Diagnostic value of free prostate specific antigen density combined with PI-RADS v2.1 for clinically significant prostate cancer with PSA 4-20 ng/mL
-
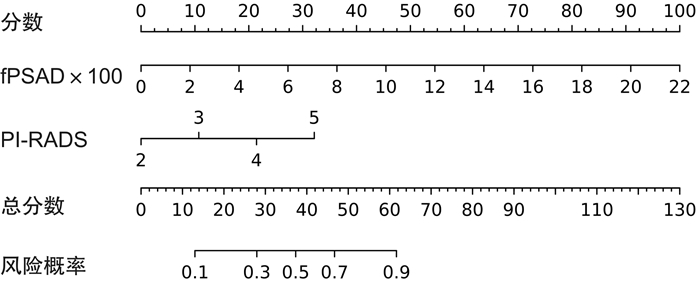
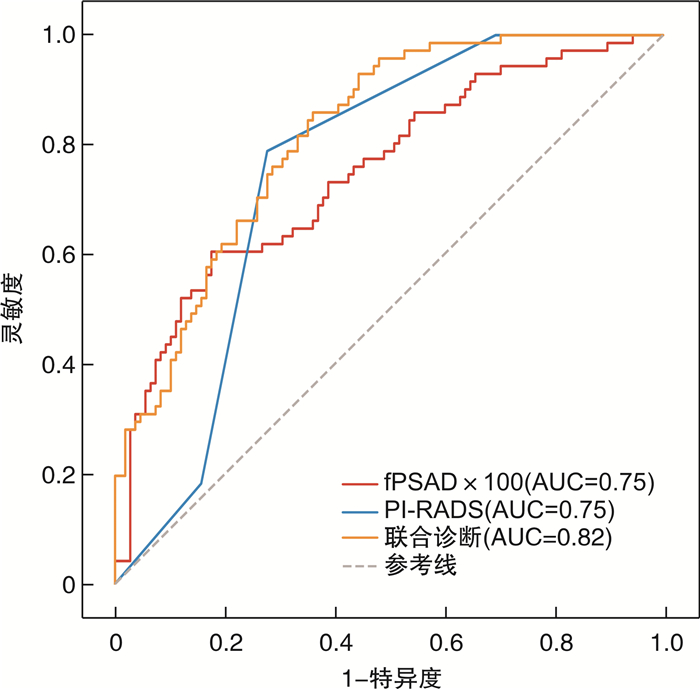
摘要: 目的 评估游离前列腺特异性抗原密度(free prostate specific antigen density,fPSAD)联合前列腺影像报告和数据系统(PI-RADS)v2.1在PSA 4~20 ng/mL时对前列腺穿刺结果为临床有意义前列腺癌(csPCa)的诊断价值。方法 回顾性分析2016年1月—2022年9月于盐城市第三人民医院PSA检测结果为4~20 ng/mL行前列腺穿刺的179例患者的临床资料,其中,临床有意义前列腺癌组71例(csPCa组),非临床有意义前列腺癌组108例(ncsPCa组)。根据PI-RADS v2.1对MRI图像进行评分,根据公式计算出前列腺体积(PV)和fPSAD;采用单因素及多因素logistic回归分析,得出csPCa的独立危险因素,绘制受试者工作特征(ROC)曲线,通过ROC曲线评估各因素单独及联合应用诊断csPCa的效能。最后绘制列线图,为临床应用该预测模型提供参考。结果 入组患者的游离前列腺特异性抗原(fPSA)、PV、fPSAD和PI-RADS v2.1评分差异均有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。fPSAD(OR=1.51,95%CI:1.51~1.84,P < 0.05)和PI-RADS v2.1评分(OR=2.63,95%CI:2.63~4.00,P < 0.05)是csPCa的独立危险因素。fPSAD联合PI-RADS v2.1评分诊断csPCa的ROC曲线下面积(AUC)为0.82,显著优于PI-RADS v2.1评分和fPSAD单独应用(AUC均为0.75),差异均有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。结论 对PSA 4~20 ng/mL患者,fPSAD、PI-RADS v2.1评分对csPCa有一定的诊断价值,两者联合应用可以提高其诊断效能。
-
关键词:
- 游离前列腺特异性抗原密度 /
- 前列腺成像报告和数据系统v2.1 /
- 临床有意义前列腺癌 /
- 诊断
Abstract: Objective To evaluate the diagnostic value of free prostate specific antigen density(fPSAD) combined with prostate imaging reporting and data system(PI-RADS) v2.1 for prostate puncture results as clinically significant prostate cancer(csPCa) at PSA 4-20 ng/mL.Methods The clinical data of PSA 4-20 ng/mL patients undergoing prostate biopsy in our hospital from January 2016 to September 2022 were retrospectively analyzed, including 71 patients with clinically significant prostate cancer(csPCa group) and 108 patients with non-clinically significant prostate cancer(ncsPCa group). MRI images were scored according to PI-RADS v2.1, and prostate volume(PV) and free prostate specific antigen density(fPSAD) were calculated according to the formula. The independent risk factors of csPCa were obtained by univariate and multivariate logistic regression analyses, and the receiver operating characteristic(ROC) curve of subjects was drawn. The effectiveness of each factor independently and jointly diagnosing csPCa were evaluated by the ROC curve. Finally, a column chart to provide reference for the clinical application of this prediction model was drawn.Results There were significant differences in free prostate specific antigen(fPSA), PV, fPSAD and PI-RADS v2.1 score among the enrolled patients(all P < 0.05). FPSAD(OR=1.51, 95%CI: 1.51-1.84, P < 0.05) and PI-RADS v2.1 score(OR=2.63, 95%CI: 2.63-4.00, P < 0.05) were independent risk factors for csPCa. The area under the ROC curve(AUC) for the combination of PI-RADS v2.1 score and fPSAD was 0.82, which is significantly superior to using PI-RADS v2.1 score or fPSAD alone(both were 0.75). The difference was statistically significant(P < 0.05).Conclusion For patients with PSA 4-20 ng/mL, fPSAD, PI-RADS v2.1 score have certain diagnostic value in csPCa, and the combination of the two can improve its diagnostic efficacy. -

-
表 1 患者基线资料表
X±S,M(P25,P75) 变量 总计(179例) ncsPCa组(108例) csPCa组(71例) P值 年龄/岁 72.28±7.85 73.11±7.86 71.03±7.67 0.083 BMI/(kg/m2) 23.65±3.63 23.50±3.65 23.89±3.57 0.475 PI-RADS 3(3,4) 3(2,4) 4(4,4) < 0.001 fPSA/(ng/mL) 1.61(0.98,2.27) 1.41(0.93,2.17) 1.85(1.08,2.53) 0.023 tPSA/(ng/mL) 10.89(8.30,14.99) 11.17(7.89,15.09) 10.52(8.95,13.60) 0.694 PV/mL 52.17(39.55,75.82) 63.14(48.35,80.73) 42.60(33.94,53.35) < 0.001 fPSAD 0.028(0.018,0.042) 0.023(0.015,0.032) 0.040(0.025,0.068) < 0.001 表 2 单因素和多因素二元logistic回归分析
参数 标准系数 优势比(OR) 95% CI P值 单因素logistic回归 tPSA 0.04 0.98 0.91~1.05 0.610 fPSA 0.16 1.47 1.08~2.05 0.020 PV 0.01 0.96 0.94~0.98 < 0.001 PI-RADS 0.19 2.76 1.92~4.12 < 0.001 fPSAD×100 0.09 1.54 1.31~1.87 < 0.001 多因素logistic回归 PI-RADS 0.20 2.63 2.63~4.00 < 0.001 fPSAD×100 0.09 1.51 1.51~1.84 < 0.001 -
[1] 李星, 曾晓勇. 中国前列腺癌流行病学研究进展[J]. 肿瘤防治研究, 2021, 48(1): 98-102. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZLFY202101019.htm
[2] 邹杰鹏, 彭佩丹, 杜跃军, 等. 前列腺穿刺活检方法相关研究进展[J]. 中华男科学杂志, 2022, 28(2): 167-172. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NKXB202202011.htm
[3] Wei CG, Chen T, Zhang YY, et al. Biparametric prostate MRI and clinical indicators predict clinically significant prostate cancer in men with "gray zone" PSA levels[J]. Eur J Radiol, 2020, 127: 108977. doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2020.108977
[4] 罗志强, 黄建文, 曹乃龙, 等. 基于PI-RADS v2评分在PSA 4~10 ng/mL患者前列腺癌预测模型的构建及验证[J]. 临床泌尿外科杂志, 2022, 37(2): 109-113, 118. https://lcmw.whuhzzs.com/article/doi/10.13201/j.issn.1001-1420.2022.02.007
[5] Kim JY, Yu JH, Sung LH, et al. Usefulness of the prostate health index in predicting the presence and aggressiveness of prostate cancer among Korean men: a prospective observational study[J]. BMC Urol, 2021, 21(1): 131. doi: 10.1186/s12894-021-00897-2
[6] 林富祥, 黄剑华, 钟羽翔, 等. 游离前列腺特异性抗原密度对前列腺穿刺活检结果的预测价值[J]. 临床泌尿外科杂志, 2021, 36(3): 219-222. https://lcmw.whuhzzs.com/article/doi/10.13201/j.issn.1001-1420.2021.03.012
[7] Ko YH, Kim BH. Should contemporary western guidelines based on studies conducted in the 2000s be adopted for the prostate-specific antigen screening policy for Asian men in the 2020s?[J]. World J Mens Health, 2022, 40(4): 543-550. doi: 10.5534/wjmh.220002
[8] 路惠茹, 梁亮, 谢宏俊, 等. 前列腺特异性抗原同源异构体2及其衍生指标对PSA 4~20 ng/mL患者前列腺癌的预测价值[J]. 现代泌尿外科杂志, 2023, 28(4): 347-350, 358. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-8291.2023.04.016
[9] Deniffel D, Healy GM, Dong X, et al. Avoiding unnecessary biopsy: MRI-based risk models versus a PI-RADS and PSA density strategy for clinically significant prostate cancer[J]. Radiology, 2021, 300(2): 369-379. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2021204112
[10] 杭天昆, 李通义, 石明凯, 等. 建立针对PSA灰区前列腺癌的临床预测模型: 一项针对SEER数据库的研究[J]. 临床泌尿外科杂志, 2022, 37(8): 606-614. https://lcmw.whuhzzs.com/article/doi/10.13201/j.issn.1001-1420.2022.08.008
[11] Song C, Park SY. Prostate cancer: diagnostic yield of modified transrectal ultrasound-guided twelve-core combined biopsy(targeted plus systematic biopsies)using prebiopsy magnetic resonance imaging[J]. Abdom Radiol(NY), 2021, 46(10): 4974-4983. doi: 10.1007/s00261-021-03179-5
[12] 陈文颖, 陈磊, 郭倩, 等. 不同血清前列腺特异抗原水平下超声引导经会阴前列腺系统穿刺与认知融合多参数磁共振成像经会阴靶向穿刺对前列腺癌诊断价值的比较[J]. 中华超声影像学杂志, 2021, 30(3): 243-248.
[13] 黄尚, 毕学成, 李腾, 等. 认知融合及影像融合在前列腺穿刺活检中的应用[J]. 临床泌尿外科杂志, 2020, 35(7): 557-561. https://lcmw.whuhzzs.com/article/doi/10.13201/j.issn.1001-1420.2020.07.010
[14] Scialpi M, Martorana E, Torre R, et al. Index lesion detection in multifocal prostate cancer: simplified PI-RADS biparametric MRI vs PI-RADS v2.1 multiparametric MRI[J]. Clin Imaging, 2023, 94: 108-115.
[15] Wen J, Tang TT, Ji YG, et al. PI-RADS v2.1 combined with prostate-specific antigen density for detection of prostate cancer in peripheral zone[J]. Front Oncol, 2022, 12: 861928.
-




 下载:
下载: