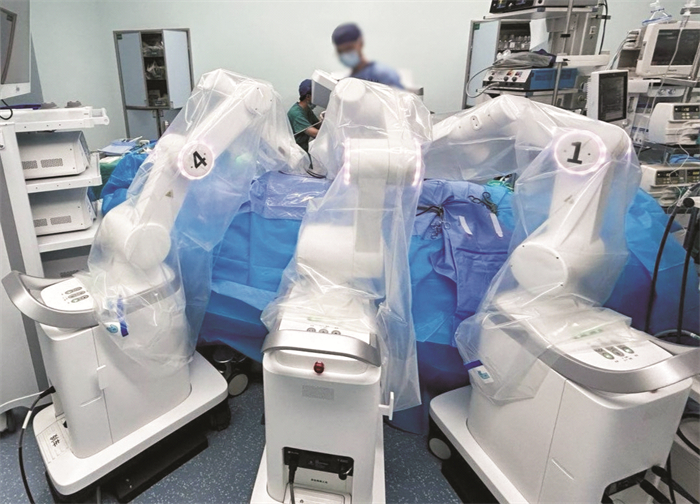
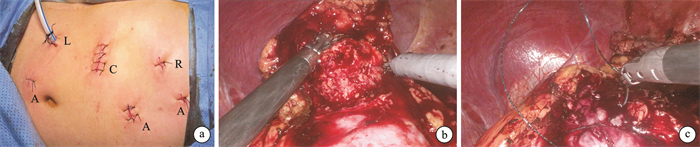
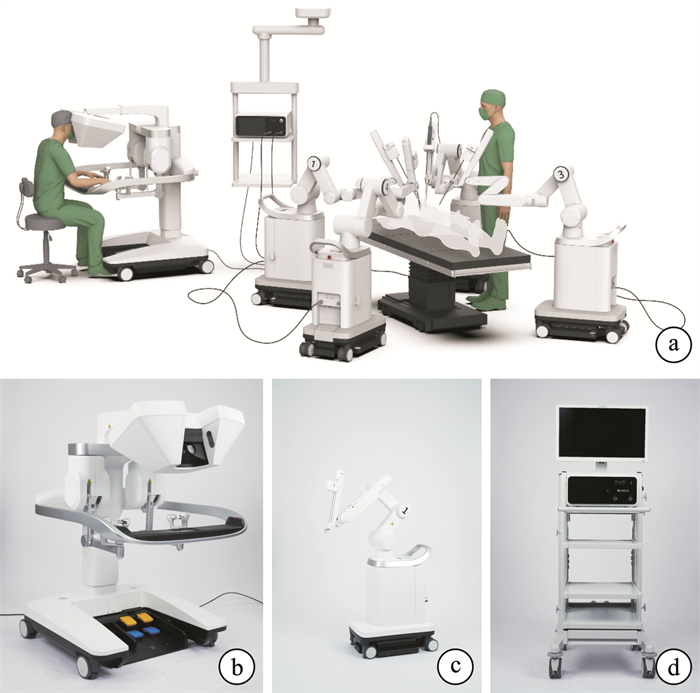
Feasibility and safety analysis of domestic modular surgical robot system-assisted partial nephrectomy
-
摘要: 目的 评估国产模块化海山一Ⓡ腔镜手术机器人辅助肾部分切除手术的有效性和安全性。方法 前瞻性纳入2024年6月—7月在郑州大学第一附属医院接受海山一Ⓡ腔镜手术机器人辅助肾部分切除术的10例患者,收集患者的一般情况、肿瘤影像学资料、术中操作相关参数、术后病理、术中及术后并发症发生情况、术者操作的主观感受等。结果 10例患者均顺利完成手术,无中转开放或腹腔镜手术。患者年龄为(56.0±13.9)岁,体重指数为(24.8±2.4) kg/m2。术前TNM分期均为T1aN0M0期,肿瘤直径为(2.0±0.9) cm,R.E.N.A.L.评分为(4.8±0.6)分。设备对接时间为(6.6±3.1) min,机械臂操作时间为(70.1±33.6) min,出血量为(57±24.5) mL,热缺血时间为(13.4±11.6) min,其中有2例患者未阻断肾动脉。术后住院时间为(6.5±1.4) d,病理切缘均为阴性,术中及术后共4例患者出现Clavien-DindoⅠ级并发症。术中操作具有很好的稳定性、灵活性及较低的延迟。结论 初步研究表明海山一Ⓡ腔镜手术机器人辅助肾部分切除术是安全可行的。Abstract: Objective To evaluate the feasibility and safety of the domestically modular CarinaTMPlatform for partial nephrectomy.Methods A prospective study was conducted, including 10 patients who underwent partial nephrectomy by the CarinaTM Platform in our hospital from June to July 2024. Data collected included patients' general conditions, tumor imaging data, intraoperative parameters, postoperative pathology, intraoperative and postoperative complications, and the subjective experience of the operators.Results All 10 patients successfully completed the surgery without conversion to open or laparoscopic surgery. The patients' age was (56.0±13.9) years, and the body mass index was (24.8±2.4) kg/m2. Preoperative TNM staging was T1aN0M0, with a tumor diameter of (2.0±0.9) cm and R.E.N.A.L score was (4.8±0.6). The docking time was (6.6±3.1) min, and the robotic arm operating time was (70.1±33.6) min. The blood loss was (57.0±24.5) mL, and the warm ischemia time was (13.4±11.6) min. Renal artery clamping avoided in 2 patients. The postoperative hospital stay was (6.5±1.4) days, and all pathological margins were negative. Four patients experienced Clavien-Dindo grade Ⅰ complications intraoperatively and postoperatively. The intraoperative manipulation was stable, flexible, and had low latency.Conclusion The preliminary study indicates that the CarinaTMPlatform-assisted partial nephrectomy is safe and feasible.
-
Key words:
- modular robot /
- renal tumor /
- partial nephrectomy
-

-
表 1 经海山一Ⓡ腔镜机器人PN患者资料
项目 患者1 患者2 患者3 患者4 患者5 患者6 患者7 患者8 患者9 患者10 性别 男 男 男 女 男 男 女 男 男 男 年龄/岁 57 55 37 74 68 61 64 61 28 55 BMI/(kg/m2) 23.6 28.1 22.9 24.7 24.5 26.7 28.2 20.8 22.9 25.4 术前肾小球滤过率/(mL/min) 96.9 104.4 113.2 53.5 78.3 92.5 93.6 62.9 105.2 95.5 R.E.N.A.L评分/分 5 4 5 5 5 6 5 4 4 5 肿瘤侧别 右 右 左 左 右 右 右 左 左 右 肿瘤大小/cm 1.2 2.5 4.0 0.6 1.7 2.5 1.8 2.0 2.5 1.2 临床分期 T1a T1a T1a T1a T1a T1a T1a T1a T1a T1a 设备对接时间/min 5 4 2 5 12 5 10 6 8 9 机械臂操作时间/min 28 53 34 62 78 139 73 79 107 48 热缺血时间/min 0 10 16 0 7 40 10 18 20 13 术中估计出血量/mL 50 50 50 20 100 100 50 50 50 50 术后肾小球滤过率/(mL/min) 81.0 80.1 102.7 60.7 61.7 59.1 93.1 57.7 99.6 89.1 病理类型 透明细胞癌 透明细胞癌 错构瘤 透明细胞癌 透明细胞癌 透明细胞癌 透明细胞癌 透明细胞癌 透明细胞癌 透明细胞癌 术后住院时长/d 5 5 5 8 8 8 6 7 8 5 切缘结果 阴性 阴性 阴性 阴性 阴性 阴性 阴性 阴性 阴性 阴性 并发症(Clavien-Dindo) 0 0 0 Ⅰ Ⅰ 0 Ⅰ 0 0 Ⅰ 稳定性评价 优 优 优 优 优 优 优 优 优 优 延迟性评价 良 优 良 优 优 优 优 良 优 优 灵活性评价 优 良 优 良 优 优 良 优 良 良 注:稳定性评价,优为稳定无颤动;延迟性评价,优为无明显延迟,良为轻微延迟;灵活性评价,优为非常灵活,良为比较灵活。 -
[1] Bahadoram S, Davoodi M, Hassanzadeh S, et al. Renal cell carcinoma: an overview of the epidemiology, diagnosis, and treatment[J]. G Ital Nefrol, 2022, 39(3): 2022-vol3.
[2] 中国抗癌协会泌尿男生殖系肿瘤专业委员会微创学组, 魏希锋, 张凯, 等. 中国肾肿瘤腹腔镜及机器人肾部分切除术专家共识[J/OL]. 泌尿外科杂志(电子版), 2021, 13(4): 1-5, 9.
[3] Ljungberg B, Albiges L, Abu-Ghanem Y, et al. European Association of Urology Guidelines on Renal Cell Carcinoma: The 2022 Update[J]. Eur Urol, 2022, 82(4): 399-410. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2022.03.006
[4] Patel M, Porter J. Robotic retroperitoneal surgery: a contemporary review[J]. Curr Opin Urol, 2013, 23(1): 51-56. doi: 10.1097/MOU.0b013e32835b61f4
[5] Crisan N, Neiculescu C, Matei D V, et al. Robotic retroperitoneal approach-a new technique for the upper urinary tract and adrenal gland[J]. Int J Med Robot, 2013, 9(4): 492-496. doi: 10.1002/rcs.1523
[6] Zihni AM, Ohu I, Cavallo JA, et al. Ergonomic analysis of robot-assisted and traditional laparoscopic procedures[J]. Surg Endosc, 2014, 28(12): 3379-3384. doi: 10.1007/s00464-014-3604-9
[7] Yu HY, Hevelone ND, Lipsitz SR, et al. Use, costs and comparative effectiveness of robotic assisted, laparoscopic and open urological surgery[J]. J Urol, 2012, 187(4): 1392-1398. doi: 10.1016/j.juro.2011.11.089
[8] Gallioli A, Territo A, Boissier R, et al. Learning Curve in Robot-assisted Kidney Transplantation: Results from the European Robotic Urological Society Working Group[J]. Eur Urol, 2020, 78(2): 239-247. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2019.12.008
[9] Kaouk J, Eltemamy M, Aminsharifi A, et al. Initial Experience with Single-port Robotic-assisted Kidney Transplantation and Autotransplantation[J]. Eur Urol, 2021, 80(3): 366-373. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2021.03.002
[10] 冯圣佳, 沈凯, 沈黎辉, 等. 机器人辅助与腹腔镜肾部分切除术治疗cT2a期肾癌的安全性和可行性比较分析[J]. 临床泌尿外科杂志, 2024, 39(8): 684-688. https://lcmw.whuhzzs.com/article/doi/10.13201/j.issn.1001-1420.2024.08.006
[11] Koukourikis P, Rha KH. Robotic surgical systems in urology: What is currently available?[J]. Investig Clin Urol, 2021, 62(1): 14-22. doi: 10.4111/icu.20200387
[12] 张忠, 代海涛, 刘远华, 等. 图迈国产机器人辅助腹腔镜在泌尿外科手术中的安全性研究[J]. 微创泌尿外科杂志, 2023, 12(4): 229-232.
[13] 李学松, 樊书菠, 熊盛炜, 等. 国产内窥镜手术机器人系统在肾部分切除术中的初步临床应用[J]. 中华泌尿外科杂志, 2021, 42(5): 375-380. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112330-20210323-00144
[14] 罗城, 郭胜杰, 张志凌, 等. 国产单孔手术机器人辅助腹腔镜下肾部分切除术的可行性及安全性分析[J]. 实用医学杂志, 2023, 39(24): 3275-3280. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-5725.2023.24.022
[15] 王杰, 张中元, 樊书菠, 等. 国产机器人辅助腹腔镜经腹膜外根治性前列腺切除及尿道周围全重建术初步经验[J]. 临床泌尿外科杂志, 2023, 38(2): 92-98. https://lcmw.whuhzzs.com/article/doi/10.13201/j.issn.1001-1420.2023.02.003
-




 下载:
下载: