Prognostic significance of tumor thrombus grading in non-metastatic clear cell renal cell carcinoma with tumor thrombus: a multi-center retrospective study
-
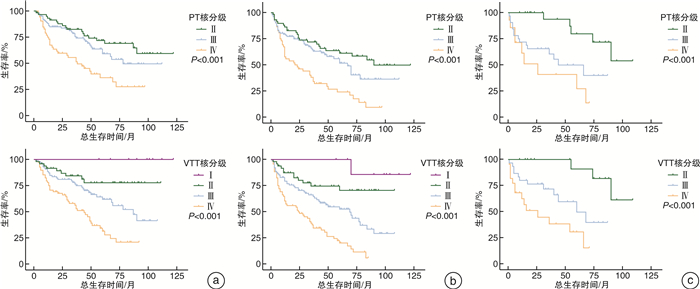
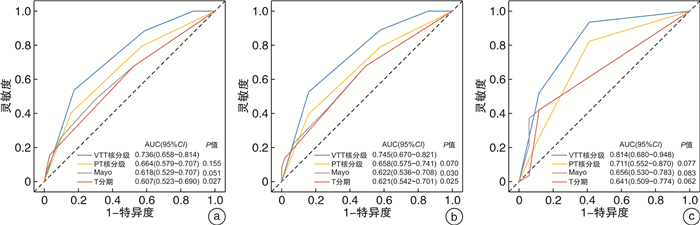
摘要: 目的 探讨非转移性肾透明细胞癌(non-metastatic clear cell renal cell cancer,nm-ccRCC)合并静脉癌栓(venous tumor thrombus,VTT)时,VTT病理特征尤其是VTT病理核分级对患者预后的预测价值。方法 回顾性分析来自中国2家医学中心(东部战区总医院、上海长海医院)于2010年1月—2021年12月收治的214例(中国队列)以及波兰2家医学中心(波兰格但斯克医学院、华沙医科大学)于2012年1月—2018年12月收治的82例(波兰队列)nm-ccRCC伴VTT患者的临床病理资料,其中中国队列男149例,女65例,平均年龄60.6岁;波兰队列男45例,女37例,平均年龄64.5岁。同时收集患者术后原发肿瘤(PT)和VTT病理切片进行重新评估,对于VTT组织进行包括WHO/ISUP核分级、是否存在坏死、肉瘤样/横纹肌样分化等评估。采用Kaplan-Meier方法绘制生存分析曲线,单因素和多因素Cox回归分析确定独立危险因素,通过受试者工作特征(ROC)曲线和曲线下面积(AUC)评估VTT核分级及其他因素预测预后的准确性。结果 中国队列PT核分级Ⅱ级60例,Ⅲ级102例,Ⅳ级52例;VTT核分级Ⅰ级9例,Ⅱ级49例,Ⅲ级88例,Ⅳ级68例。波兰队列PT核分级Ⅱ级26例,Ⅲ级39例,Ⅳ级17例;VTT核分级Ⅱ级20例,Ⅲ级37例,Ⅳ级25例。2个队列患者中位总生存期(OS)分别为87个月和68个月;中位无病生存期(DFS)时间为58个月(波兰队列无DFS);中国队列5年总生存率为57.1%,5年中位无病生存率为47.4%;波兰队列5年总生存率为55.6%。Kaplan-Meier生存曲线表明PT、VTT核分级均能良好地区分患者生存情况,单因素分析结果中PT、VTT核分级均为预后危险因素,多因素分析结果表明PT核分级不再是独立危险因素,但VTT核分级仍有意义。ROC曲线进一步证实VTT核分级相较于PT核分级、Mayo分级和T分期具有更好的预测性。结论 在nm-ccRCC伴VTT患者中,VTT核分级有助于预测预后,且预测准确性高于PT核分级。因其长期受忽视的现状以及对预后的重要性,将VTT核分级纳入病理报告来提供更多的预后相关信息,具有重要的临床意义。Abstract: Objective To investigate the predictive value by evaluating comprehensive pathological characteristics of non-metastatic clear cell renal cell carcinoma(nm-ccRCC) with venous tumor thrombus(VTT), especially the pathological grading of VTT.Methods Clinicopathological and prognosis data of 214 cases of nm-ccRCC with VTT during Jan. 2010 to Dec. 2021 from Jinling Hospital and Changhai Hospital in China and 82 cases during Jan. 2012 to Dec. 2018 from the Medical University of Gdańsk and the Medical University of Warsaw in Poland were collected and analyzed retrospectively. China cohort included 149 males and 65 females. The average age was 60.6 years. Poland cohort included 45 males and 37 females. The average age was 64.5 years. Postoperative tumor and tumor thrombus pathological data were collected for reassessment. The pathological information of tumor and VTT were recorded, including nuclear grading of tumor and tumor thrombus, necrosis, sarcomatoid or rhabdoid features. The Kaplan-Meier method with log-rank test was used for survival analysis and comparisons. Univariable and multivariable Cox regression analyses were performed to identify independent predictors associated with survival outcome. Time-dependent receiver operating characteristic(ROC) analysis and area under the curve(AUC) were used to measure prognostic accuracy.Results In China cohort, patients' numbers of PT grading Ⅱ, Ⅲ, Ⅳ were 60, 102, 52, respectively. Patients' numbers of VTT grading Ⅰ, Ⅱ, Ⅲ, Ⅳ were 9, 49, 88, 68, respectively. In Poland cohort, patients' numbers of PT grading Ⅱ, Ⅲ, Ⅳ were 26, 39, 17, respectively. Patients' numbers of VTT grading Ⅱ, Ⅲ, Ⅳ were 20, 37, 25, respectively. Median overall survival(OS) of China and Poland cohort: 87, 68 months. Median disease-free survival(DFS) of China cohort: 58 months. Five-year overall survival rate of China and Poland cohort: 57.1%, 55.6%. Five-year disease free survival rate of China cohort: 47.4%. The Kaplan-Meier survival curve showed that PT and VTT nuclear grading could distinguish the survival of patients. Univariate analysis showed that PT and VTT nuclear grading were prognostic risk factors. Multivariate analysis showed that PT nuclear grading was no longer an independent risk factor for OS and DFS, but VTT nuclear grading was still significant. ROC showed that VTT grading exhibited better predictability than other indicators.Conclusion In nm-ccRCC with VTT patients, VTT nuclear grading can help predict the prognosis, and the prediction accuracy is higher than PT nuclear grading. Due to its long-term neglected status and importance to prognosis, it is necessary to include VTT nuclear grading in pathological reports to attract attention.
-

-
表 1 中国与波兰队列患者临床病理资料比较
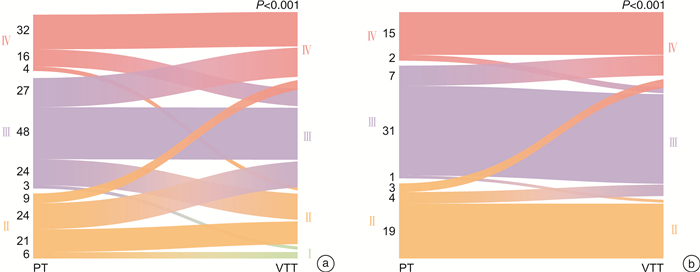
例(%),X±S,M(Q1,Q3) 项目 中国队列(亚裔黄种人)(214例) 波兰队列(白种人)(82例) P值 项目 中国队列(亚裔黄种人)(214例) 波兰队列(白种人)(82例) P值 年龄/岁 60.6±11.3 64.5±10.3 0.010 T分期 < 0.001 性别 0.017 T3a 86(40.2) 69(84.2) 男 149(69.6) 45(54.9) T3b 111(51.9) 11(13.4) 女 65(30.4) 37(45.1) T3c 9(4.2) 0 住院天数/d 12.0 13.0 0.005 T4 8(3.7) 2(2.4) (8.0,16.0) (12.0,17.0) PT核分级 0.741 血尿 0.788 Ⅰ 0 0 无 140(65.4) 55(67.1) Ⅱ 60(28.0) 26(31.7) 有 74(34.6) 27(32.9) Ⅲ 102(47.7) 39(47.6) 腰痛 0.592 Ⅳ 52(24.3) 17(20.7) 无 168(78.5) 62(75.6) 肿瘤坏死 0.603 有 46(21.5) 20(24.4) 无 122(57.0) 44(53.7) 高血压 0.863 有 92(43.0) 38(46.3) 无 138(64.5) 52(63.4) 肿瘤肉瘤样变 0.488 有 76(35.5) 30(36.6) 无 184(86.0) 73(89.0) 糖尿病 < 0.001 有 30(14.0) 9(11.0) 无 189(88.3) 58(70.7) 肿瘤横纹肌样变 0.185 有 25(11.7) 24(29.3) 无 190(88.8) 77(93.9) 手术方式 < 0.001 有 24(11.2) 5(6.1) 开放 134(62.6) 78(95.1) 肾周脂肪侵犯 0.023 腹腔镜 80(37.4) 4(4.9) 无 166(77.6) 53(64.6) 输血 < 0.001 有 48(22.4) 29(35.4) 无 83(38.8) 75(91.5) VTT核分级 0.288 有 131(61.2) 7(8.5) Ⅰ 9(4.2) 0 辅助治疗 0.200 Ⅱ 49(22.9) 20(24.4) 无 154(72.0) 65(79.3) Ⅲ 88(41.1) 37(45.1) 有 60(28.0) 17(20.7) Ⅳ 68(31.8) 25(30.5) 肿瘤侧别 0.561 癌栓坏死 左 86(40.2) 36(43.9) 无 143(66.8) 右 128(59.8) 46(56.1) 有 71(33.2) 肿瘤直径/cm 7.6(5.6,9.7) 8.3(6.0,11.0) 0.050 癌栓肉瘤样变 0.857 癌栓分级(Mayo) < 0.001 无 197(92.1) 76(92.7) 0 86(40.2) 69(84.2) 有 17(7.9) 6(7.3) Ⅰ 45(21.0) 2(2.4) 癌栓横纹肌样变 0.010 Ⅱ 53(24.8) 4(4.9) 无 197(92.1) 67(81.7) Ⅲ 21(9.8) 7(8.5) 有 17(7.9) 15(18.3) Ⅳ 9(4.2) 0 5年总生存率/% 57.1 55.6 5年无病生存率/% 47.4 表 2 中国与波兰队列OS的Cox回归单因素及多因素分析
因素 中国队列(214例) 波兰队列(82例) 单因素分析 多因素分析 单因素分析 多因素分析 HR(95% CI) P值 HR(95% CI) P值 HR(95% CI) P值 HR(95% CI) P值 年龄 1.009
(0.991~1.029)0.329 0.966
(0.933~1.001)0.055 性别 女vs男 1.360
(0.877~2.109)0.170 0.812
(0.383~1.722)0.588 住院天数 1.011
(0.987~1.035)0.386 1.017
(0.928~1.114)0.725 血尿 有vs无 0.970
(0.616~1.526)0.894 2.275
(1.080~4.794)0.031 腰痛 有vs无 1.448
(0.897~2.337)0.130 1.630
(0.708~3.754)0.251 高血压 有vs无 1.180
(0.758~1.836)0.463 1.087
(0.505~2.341)0.831 糖尿病 有vs无 0.678
(0.313~1.468)0.324 1.045
(0.461~2.369)0.917 手术方式 开放vs腹腔镜 1.099
(0.701~1.721)0.681 0.444
(0.060~3.277)0.426 输血 有vs无 1.546
(0.964~2.482)0.071 1.762
(0.531~5.845)0.354 辅助治疗 有vs无 1.131
(0.709~1.805)0.605 1.111
(0.474~2.603)0.809 肿瘤侧别 左vs右 1.103
(0.713~1.708)0.659 0.890
(0.414~1.914)0.765 肿瘤直径 1.092
(1.025~1.163)0.006 1.070
(0.966~1.185)0.192 癌栓分级(Mayo) 0 1 1 1 1 Ⅰ 1.104
(0.592~2.058)0.756 0.780
(0.411~1.482)0.448 1.349
(0.178~10.201)0.772 2.259
(0.252~20.249)0.467 Ⅱ 1.389
(0.775~2.492)0.270 1.290
(0.708~2.353)0.406 8.432
(2.683~26.494)< 0.001 3.239
(0.920~11.401)0.067 Ⅲ 2.995
(1.623~5.527)< 0.001 1.698
(0.906~3.181)0.098 8.735
(3.485~21.899)< 0.001 14.045
(4.406~44.772)< 0.001 Ⅳ 2.605
(1.070~6.340)0.035 3.702
(1.466~9.344)0.006 T分期 T3a 1 1 T3b 1.415
(0.874~2.290)0.158 6.288
(2.789~14.177)< 0.001 T3c 2.607
(1.071~6.344)0.035 T4 3.439
(1.489~7.946)0.004 4.180
(0.947~18.448)0.059 PT核分级 Ⅰ~Ⅱ 1 1 Ⅲ 1.440
(0.810~2.560)0.214 4.312
(1.414~13.150)0.010 Ⅳ 3.021
(1.693~5.390)< 0.001 7.228
(2.175~24.026)0.001 肿瘤坏死 有vs无 1.241
(0.810~1.899)0.321 2.378
(1.116~5.067)0.025 肿瘤肉瘤样变 有vs无 3.705
(2.331~5.891)< 0.001 2.814
(1.732~4.573)< 0.001 5.033
(2.142~11.828)< 0.001 3.999
(1.330~12.029)0.014 肿瘤横纹肌样变 有vs无 1.891
(1.065~3.358)0.030 2.150
(0.279~16.557)0.462 肾周脂肪侵犯 有vs无 2.688
(1.734~4.168)< 0.001 2.379
(1.504~3.763)< 0.001 2.514
(1.200~5.270)0.015 2.949
(1.246~6.981)0.014 VTT核分级 Ⅰ~Ⅱ 1 1 1 1 Ⅲ 2.830
(1.348~5.943)0.006 2.424
(1.134~5.181)0.022 5.888
(1.289~26.891)0.022 3.474
(0.627~19.242)0.154 Ⅳ 6.199
(2.997~12.824)< 0.001 4.460
(2.104~9.454)< 0.001 13.648
(2.945~63.254)< 0.001 8.277
(1.526~44.904)0.014 癌栓坏死 有vs无 1.309
(0.843~2.034)0.231 癌栓肉瘤样变 有vs无 3.225
(1.777~5.851)< 0.001 1.778
(0.611~5.172)0.291 癌栓横纹肌样变 有vs无 3.929
(2.151~7.176)< 0.001 1.432
(0.540~3.800)0.471 表 3 中国队列DFS的Cox回归单因素及多因素分析
因素 中国队列(214例) 单因素分析 多因素分析 HR(95% CI) P值 HR(95% CI) P值 年龄 1.009(0.992~1.026) 0.289 性别 女vs男 1.163(0.787~1.718) 0.448 住院天数 1.002(0.980~1.025) 0.842 血尿 有vs无 1.032(0.697~1.529) 0.874 腰痛 有vs无 1.429(0.935~2.183) 0.099 高血压 有vs无 1.043(0.703~1.549) 0.833 糖尿病 有vs无 0.532(0.259~1.093) 0.086 手术方式 开放vs腹腔镜 0.883(0.595~1.311) 0.537 输血 有vs无 1.366(0.912~2.045) 0.130 辅助治疗 有vs无 1.232(0.819~1.851) 0.316 肿瘤侧别 左vs右 1.063(0.727~1.554) 0.751 肿瘤直径 1.056(0.998~1.118) 0.058 癌栓分级(Mayo) 0 1 1 Ⅰ 1.468(0.878~2.455) 0.143 1.159(0.683~1.966) 0.585 Ⅱ 1.579(0.948~2.627) 0.079 1.433(0.850~2.418) 0.177 Ⅲ 3.295(1.868~5.813) < 0.001 1.927(1.083~3.429) 0.026 Ⅳ 1.979(0.828~4.728) 0.125 2.490(1.023~6.061) 0.044 T分期 T3a T3b 1.632(1.072~2.484) 0.022 T3c 1.985(0.831~4.743) 0.123 T4 6.141(2.804~13.449) < 0.001 PT核分级 Ⅰ~Ⅱ 1 Ⅲ 1.446(0.877~2.384) 0.148 Ⅳ 3.061(1.841~5.089) < 0.001 肿瘤坏死 有vs无 1.061(0.730~1.542) 0.758 肿瘤肉瘤样变 有vs无 2.795(1.817~4.299) < 0.001 1.883(1.202~2.949) 0.006 肿瘤横纹肌样变 有vs无 2.502(1.552~4.032) < 0.001 肾周脂肪侵犯 有vs无 2.313(1.562~3.425) < 0.001 1.837(1.221~2.762) 0.003 VTT核分级 Ⅰ~Ⅱ 1 1 Ⅲ 2.788(1.496~5.196) 0.001 2.447(1.297~4.617) 0.006 Ⅳ 6.095(3.296~11.273) < 0.001 4.515(2.380~8.563) < 0.001 癌栓坏死 有vs无 1.329(0.900~1.962) 0.152 癌栓肉瘤样变 有vs无 3.158(1.848~5.397) < 0.001 癌栓横纹肌样变 有vs无 4.003(2.327~6.889) < 0.001 -
[1] Blute ML, Leibovich BC, Lohse CM, et al. The Mayo Clinic experience with surgical management, complications and outcome for patients with renal cell carcinoma and venous tumour thrombus[J]. BJU Int, 2004, 94(1): 33-41. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-410X.2004.04897.x
[2] Zapała Ł, Sharma S, Kunc M, et al. Analysis of clinicopathological factors influencing survival in patients with renal cell carcinoma and venous tumor thrombus[J]. J Clin Med, 2021, 10(17): 3852. doi: 10.3390/jcm10173852
[3] Kaptein FHJ, van der Hulle T, Braken SJE, et al. Prevalence, treatment, and prognosis of tumor thrombi in renal cell carcinoma[J]. JACC CardioOncol, 2022, 4(4): 522-531. doi: 10.1016/j.jaccao.2022.07.011
[4] Ljungberg B, Albiges L, Abu-Ghanem Y, et al. European association of urology guidelines on renal cell carcinoma: the 2019 update[J]. Eur Urol, 2019, 75(5): 799-810. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2019.02.011
[5] Garg H, Psutka SP, Hakimi AA, et al. A decade of robotic-assisted radical nephrectomy with inferior vena cava thrombectomy: a systematic review and meta-analysis of perioperative outcomes[J]. J Urol, 2022, 208(3): 542-560. doi: 10.1097/JU.0000000000002829
[6] Gu LY, Li HZ, Wang ZH, et al. A systematic review and meta-analysis of clinicopathologic factors linked to oncologic outcomes for renal cell carcinoma with tumor thrombus treated by radical nephrectomy with thrombectomy[J]. Cancer Treat Rev, 2018, 69: 112-120. doi: 10.1016/j.ctrv.2018.06.014
[7] Wang BS, Ma RZ, Liu YQ, et al. Body mass index as an independent risk factor for inferior vena cava resection during thrombectomy for venous tumor thrombus of renal cell carcinoma[J]. World J Surg Oncol, 2019, 17(1): 17. doi: 10.1186/s12957-019-1560-5
[8] Leibovich BC, Blute ML, Cheville JC, et al. Prediction of progression after radical nephrectomy for patients with clear cell renal cell carcinoma: a stratification tool for prospective clinical trials[J]. Cancer, 2003, 97(7): 1663-1671. doi: 10.1002/cncr.11234
[9] Lam JS, Shvarts O, Leppert JT, et al. Postoperative surveillance protocol for patients with localized and locally advanced renal cell carcinoma based on a validated prognostic nomogram and risk group stratification system[J]. J Urol, 2005, 174(2): 466-472;discussion 472;quiz 801. doi: 10.1097/01.ju.0000165572.38887.da
[10] Rodriguez Faba O, Linares E, Tilki D, et al. Impact of microscopic wall invasion of the renal vein or inferior vena cava on cancer-specific survival in patients with renal cell carcinoma and tumor thrombus: a multi-institutional analysis from the international renal cell carcinoma-venous thrombus consortium[J]. Eur Urol Focus, 2018, 4(3): 435-441. doi: 10.1016/j.euf.2017.01.009
[11] Bertini R, Roscigno M, Freschi M, et al. Impact of venous tumour thrombus consistency(solid vs friable)on cancer-specific survival in patients with renal cell carcinoma[J]. Eur Urol, 2011, 60(2): 358-365. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2011.05.029
[12] Moreira DM, Gershman B, Lohse CM, et al. Paraneoplastic syndromes are associated with adverse prognosis among patients with renal cell carcinoma undergoing nephrectomy[J]. World J Urol, 2016, 34(10): 1465-1472. doi: 10.1007/s00345-016-1793-7
[13] Paner GP, Stadler WM, Hansel DE, et al. Updates in the eighth edition of the tumor-node-metastasis staging classification for urologic cancers[J]. Eur Urol, 2018, 73(4): 560-569. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2017.12.018
[14] Zheng RS, Zhang SW, Zeng HM, et al. Cancer incidence and mortality in China, 2016[J]. J Natl Cancer Cent, 2022, 2(1): 1-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jncc.2022.02.002
[15] 熊波波, 张劲松, 李宁, 等. 机器人手术系统在肾癌腔静脉癌栓取出术中的应用进展[J]. 中华泌尿外科杂志, 2020, 41(4): 314-317. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112330-20191022-00461
[16] 黄庆波, 彭程, 马鑫, 等. 机器人辅助腹腔镜Mayo Ⅲ~Ⅳ级下腔静脉癌栓取出术的经验总结(附5例报告)[J]. 中华泌尿外科杂志, 2019, 40(2): 81-85. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1000-6702.2019.02.001
[17] 王声政, 范雅峰, 王健阁, 等. 单一体位机器人腹腔镜肝后下腔静脉癌栓取出术的初步体会[J]. 中华泌尿外科杂志, 2022, 43(1): 23-27.
[18] 刘志, 汪雄, 周佳维, 等. 伴有静脉癌栓肾癌患者手术效果及其相关预后因素分析[J]. 临床泌尿外科杂志, 2023, 38(4): 265-270. https://lcmw.whuhzzs.com/article/doi/10.13201/j.issn.1001-1420.2023.04.006
[19] Ljungberg B, Albiges L, Abu-Ghanem Y, et al. European association of urology guidelines on renal cell carcinoma: the 2022 update[J]. Eur Urol, 2022, 82(4): 399-410. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2022.03.006
[20] Stewart GD, Welsh SJ, Ursprung S, et al. A Phase Ⅱ study of neoadjuvant axitinib for reducing the extent of venous tumour thrombus in clear cell renal cell cancer with venous invasion(NAXIVA)[J]. Br J Cancer, 2022, 127(6): 1051-1060. doi: 10.1038/s41416-022-01883-7
[21] Wolff I, May M, Hoschke B, et al. Do we need new high-risk criteria for surgically treated renal cancer patients to improve the outcome of future clinical trials in the adjuvant setting?Results of a comprehensive analysis based on the multicenter CORONA database[J]. Eur J Surg Oncol, 2016, 42(5): 744-750. doi: 10.1016/j.ejso.2016.01.009
[22] 黄庆波, 彭程, 顾良友, 等. 肾肿瘤伴静脉瘤栓"301分级系统"及手术策略(附100例病例分析)[J]. 微创泌尿外科杂志, 2017, 6(6): 328-332. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WCMN201706003.htm
[23] Frank I, Blute ML, Cheville JC, et al. An outcome prediction model for patients with clear cell renal cell carcinoma treated with radical nephrectomy based on tumor stage, size, grade and necrosis: the SSIGN score[J]. J Urol, 2002, 168(6): 2395-2400. doi: 10.1016/S0022-5347(05)64153-5
[24] Yang B, Xia HZ, Xu CX, et al. Impact of sarcomatoid differentiation and rhabdoid differentiation on prognosis for renal cell carcinoma with vena caval tumour thrombus treated surgically[J]. BMC Urol, 2020, 20(1): 14. doi: 10.1186/s12894-020-0584-z
[25] Abel EJ, Masterson TA, Karam JA, et al. Predictive nomogram for recurrence following surgery for nonmetastatic renal cell cancer with tumor Thrombus[J]. J Urol, 2017, 198(4): 810-816. doi: 10.1016/j.juro.2017.04.066
-




 下载:
下载: