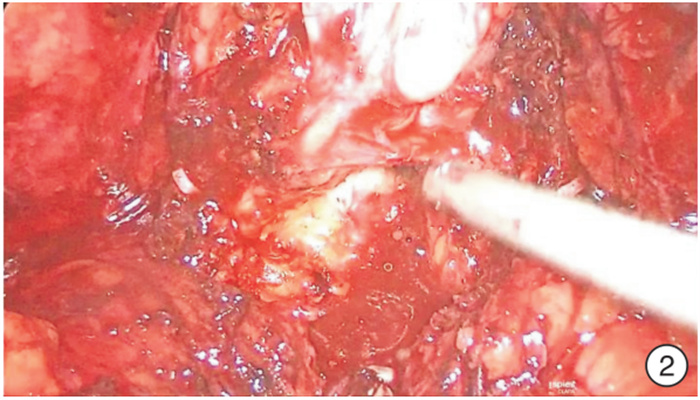
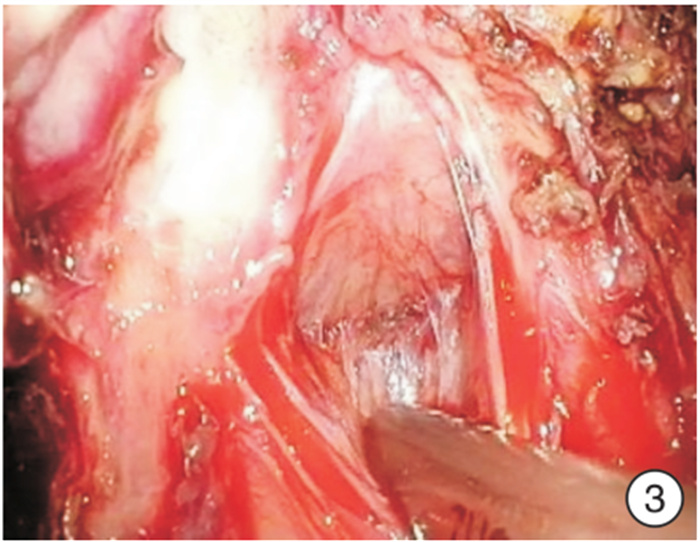
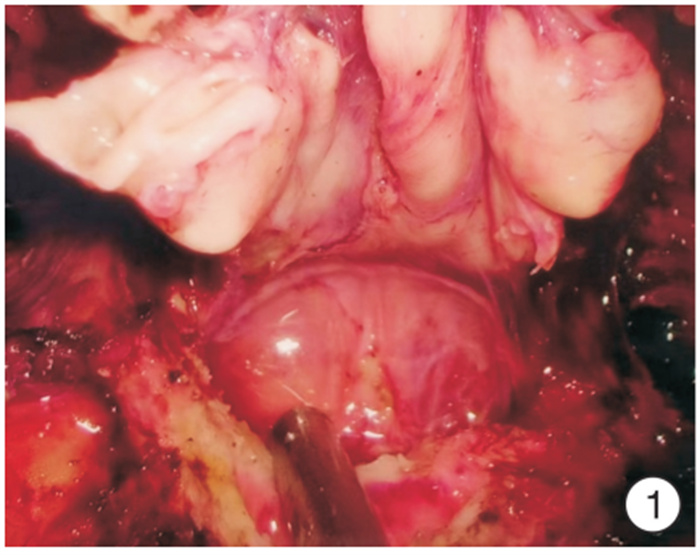
Arch of Denonvilliers' fascia as an anatomical marker in prevention of rectal injury during laparoscopic radical prostatectomy
-
摘要: 目的 狄氏筋膜和前列腺包膜融合处呈现一横行隆起,命名为狄氏筋膜弓。探讨狄氏筋膜弓作为切开狄氏筋膜的解剖标志在预防腹腔镜前列腺根治术直肠损伤中的作用。 方法 2018年1月—2021年11月河南省人民医院泌尿外科对210例TNM病理分期为T2a~T4期的前列腺癌患者行经腹膜外途径腹腔镜前列腺癌根治术。前期101例(对照组)分离狄氏筋膜方法为提起双侧输精管精囊,切开狄氏筋膜,在直肠前脂肪分离到前列腺尖部,即筋膜外法;后期109例(试验组)分离狄氏筋膜方法为游离狄氏筋膜时,紧贴精囊、输精管向尾侧钝性推狄氏筋膜,至剥离不动为止,即到射精管平面,此处因狄氏筋膜返折形成一白色横行隆起,本人为其命名为狄氏筋膜弓。沿弓剪开:直接进入前列腺包膜和狄氏筋膜之间间隙;狄氏筋膜前弓下剪开:进入直肠前脂肪层,再次牵拉直肠前脂肪,紧贴前列腺分离,进入狄氏筋膜和前列腺包膜之间隙,继续钝性分离至前列腺尖部和侧血管蒂,即筋膜内法。比较2组手术时间、出血量、直肠损伤和尿漏等情况。 结果 210例手术均获成功。对照组和试验组平均手术时间分别为(210±19.6) min和(120±18.7) min,平均出血量分别为(110±9.7) mL和(50±4.5) mL,直肠损伤分别为6例和1例,尿漏分别为4例和1例;试验组中因膀胱颈三角区裂伤改为开放手术1例。对照组6例直肠损伤中:4例术中发现,一期缝合愈合,2例术后出现膀胱直肠瘘,先行结肠造口术,分别留置尿管6、8个月后瘘愈合再关闭造口。试验组1例直肠损失,术中发现,一期缝合愈合。直肠损伤部位:在精囊分离狄氏筋膜处3例,前列腺底部2例,前列腺尖部2例。2组直肠损伤比较差异有统计学意义(χ2=4.11,P=0.04)。 结论 狄氏筋膜弓作为横行切开狄氏筋膜的解剖标志可以减少腹腔镜前列腺癌根治术直肠损伤的发生。Abstract: Objective The fusion of Denonvilliers' fascia and prostatic capsule presents a transverse eminence termed Arch of Denonvilliers' fascia. The role of Denonvilliers' fascia arch as an anatomical marker in the prevention of rectal injury during laparoscopic radical prostatectomy is investigated. Methods From January 2018 to November 2021, 210 prostate cancer cases with TNM pathological stage T2a-T4 successfully underwent laparoscopic radical prostatectomy through extraperitoneal approach. The previous 101 cases(control group) were operated by extrafascial method. The latter 109 cases were in the experimental group. Denonvilliers' fascia was pushed to the caudal, close to the seminal vesicle and vas deferens, until pushing motionless. Namely to the in-plane ejaculation, here Denonvilliers' fascia forms a transverse fold uplift named Denonvilliers' fascia arch. Denonvilliers' fascia was cut open in this arch belows lightly, entering the fat layer before rectum. Again pulling the fat before rectum, and separating the prostate closely, entered the gap between Denonvilliers' fascia and prostate capsule. Then, a blunt dissection to the tip of the prostate and lateral vascular pedicle was performed. It's called intrafascial method.Later operation steps were similar to the control group. The operative time, blood loss volume, rectal injury and urine leakage cases were compared between two groups. Results All the 210 operations were successfully performed. The mean operating time, blood loss volume, rectal injury cases, urine leakage cases in control group and experimental group were(210.0±19.6) min and(120.0±18.7) min, (110.0±9.7) mL and(50.0±4.5) mL, 6 cases versus 1 case and 4 cases versus 1 case respectively. Among the 6 cases of rectal injuries in the control group, 4 cases were found intraoperatively and were sutured in two-layered way and healed. Other 2 cases were found postoperatively with cysto-rectal fistula. Colostomy was performed and the fistula healed after indwelling catheter for 6 or 8 months. One case in the experimental group who was found rectal injuries intraoperatively was sutured in two-layered way and healed. Three cases of rectal injuries located at Denonvilliers' fascia, 2 cases at the base of the prostate, and 2 cases at the tip of the prostate. A significant higher incidence of rectal injury was found in the control group than that in the experimental group(χ2=4.11, P=0.04). Conclusion The Denonvilliers' fascia arch can be used as an anatomical marker for incision transverse Denonvilliers' fascia to reduce the incidence of rectal injury during laparoscopic radical prostatectomy.
-

-
[1] 李辉, 杨超, 汪凯红, 等. 改良前入路保留Retzius间隙机器人辅助腹腔镜根治性前列腺筋膜内切除术在10例前列腺癌患者的应用[J]. 现代泌尿外科杂志, 2023, 28(3): 201-205. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MNWK202303005.htm
[2] 占习双, 刘全明, 吴天鹏. 侧方精囊入路保留完整膀胱颈口前列腺癌根治术患者即刻尿控临床效果[J]. 临床泌尿外科杂志, 2023, 38(12): 942-947. https://lcmw.whuhzzs.com/article/doi/10.13201/j.issn.1001-1420.2023.12.010
[3] 郭潇潇, 朱生才, 侯惠民, 等. 前列腺癌根治术对75岁及以上患者生存情况的影响[J]. 中华老年医学杂志, 2019, 38(3): 278-282.
[4] Rocco B, Giorgia G, Simone A, et al. Rectal perforation during pelvic surgery[J]. Eur Urol Open Sci, 2022, 44: 54-59. doi: 10.1016/j.euros.2022.04.006
[5] 吴恭瑾, 秦泽, 刁龙, 等. 腹腔镜前列腺癌根治术直肠损伤因素及处理[J]. 国际泌尿系统杂志, 2019, 39(5): 895-897. https://cpfd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CPFDTOTAL-ZJKX201906002140.htm
[6] Luchaichana N, Ramart P. Management of rectal injury and rectourinary fistula from radical prostatectomy[J]. Urol Ann, 2023, 15(1): 31-34. doi: 10.4103/ua.ua_179_21
[7] 王帅, 张大宏. 腹腔镜根治性前列腺切除术中并发直肠损伤的处理经验[J]. 中华泌尿外科杂志, 2019, 40(8): 592-595.
[8] Dovey ZS, Tewari AK. Anatomical robotic prostatectomy: technical factors to achieve superb continence and erectile function[J]. Transl Androl Urol, 2020, 9(2): 887-897. doi: 10.21037/tau.2020.01.15
[9] Hoeh B, Wenzel M, Hohenhorst L, et al. Anatomical fundamentals and current surgical knowledge of prostate anatomy related to functional and oncological outcomes for robotic-assisted radical prostatectomy[J]. Front Surg, 2021, 8: 825183.
[10] Li Y, Zhao YM, Ma YB, et al. The"Y"-shaped Denonvilliers' fascia and its adjacent relationship with the urogenital fascia based on a male cadaveric anatomical study[J]. BMC Surg, 2023, 23(1): 13.
[11] Huang JL, Liu J, Fang JF, et al. Identification of the surgical indication line for the Denonvilliers' fascia and its anatomy in patients with rectal cancer[J]. Cancer Commun(Lond), 2020, 40(1): 25-31.
[12] García-Gausí M, García-Armengol J, Pellino G, et al. Navigating surgical anatomy of the Denonvilliers' fascia and dissection planes of the anterior mesorectum with a cadaveric simulation model[J]. Updates Surg, 2022, 74(2): 629-636.
[13] Tzelves L, Protogerou V, Varkarakis I. Denonvilliers' Fascia: the prostate border to the outside world[J]. Cancers(Basel), 2022, 14(3): 688.
[14] Wagaskar VG, Mittal A, Sobotka S, et al. Hood technique for robotic radical prostatectomy-preserving periurethral anatomical structures in the space of retzius and sparing the pouch of Douglas, enabling early return of continence without compromising surgical margin rates[J]. Eur Urol, 2021, 80(2): 213-221.
[15] Lu XW, He C, Zhang SH, et al. Denonvilliers' fascia acts as the fulcrum and hammock for continence after radical prostatectomy[J]. BMC Urol, 2021, 21(1): 176.
-




 下载:
下载: