-
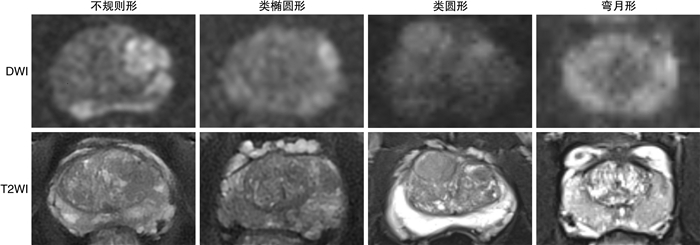
摘要: 目的 分析多参数磁共振成像(multiparametric magnetic resonance imaging,mpMRI)和超声图像认知融合靶向穿刺的核心区域的影像特征。方法 回顾性分析复旦大学附属肿瘤医院泌尿外科2022年1月—2023年10月实施前列腺认知融合靶向穿刺联合系统穿刺的255例患者临床资料。对比同期531例仅行系统穿刺患者,探讨前列腺癌及临床有意义前列腺癌(clinically significant prostate cancer,csPCa)的检出率,分析靶向穿刺的核心区域在mpMRI及超声图像上的影像特征。结果 靶向穿刺联合系统穿刺组和仅系统穿刺组患者前列腺癌检出率分别为82.0%(209/255)和44.1%(234/531),csPCa检出率分别为65.5%(167/255)和32.6%(173/531),2组患者前列腺癌检出率和csPCa检出率比较差异均有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。靶向穿刺核心区域在磁共振图像上有4种不同的形态特征,分别为不规则形、类椭圆形、类圆形和弯月形,占比分别为60.0%(153/255)、18.0%(46/255)、12.2%(31/255)和9.8%(25/255),且不规则形患者的血前列腺特异性抗原(prostate specific antigen,PSA)高于其他3种(P=0.001)。核心区域超声图像形态类似磁共振图像,但边缘较为模糊,且回声性质为低回声区的占比79.6%(203/255),其余为等回声或高回声区。结论 正确理解前列腺磁共振图像信息以及对靶向穿刺核心区域影像特征的把握,是成功进行前列腺靶向穿刺的关键所在。Abstract: Objective To analyze the imaging features of the core area in cognitive fusion targeted biopsy using mpMRI and ultrasound images.Methods A retrospective analysis was conducted on the clinical data of 255 patients who underwent prostate cognitive fusion targeted biopsy with a combined system at the Urology Department of Fudan University Shanghai Cancer Center from January 2022 to October 2023. Compared with 531 patients who underwent only systematic biopsy during the same period, the detection rates of prostate cancer and clinically significant prostate cancer(csPCa) were explored, and the morphological characteristics of the core area in targeted biopsy on mpMRI and ultrasound images were evaluated and analyzed.Results The detection rates of prostate cancer in the targeted biopsy combined with systematic biopsy group and the systematic biopsy-only group were 82.0%(209/255) and 44.1%(234/531) respectively, and the csPCa detection rates were 65.5%(167/255) and 32.6%(173/531) respectively, with statistically significant differences in the detection rates of prostate cancer and csPCa between the two groups(P < 0.05). There were four different morphological characteristics of the targeted biopsy core area in MRI images: irregular, ellipsoid-like, round-like, and crescent, accounting for 60.0%(153/255), 18.0%(46/255), 12.2%(31/255), and 9.8%(25/255) respectively, and the patients with irregular shape had higher blood PSA levels than the other three groups(P=0.001). The morphology of the core area in ultrasound images was similar to that in MRI images, but with more blurred edges, and the proportion of hypoechoic areas was 79.6%(203/255), with the rest being isoechoic or hyperechoic.Conclusion Correct understanding of prostate MRI image information and grasping the imaging features of the targeted biopsy core area are key to the successful performance of prostate targeted biopsy.
-
Key words:
- prostate cancer /
- targeted biopsy /
- cognitive fusion /
- imaging features
-

-
表 1 2组的基线资料比较
M(P25,P75) 项目 靶向穿刺联合系统穿刺组(255例) 系统穿刺组(531例) U P值 年龄/岁 69.0(66.0,73.0) 68.0(62.0,82.0) 47 143.0 0.005 PSA/(ng/mL) 12.4(6.9,33.7) 9.39(5.6,23.1) 64 453.5 < 0.001 前列腺体积/mL 35.4(30.0,45.5) 33.8(31.5,52.1) 42 662.0 0.051 f/tPSA 0.12(0.11,0.15) 0.17(0.15,0.19) 53 217.0 < 0.001 表 2 2组的穿刺病理结果比较
例(%) 组别 前列腺癌 csPCa 靶向穿刺联合系统穿刺组(255例) 209(82.0) 167(65.5) 系统穿刺组(531例) 234(44.1) 173(32.6) χ2 120.3 141.7 P值 < 0.001 < 0.001 表 3 靶向穿刺核心区域影像特征
例(%),M(P25,P75) 项目 mpMRI图像上的形态特征 F P值 不规则形 类椭圆形 类圆形 弯月形 例数 153(60.0) 46(18.0) 31(12.2) 25(9.8) 15.978 0.001 PSA/(ng/mL) 56.8(10.0,67.5) 25.5(7.5,40.2) 28.4(8.5,32.8) 13.8(7.0,19.7) -
[1] Sosenko A, Owens RG, Yang AL, et al. Non-infectious complications following transrectal prostate needle biopsy-Outcomes from over 8000 procedures[J]. Prostate Int, 2022, 10(3): 158-161. doi: 10.1016/j.prnil.2022.04.002
[2] Bodar Y, Zwezerijnen B, van der Voorn PJ, et al. Prospective analysis of clinically significant prostate cancer detection with[18F]DCFPyL PET/MRI compared to multiparametric MRI: a comparison with the histopathology in the radical prostatectomy specimen, the ProStaPET study[J]. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging, 2022, 49(5): 1731-1742. doi: 10.1007/s00259-021-05604-9
[3] Xiang J, Yan H, Li J, et al. Transperineal versus transrectal prostate biopsy in the diagnosis of prostate cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. World J Surg Oncol, 2019, 17(1): 31. doi: 10.1186/s12957-019-1573-0
[4] Nakanishi Y, Ito M, Fukushima H, et al. Who Can Avoid Systematic Biopsy Without Missing Clinically Significant Prostate Cancer in Men Who Undergo Magnetic Resonance Imaging-Targeted Biopsy?[J]. Clin Genitourin Cancer, 2019, 17(3): e664-e671. doi: 10.1016/j.clgc.2019.03.011
[5] Schlemmer HP, Krause BJ, Schutz V, et al. Imaging of Prostate Cancer[J]. DtschArztebl Int, 2021, 118(42): 713-719.
[6] Eklund M, Jäderling F, Discacciati A, et al. MRI-Targeted or Standard Biopsy in Prostate Cancer Screening[J]. N Engl J Med, 2021, 385(10): 908-920. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2100852
[7] Kasivisvanathan V, Rannikko AS, Borghi M, et al. MRI-Targeted or Standard Biopsy for Prostate-Cancer Diagnosis[J]. N Engl J Med, 2018, 378(19): 1767-1777. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1801993
[8] 施云峰, 曹锴, 刘晓武, 等. 认知融合MRI和超声引导靶向穿刺在前列腺前部肿瘤诊断中的临床应用[J]. 临床泌尿外科杂志, 2023, 38(4): 251-254. https://lcmw.whuhzzs.com/article/doi/10.13201/j.issn.1001-1420.2023.04.003
[9] Barone B, Napolitano L, Calace FP, et al. Reliability of Multiparametric Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Patients with a Previous Negative Biopsy: Comparison with Biopsy-Naïve Patients in the Detection of Clinically Significant Prostate Cancer[J]. Diagnostics(Basel), 2023, 13(11): 1939.
[10] 汪磊, 赵子臣, 果宏峰, 等. 全息影像在经会阴前列腺靶向穿刺中的应用[J]. 中华泌尿外科杂志, 2022, 43(2): 111-115.
[11] Morote J, Borque-Fernando A, Triquell M, et al. The Barcelona Predictive Model of Clinically Significant Prostate Cancer[J]. Cancers(Basel), 2022, 14(6): 1589.
[12] 林国文, 戴波, 叶定伟, 等. 多参数磁共振和68Ga-PSMA PET/CT图像间接融合引导前列腺靶向穿刺活检的临床分析[J]. 中华泌尿外科杂志, 2022, 43(7): 484-489.
[13] Solari EL, Gafita A, Schachoff S, et al. The added value of PSMA PET/MR radiomics for prostate cancer staging[J]. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging, 2022, 49(2): 527-538.
[14] Ahdoot M, Wilbur AR, Reese SE, et al. MRI-Targeted, Systematic, and Combined Biopsy for Prostate Cancer Diagnosis[J]. N Engl J Med, 2020, 382(10): 917-928.
[15] Morote J, Picola N, Munoz-Rodriguez J, et al. A Diagnostic Accuracy Study of Targeted and Systematic Biopsies to Detect Clinically Significant Prostate Cancer, including a Model for the Partial Omission of Systematic Biopsies[J]. Cancers(Basel), 2023, 15(18): 4543.
[16] Rouvière O, Puech P, Renard-Penna R, et al. Use of prostate systematic and targeted biopsy on the basis of multiparametric MRI in biopsy-naive patients(MRI-FIRST): a prospective, multicentre, paired diagnostic study[J]. Lancet Oncol, 2019, 20(1): 100-109.
[17] Turkbey B, Rosenkrantz AB, Haider MA, et al. Prostate Imaging Reporting and Data System Version 2.1: 2019 Update of Prostate Imaging Reporting and Data System Version 2[J]. Eur Urol, 2019, 76(3): 340-351.
[18] Chang AI, Park BK. New TRUS Techniques and Imaging Features of PI-RADS 4 or 5: Influence on Tumor Targeting[J]. Front Oncol, 2021, 11: 608409.
[19] Ferraro DA, Becker AS, Kranzbühler B, et al. Diagnostic performance of 68Ga-PSMA-11 PET/MRI-guided biopsy in patients with suspected prostate cancer: a prospective single-center study[J]. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging, 2021, 48(10): 3315-3324.
[20] Liu Y, Yu H, Liu J, et al. A Pilot Study of 18F-DCFPyL PET/CT or PET/MRI and Ultrasound Fusion Targeted Prostate Biopsy for Intra-Prostatic PET-Positive Lesions[J]. Front Oncol, 2021, 11: 612157.
-

| 引用本文: | 林国文, 戴波, 叶定伟, 等. 前列腺靶向穿刺核心区域的影像特征分析[J]. 临床泌尿外科杂志, 2024, 39(1): 54-57. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.1001-1420.2024.01.010 |
| Citation: | LIN Guowen, DAI Bo, YE Dingwei, et al. Imaging feature analysis of the core area in prostate targeted biopsy[J]. J Clin Urol, 2024, 39(1): 54-57. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.1001-1420.2024.01.010 |
- Figure 1.



 下载:
下载: