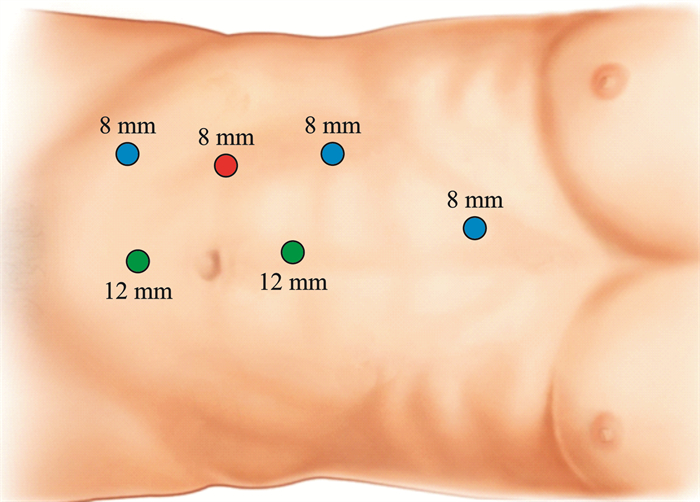
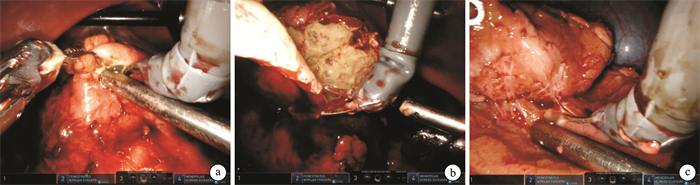
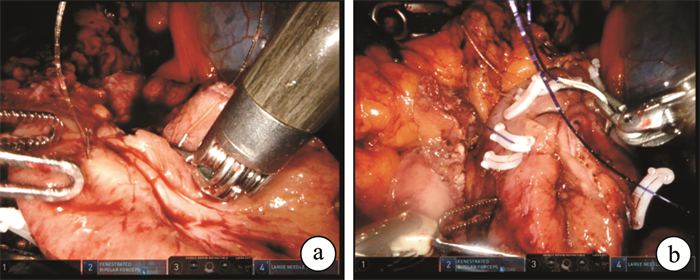
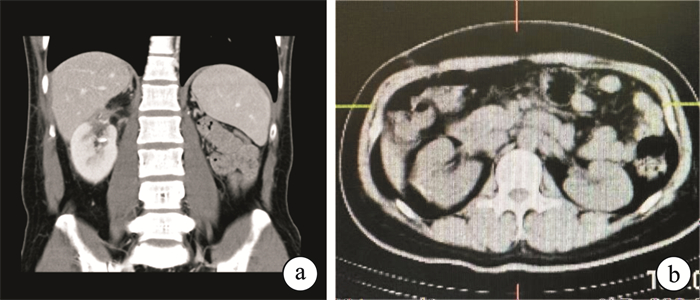
Robot-assisted laparoscopic nephron-sparing surgery for "de-roofing and peeling bottom" of renal tuberculosis: a report of 2 cases
-
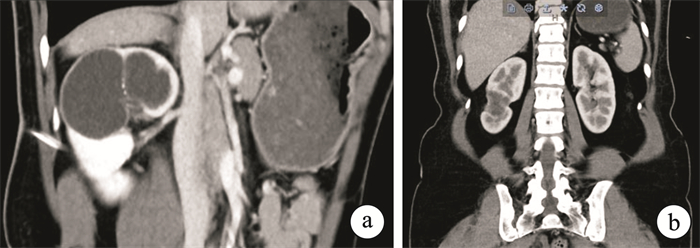
摘要: 目的 评价“去顶削底”技术在肾部分切除术治疗局部肾结核中的安全性和可行性。方法 2例肾结核患者术前均进行12个月以上抗结核治疗,通过CT影像学充分评估后在全身麻醉下行机器人辅助腹腔镜肾结核“去顶削底”保留肾单位手术。结果 2例患者术后病理学证实为肾结核,手术成功率为100%,均未出现手术并发症;患者术后血沉、尿常规、血常规恢复正常,术后血肌酐与术前相比无明显改变,肾小球滤过率稍有下降;患者术后继续进行抗结核治疗,停药随访期间患者无结核复发。术后1年复查影像学提示患肾形态良好。其中1例患者完成回肠膀胱扩大手术,未见腹腔粘连。结论 机器人辅助腹腔镜“去顶削底”技术治疗局限性肾结核,疗效确切,具有一定的安全性和可行性。
-
关键词:
- 机器人辅助腹腔镜 /
- 肾结核 /
- “去顶削底”保留肾单位
Abstract: Objective To evaluate the safety and feasibility of "de-roofing and peeling bottom" technique in partial nephrectomy for local renal tuberculosis.Methods After preoperative anti-tuberculosis treatment for more than 12 months and adequate evaluation by CT scan, two patients with renal tuberculosis underwent robot-assisted laparoscopic "de-roofing and peeling bottom" nephron-sparing surgery under general anesthesia.Results Two patients were diagnosed as renal tuberculosis by postoperative pathology. The success rate of operation was 100%, and no complications occurred. The erythrocyte sedimentation rate, urine routine and blood routine returned to normal after operation. There was no significant change in serum creatinine after operation, and the glomerular filtration rate decreased slightly. The patients continued anti-tuberculosis therapy after operation, and no tuberculosis recurrence occurred during the follow-up period after drug withdrawal. The imaging examination at 1 year after operation showed that the shape of the affected kidney was good. One patient underwent ileal cystoplasty without abdominal adhesion.Conclusion The robot-assisted laparoscopic "de-roofing and peeling bottom" technique was an effective, safe and feasible treatment for localized renal tuberculosis. -

-
表 1 肾结核分期
分期 描述 K 肾脏内结核病灶评估 K1(早期) 单个结核小病灶a),影像学提示为圆形或类圆形低密度灶,边缘模糊,周边伴有钙化斑。 K2(中期) 1.5 cm < 单个或多个病灶整体≤肾脏1/3b)。 K2a(局限集中型) 单个大病灶或多个小病灶局限肾脏某一部位,整体小于肾脏1/3。 K2b(分散型) 多个小病灶分散于肾脏,整体小于肾脏1/3。 K3(中晚期) 肾脏1/3 < 多个结核病灶整体≤肾脏2/3,患肾eGFR≥10 mL/min K4(晚期) 多个结核病灶整体>肾脏2/3,肾实质广泛破坏,甚至完全钙化,患肾eGFR < 10 mL/min 注:a)小病灶为直径≤1.5 cm,大病灶为直径>1.5 cm;b)部分肾结核患者存在肾萎缩情况,以结核病灶所占肾脏比例进行分期。 表 2 2例患者术中和术后指标
指标 结果 手术时间/min 200/240 热缺血时间/min 30/35 出血量/mL 80/150 引流时间/d 4/5 术后抗结核治疗时间/月 6/6 术后血肌酐/(μmol/L) 161/64 术后患肾GFR/(mL/min) 26.6/19.2 -
[1] Global tuberculosis control: key findings from the December 2009 WHO report[J]. Wkly Epidemiol Rec, 2010, 85(9): 69-80.
[2] Gozdas HT, Caliskan S. Challenges in the diagnosis of renal tuberculosis[J]. Kaohsiung J Med Sci, 2015, 31(9): 493. doi: 10.1016/j.kjms.2015.04.011
[3] Figueiredo AA, Lucon AM, Gomes CM, et al. Urogenital tuberculosis: patient classification in seven different groups according to clinical and radiological presentation[J]. Int Braz J Urol, 2008, 34(4): 422-432;discussion 432. doi: 10.1590/S1677-55382008000400004
[4] 况夏雨, 陈昌庆, 袁清, 等. 32例结核性膀胱挛缩患者临床特点分析[J]. 解放军医学院学报, 2016, 37(9): 944-947. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-5227.2016.09.007
[5] Kim EJ, Lee W, Jeong WY, et al. Chronic kidney disease with genitourinary tuberculosis: old disease but ongoing complication[J]. BMC Nephrol, 2018, 19(1): 193. doi: 10.1186/s12882-018-0994-2
[6] 彭启伦, 王坤杰, 彭海涛. 不典型肾结核的诊断治疗[J]. 华西医学, 2012, 27(8): 1168-1170.
[7] Tong X, Zhang J, Tang YZ, et al. Enhancing efficacy and safety in laparoscopic partial nephrectomy for localized renal tuberculosis: the skirted continuous suture technique[J]. Med Sci Monit, 2024, 30: e940146.
[8] Ljunggren E. Indications for nephrectomy, nephro-ureterectomy and partial nephrectomy in renal tuberculosis[J]. J Urol, 1957, 78(5): 499-504. doi: 10.1016/S0022-5347(17)66470-X
[9] Wong SH, Lau WY. The surgical management of non-functioning tuberculous kidneys[J]. J Urol, 1980, 124(2): 187-191. doi: 10.1016/S0022-5347(17)55367-7
[10] Puigvert A, Gittes RF. Partial nephrectomy in the solitary kidney. Ⅱ. Experience with 20 cases of renal tuberculosis[J]. J Urol, 1968, 100(3): 243-250. doi: 10.1016/S0022-5347(17)62514-X
[11] 李晓东, 王玉杰, 拜合提亚·阿扎提, 等. 腹腔镜和开放手术进行结核肾脏切除的疗效评价[J]. 现代泌尿外科杂志, 2021, 26(2): 116-119.
[12] Bloom S, Wechsler H, Lattimer JK. Results of a long-term study of non-functioning tuberculous kidneys[J]. J Urol, 1970, 104(5): 654-657. doi: 10.1016/S0022-5347(17)61803-2
[13] Wyrens RG. Indication for extirpative renal operation for tuberculosis[J]. J Urol, 1962, 87: 1-8. doi: 10.1016/S0022-5347(17)64896-1
-




 下载:
下载: