Robot-assisted augmentation ileocystoplasty with totally intracorporeal reconstruction: technique description and preliminary efficacy
-
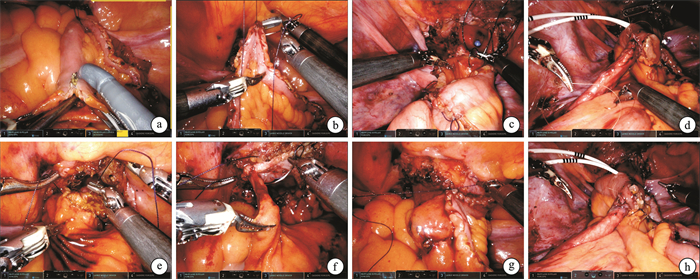
摘要: 目的 探讨机器人辅助全腹腔内Studer式回肠膀胱扩大成形术的可行性及安全性,总结初步疗效和临床技术经验。方法 回顾性分析2019年5月—2024年3月于陆军军医大学第一附属医院行机器人辅助全腹腔内Studer式回肠膀胱扩大成形术7例患者的临床资料。男2例,女5例;年龄12~63岁,平均40.4岁;体重指数(body mass index,BMI)18.1~34.7 kg/m2,平均25.0 kg/m2;放射性、化学性膀胱挛缩和神经源性膀胱功能障碍各1例,结核膀胱挛缩4例。其中3例患者因输尿管膀胱开口狭窄同期行输尿管膀胱再植。膀胱容量50~110 mL,平均80 mL。手术采用达芬奇机器人手术系统:于膀胱顶壁横行贯穿切开膀胱壁全层;全腔内截取近末端回肠30~35 cm,助手辅助侧侧吻合恢复肠道连续性;截取的回肠去肠管化,复制开放手术方式缝制Studer式储尿囊袋,留远侧边与膀胱切开口吻合。必要时,输尿管吻合于Studer式膀胱囊袋输入袢侧壁。围术期采用加速康复外科方案。结果 7例患者手术均顺利,无术中并发症。手术时间为110~205 min,平均161 min;估计失血量为50~300 mL,平均133 mL;肛门排气时间1~5 d,平均3 d。其中放射性膀胱挛缩患者术后出现回肠膀胱瘘,行腹腔镜回肠膀胱瘘修补术。1例患者出现症状性下尿路感染,予抗生素治疗后好转。神经源性膀胱功能障碍患者术后予间歇清洁导尿以排空膀胱,余6例患者均自主排尿,无明显尿失禁及显著残余尿。术后半年膀胱容量测定280~405 mL,平均323 mL;末次随访,未出现新发肾功能不全。结论 机器人辅助全腹腔内Studer式回肠膀胱扩大成形术是安全、可行的,更多潜在的益处值得进一步探索。Abstract: Objective To explore the feasibility and safety of robot-assisted totally intracorporeal Studer-style augmentation ileocystoplasty and to summarize the preliminary efficacy and technical experience.Methods A retrospective analysis was conducted on the clinical characteristics of 7 patients who underwent robot-assisted totally intracorporeal Studer-style augmentation ileocystoplasty in our center from May 2019 to March 2024. There were 2 males and 5 females, aged 12 to 63 years, with an average age of 40.4 years. Body mass index(BMI) ranged from 18.1 to 34.7 kg/m2, with an average of 25.0 kg/m2. There was 1 case each of radiation-induced bladder contracture, chemical bladder contracture, and neurogenic bladder dysfunction, and 4 cases of tuberculosis bladder contracture. Three patients underwent simultaneous ureteral reimplantation due to ureter stenosis. Bladder capacity ranged from 50 to 110 mL, with an average of 80 mL. The Da Vinci robotic surgical system was adopted: 1st. Transversely incising the full thickness of the bladder wall at the bladder dome. 2nd. Totally intracorporeal resection of 30-35 cm of the near-terminal ileum, with side-to-side anastomosis to restore intestinal continuity assisted by an assistant. 3rd. Detubularization of the resected ileum, sewing a Studer type urinary reservoir in a manner similar to open surgery, leaving the distal edge anastomosed with the bladder incision. If necessary, the ureters were anastomosed to the lateral wall of the input loop of the Studer bladder reservoir. An enhanced recovery after surgery(ERAS) protocol was employed.Results All 7 patients underwent operation successfully without intraoperative complications. The operation time was 110 to 205 min, with an average of 161 min. Estimated blood loss was 50 to 300 mL, with an average of 133 mL. The time to first anal gas passage was 1 to 5 days, with an average of 3 days. The patient with radiation-induced bladder contracture developed an ileal bladder fistula postoperatively and underwent laparoscopic repair. One patient developed symptomatic lower urinary tract infection, which improved after antibiotic treatment. The patient with neurogenic bladder dysfunction was provided with clean intermittent catheterization to empty the bladder, while the remaining 6 patients had spontaneous voiding without significant urinary incontinence or notable residual urine. Six months postoperatively, bladder capacity was measured at 280 to 405 mL, with an average of 323 mL. At the last follow-up, no new onset of renal insufficiency was observed.Conclusion Robot-assisted totally intracorporeal Studer-style augmentation ileocystoplasty is safe and feasible. Further exploration of potential benefits is warranted.
-
Key words:
- augmentation cystoplasty /
- robot-assisted surgery /
- totally intracorporeal /
- ileum /
- bladder contracture
-

-
表 1 患者的基本信息和手术参数
例序 性别 年龄/岁 诊断 BMI/(kg/m2) ASA评分 手术时间/min 估计失血量/mL 输尿管再植 1 男 27 结核性膀胱挛缩 18.1 1 135 100 否 2 女 31 结核性膀胱挛缩 32.3 2 180 100 是 3 女 12 神经源性膀胱 25.0 1 167 50 否 4 男 57 结核性膀胱挛缩 25.0 2 165 120 是 5 女 63 化学性膀胱挛缩 19.8 2 168 300 是 6 女 48 放射性膀胱挛缩 20.1 2 205 180 否 7 女 45 结核性膀胱挛缩 34.7 2 110 80 否 -
[1] Budzyn J, Trinh H, Raffee S, et al. Bladder augmentation(enterocystoplasty): the current state of a historic operation[J]. Curr Urol Rep, 2019, 20(9): 50. doi: 10.1007/s11934-019-0919-z
[2] Grilo N, Chartier-Kastler E, Grande P, et al. Robot-assisted supratrigonal cystectomy and augmentation cystoplasty with totally intracorporeal reconstruction in neurourological patients: technique description and preliminary results[J]. Eur Urol, 2021, 79(6): 858-865. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2020.08.005
[3] Veeratterapillay R, Thorpe AC, Harding C. Augmentation cystoplasty: Contemporary indications, techniques and complications[J]. Indian J Urol, 2013, 29(4): 322-327. doi: 10.4103/0970-1591.120114
[4] Piramide F, Turri F, Amparore D, et al. Atlas of intracorporeal orthotopic neobladder techniques after robot-assisted radical cystectomy and systematic review of clinical outcomes[J]. Eur Urol, 2024, 85(4): 348-360. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2023.11.017
[5] Zhou XZ, Zheng J, He P, et al. Refinement surgical technique, and perioperative and functional outcomes in patients with robotic intracorporeal hautmann orthotopic neobladder[J]. Urology, 2020, 138: 45-51. doi: 10.1016/j.urology.2020.01.025
[6] 周晓洲, 郑霁, 刘洋, 等. 机器人辅助女性根治性膀胱切除全腹腔内原位回肠W形新膀胱术的初步疗效[J]. 中华泌尿外科杂志, 2018, 39(8): 596-600. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1000-6702.2018.08.010
[7] Lin TX, Li KW, Liu H, et al. Enhanced recovery after surgery for radical cystectomy with ileal urinary diversion: a multi-institutional, randomized, controlled trial from the Chinese bladder cancer consortium[J]. World J Urol, 2018, 36(1): 41-50. doi: 10.1007/s00345-017-2108-3
[8] Cheng PJ, Myers JB. Augmentation cystoplasty in the patient with neurogenic bladder[J]. World J Urol, 2020, 38(12): 3035-3046. doi: 10.1007/s00345-019-02919-z
[9] Gill IS, Rackley RR, Meraney AM, et al. Laparoscopic enterocystoplasty[J]. Urology, 2000, 55(2): 178-181. doi: 10.1016/S0090-4295(99)00526-9
[10] 李新飞, 程嗣达, 孙永明, 等. 机器人辅助腹腔镜回肠膀胱扩大术治疗结核性膀胱挛缩的初步经验[J]. 临床泌尿外科杂志, 2020, 35(8): 610-614. https://lcmw.whuhzzs.com/article/doi/10.13201/j.issn.1001-1420.2020.08.005
[11] Elliott SP, Meng MV, Anwar HP, et al. Complete laparoscopic ileal cystoplasty[J]. Urology, 2002, 59(6): 939-943. doi: 10.1016/S0090-4295(02)01605-9
[12] Gundeti MS, Eng MK, Reynolds WS, et al. Pediatric robotic-assisted laparoscopic augmentation ileocystoplasty and mitrofanoff appendicovesicostomy: complete intracorporeal: initial case report[J]. Urology, 2008, 72(5): 1144-1147. doi: 10.1016/j.urology.2008.06.070
[13] 刘洋, 周晓洲, 付炯, 等. 机器人辅助女性保留生殖器官膀胱根治性切除联合全腔内原位回肠新膀胱重建的初步经验[J]. 临床泌尿外科杂志, 2024, 39(6): 483-487. https://lcmw.whuhzzs.com/article/doi/10.13201/j.issn.1001-1420.2024.06.004
[14] Chen ZW, He P, Zhou XZ, et al. Preliminary functional outcome following robotic intracorporeal orthotopic ileal neobladder suspension with round ligaments in women with bladder cancer[J]. Eur Urol, 2022, 82(3): 295-302. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2021.11.012
[15] 李学松, 陈思鹭, 李志华, 等. 机器人辅助腹腔镜完全体内重建回肠代双侧输尿管联合回肠膀胱扩大术[J/OL]. 中华腔镜泌尿外科杂志(电子版), 2024, 18(2): 200.
[16] Kushwaha SS, Kalra S, Dorairajan LN, et al. Robot-assisted complex urinary tract reconstruction using intestinal segments: redefining the paradigm[J]. J Robot Surg, 2023, 17(3): 1113-1123. doi: 10.1007/s11701-023-01525-x
[17] 朱李, 祁小龙, 徐智慧, 等. 机器人辅助回肠膀胱扩大术治疗神经源性膀胱的初步经验[J]. 中华泌尿外科杂志, 2021, 42(2): 104-109. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112330-20191022-00458
[18] Gould JJ, Stoffel JT. Robotic enterocystoplasty: technique and early outcomes[J]. J Endourol, 2011, 25(1): 91-95. doi: 10.1089/end.2010.0230
[19] Ji HX, Pan JH, Shen WH, et al. Identification and management of emptying failure in male patients with orthotopic neobladders after radical cystectomy for bladder cancer[J]. Urology, 2010, 76(3): 644-648. doi: 10.1016/j.urology.2010.03.075
-





 下载:
下载: