPR1B, LAT) were screened by multivariate Cox analysis. A prognostic model was constructed based on these 10 IRGs, and the prognosis score model AUC under the ROC curve was 0.758. The survival curve showed that the prognosis of the high risk group and low risk group which based on the median risk score was statistically significant (P < 0.05), and the multivariate analysis showed that the risk score of the model was an independent predictor of the prognosis of ccRCC.Conclusion IRGs in ccRCC are closely related to the prognosis of patients, and the risk scoring model constructed based on them can not only effectively predict the prognosis of ccRCC, but also be used as a prognostic biomarker for ccRCC patients.
-
Key words:
- clear cell renal cell carcinoma /
- immunity /
- prognosis /
- prognostic model /
- bioinformatics
-

-
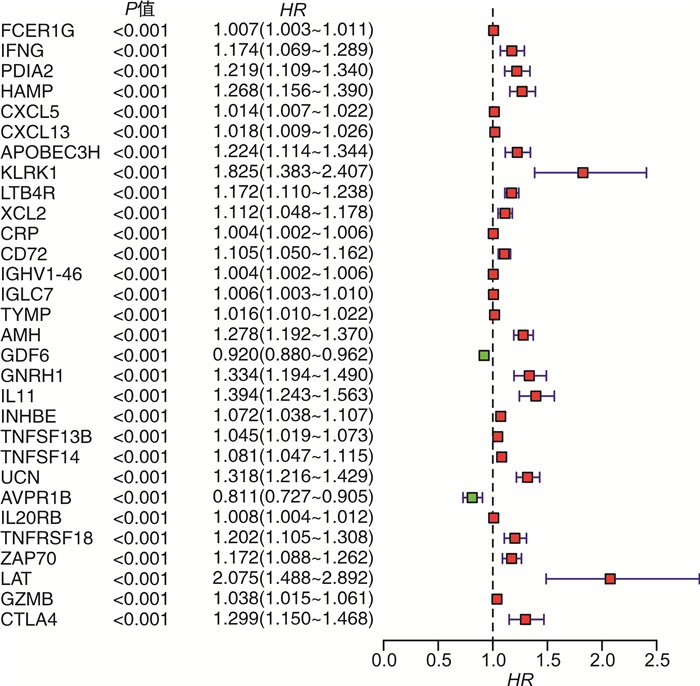
表 1 多因素Cox回归分析筛选ccRCC构建预测评分模型的IRGs
基因 β HR 95%CI P值 PDIA2 0.200 1.227 1.10~1.37 < 0.001 HAMP 0.200 1.216 1.08~1.37 < 0.001 CXCL5 0.010 1.008 1.00~1.02 0.015 KLRK1 0.530 1.704 1.16~2.50 < 0.001 LTB4R 0.080 1.088 1.01~1.18 0.030 CRP 0.003 1.003 1.00~1.01 < 0.001 IL11 0.320 1.378 1.22~1.55 < 0.001 UCN 0.220 1.243 1.11~1.40 < 0.001 AVPR1B -0.120 0.884 0.79~0.98 0.020 LAT -0.570 0.566 0.31~1.03 0.006 -
[1] Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2020[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2020, 70(1): 7-30. doi: 10.3322/caac.21590
[2] Inamura K. Renal cell tumors: understanding their molecular pathological epidemiology and the 2016 WHO classification[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2017, 18(10): 2195. doi: 10.3390/ijms18102195
[3] Zimpfer A, Glass Ä, Zettl H, et al. Renal cell carcinoma diagnosis and prognosis within the context of the WHO classification 2016[J]. Urologe A, 2019, 58(9): 1057-1065. doi: 10.1007/s00120-019-0952-z
[4] Deng J, Li L, Xia HM, et al. A comparison of the prognosis of papillary and clear cell renal cell carcinoma: evidence from a meta-analysis[J]. Medicine, 2019, 98(27): e16309. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000016309
[5] Topalian SL, Hodi FS, Brahmer JR, et al. Five-year survival and correlates among patients with advanced melanoma, renal cell carcinoma, or non-small cell lung cancer treated with nivolumab[J]. JAMA Oncol, 2019, 5(10): 1411-1420. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2019.2187
[6] Goleva E, Lyubchenko T, Kraehenbuehl L, et al. Our current understanding of checkpoint inhibitor therapy in cancer immunotherapy[J]. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol, 2021, 126(6): 630-638. doi: 10.1016/j.anai.2021.03.003
[7] Atkins MB, Tannir NM. Current and emerging therapies for first-line treatment of metastatic clear cell renal cell carcinoma[J]. Cancer Treat Rev, 2018, 70: 127-137. doi: 10.1016/j.ctrv.2018.07.009
[8] Ueda K, Suekane S, Kurose H, et al. Prognostic value of PD-1 and PD-L1 expression in patients with metastatic clear cell renal cell carcinoma[J]. Urol Oncol, 2018, 36(11): 499. e9-499. e16. doi: 10.1016/j.urolonc.2018.07.003
[9] Chen LJ, Zhu DW, Feng J, et al. Overexpression of HHLA2 in human clear cell renal cell carcinoma is significantly associated with poor survival of the patients[J]. Cancer Cell Int, 2019, 19: 101. doi: 10.1186/s12935-019-0813-2
[10] Nolè F, Iacovelli R, Verri E, et al. Prognostic role of PD-L1 expression in renal cell carcinoma. A systematic review and meta-analysis [J]. Ann Oncol, 2015, 26: vi57.
[11] Tomczak K, Czerwińska P, Wiznerowicz M. The Cancer Genome Atlas(TCGA): an immeasurable source of knowledge[J]. Contemp Oncol, 2015, 19(1A): A68-A77.
[12] Yates AD, Achuthan P, Akanni W, et al. Ensembl 2020[J]. Nucleic Acids Res, 2020, 48(D1): D682-D688.
[13] Carlevaro-Fita J, Liu LB, Zhou Y, et al. LnCompare: gene set feature analysis for human long non-coding RNAs[J]. Nucleic Acids Res, 2019, 47(W1): W523-W529. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkz410
[14] Ritchie ME, Phipson B, Wu D, et al. Limma powers differential expression analyses for RNA-sequencing and microarray studies[J]. Nucleic Acids Res, 2015, 43(7): e47. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkv007
[15] Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2019[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2019, 69(1): 7-34. doi: 10.3322/caac.21551
[16] Hahn AW, Klaassen Z, Agarwal N, et al. First-line treatment of metastatic renal cell carcinoma: a systematic review and network meta-analysis[J]. Eur Urol Oncol, 2019, 2(6): 708-715. doi: 10.1016/j.euo.2019.09.002
[17] 江卫星, 寿建忠. 转移性肾细胞癌免疫治疗的现状与进展[J]. 中华泌尿外科杂志, 2017, 38(7): 555-558. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1000-6702.2017.07.022
[18] Wang ZL, Wang Z, Li GZ, et al. Immune cytolytic activity is associated with genetic and clinical properties of glioma[J]. Front Immunol, 2019, 10: 1756. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.01756
[19] Wu XB, Liang YH, Chen X, et al. Identification of survival risk and immune-related characteristics of kidney renal clear cell carcinoma[J]. J Immunol Res, 2022, 2022: 6149369.
[20] Wang XY, Xia ZN, Li ZY, et al. Development of a SETD2-related immune prognostic signature in clear cell renal cell carcinoma[J]. Medicine, 2022, 101(31): e29561. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000029561
[21] Xu F, Huang XL, Li YY, et al. m6A-related lncRNAs are potential biomarkers for predicting prognoses and immune responses in patients with LUAD[J]. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids, 2021, 24: 780-791. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2021.04.003
[22] Xing XL, Liu Y, Liu JH, et al. A nomogram integrating ferroptosis-and immune-related biomarker for prediction of prognosis and diagnosis in kidney renal clear cell carcinoma[J]. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci, 2022, 26(17): 6176-6186.
[23] Wan BB, Liu B, Huang YA, et al. Prognostic value of immune-related genes in clear cell renal cell carcinoma[J]. Aging, 2019, 11(23): 11474-11489.
[24] Guan ZF, Li C, Fan JH, et al. Androgen receptor(AR)signaling promotes RCC progression via increased endothelial cell proliferation and recruitment by modulating AKT→NF-κB→CXCL5 signaling[J]. Sci Rep, 2016, 6: 37085.
[25] Bai SH, Wu YY, Yan YL, et al. Construct a circRNA/miRNA/mRNA regulatory network to explore potential pathogenesis and therapy options of clear cell renal cell carcinoma[J]. Sci Rep, 2020, 10(1): 13659.
[26] Hua XL, Chen JA, Su Y, et al. Identification of an immune-related risk signature for predicting prognosis in clear cell renal cell carcinoma[J]. Aging, 2020, 12(3): 2302-2332.
[27] Tan HS, Jiang WH, He Y, et al. KRT8 upregulation promotes tumor metastasis and is predictive of a poor prognosis in clear cell renal cell carcinoma[J]. Oncotarget, 2017, 8(44): 76189-76203.
[28] Zhan YT, Zhang RR, Li CX, et al. A microRNA-clinical prognosis model to predict the overall survival for kidney renal clear cell carcinoma[J]. Cancer Med, 2021, 10(17): 6128-6139.
[29] Shen YH, Cao YH, Zhou L, et al. Construction of an endoplasmic reticulum stress-related gene model for predicting prognosis and immune features in kidney renal clear cell carcinoma[J]. Front Mol Biosci, 2022, 9: 928006.
[30] Lu CB, Wang YQ, Nie L, et al. Comprehensive analysis of cellular senescence-related genes in the prognosis, tumor microenvironment, and immunotherapy/chemotherapy of clear cell renal cell carcinoma[J]. Front Immunol, 2022, 13: 934243.
-




 下载:
下载: